A Dart port of the $1 Unistroke Recognizer with some enhancements:
- The Protractor enhancement
- A way to get a "perfect" (canonical) shape from the user's stroke
- A better suited algorithm for detecting straight lines
- Type safety (with the
DefaultUnistrokeNamesenum, or another if you're using custom unistrokes)
By default it recognizes lines, circles, rectangles, and triangles. But you can also recognize any custom unistrokes (see below).
I'm building and maintaining this package for my open source note-taking app, Saber.
final points = <Offset>[...];
final recognized = recognizeUnistroke(points);
if (recognized == null) {
print('No match found');
} else {
// e.g. DefaultUnistrokeNames.circle
print('Stroke recognized as ${recognized.name}');
}The Protractor enhancement is enabled by default. You can disable it by setting useProtractor to false.
final recognized = recognizeUnistroke(
points,
useProtractor: false,
);You can get a "perfect" shape from the user's stroke by calling one of the following methods on the RecognizedUnistroke object:
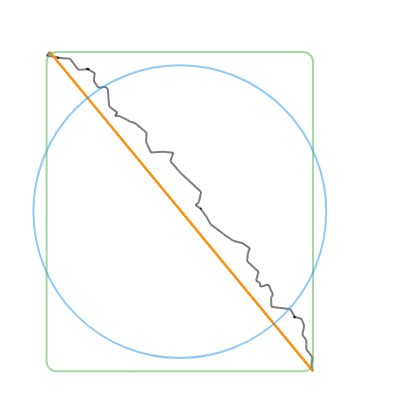
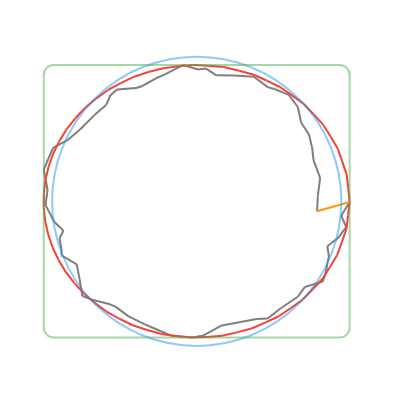
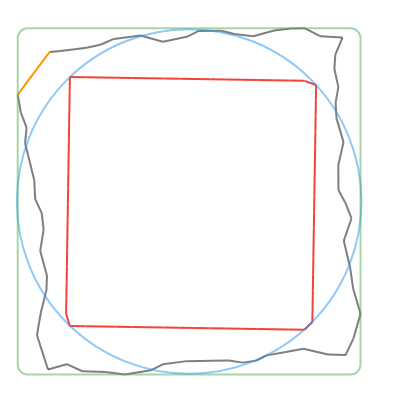
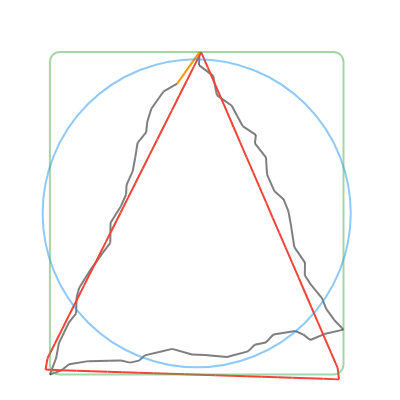
convertToCanonicalPolygon(): Returns the closest template match, scaled and translated to match the input gesture. Note that this method returns a list of points, instead of a perfect circle or rectangle like the other methods. (Shown in 🔴red in the examples below.)convertToLine(): Returns the first and last input points. (Shown in 🟠orange in the examples below.)convertToCircle(): Returns the radius and center of the best-fit circle. (Shown in 🔵blue in the examples below.)convertToOval(): The same asconvertToCircle()but doesn't take the average of the width and height. (Not shown in the examples below.)convertToRect(): Returns theRectof the best-fit (bounding box) rectangle. Tip: you can round the corners of the Rect withRRect.fromRectAndRadius. (Shown in 🟢green in the examples below.)
| Line | Circle | Rectangle | Triangle | Star |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
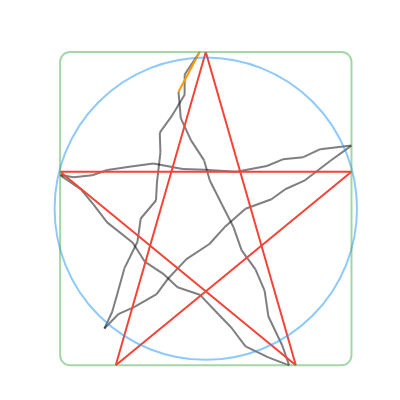 |
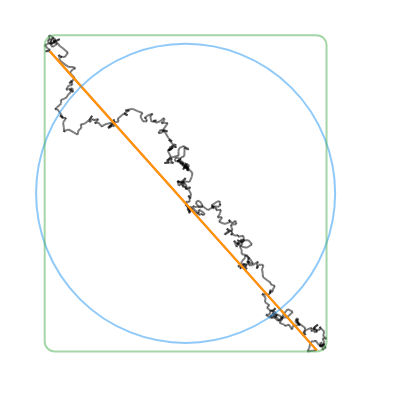 |
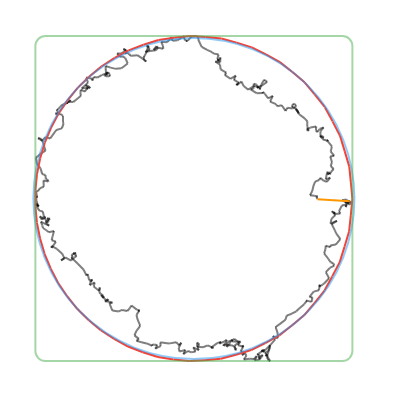 |
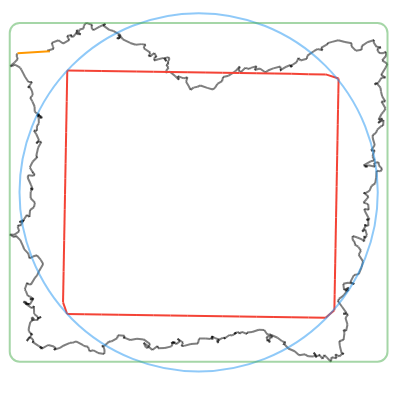 |
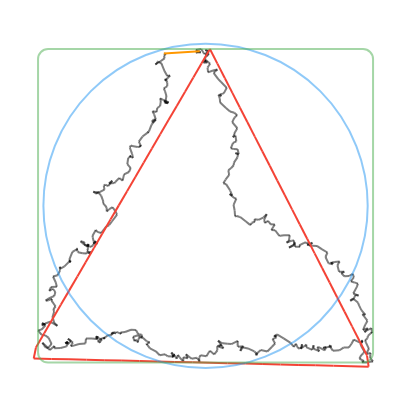 |
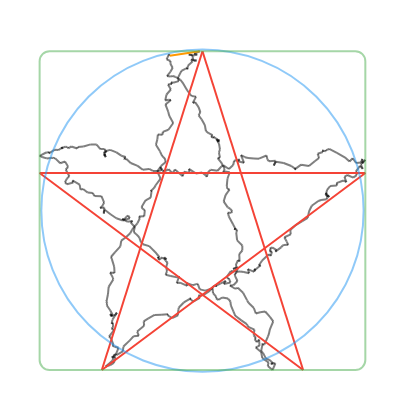 |
final recognized = recognizeUnistroke(points);
switch (recognized?.name) {
case null:
break;
case DefaultUnistrokeNames.line:
final (start, end) = recognized!.convertToLine();
canvas.drawLine(start, end, paint);
case DefaultUnistrokeNames.circle:
final (center, radius) = recognized!.convertToCircle();
canvas.drawCircle(center, radius, paint);
case DefaultUnistrokeNames.rectangle:
final rect = recognized!.convertToRect();
if (youWantARoundedRectangle) {
canvas.drawRRect(
RRect.fromRectAndRadius(rect, Radius.circular(10)),
paint,
);
} else {
canvas.drawRect(rect, paint);
}
case DefaultUnistrokeNames.triangle:
case DefaultUnistrokeNames.star:
final polygon = recognized!.convertToCanonicalPolygon();
canvas.drawPoints(PointMode.polygon, polygon, paint);
}You can recognize custom unistrokes by setting the referenceUnistrokes list.
Note that this will disable the default unistroke templates defined in default$1Unistrokes.
If your key type isn't DefaultUnistrokeNames, you'll need to call
recognizeCustomUnistroke<MyKey>(...) instead of recognizeUnistroke(),
which will return a RecognizedCustomUnistroke<MyKey> instead of a
RecognizedUnistroke.
Also note that straight lines are a special case in the default unistroke templates, and aren't available by default with custom unistroke templates. To recognize straight lines, see the Straight lines section below.
enum MyUnistrokeNames {
circle,
rectangle,
triangle,
leaf,
}
referenceUnistrokes = <Unistroke<MyUnistrokeNames>>[
Unistroke(MyUnistrokeNames.circle, [...]),
Unistroke(MyUnistrokeNames.rectangle, [...]),
Unistroke(MyUnistrokeNames.triangle, [...]),
Unistroke(MyUnistrokeNames.leaf, [...]),
];
final recognized = recognizeCustomUnistroke<MyUnistrokeNames>(points);Alternatively, you can temporarily override the referenceUnistrokes list for a single call to recognizeUnistroke by setting the overrideReferenceUnistrokes list.
final recognized = recognizeCustomUnistroke<MyUnistrokeNames>(
points,
overrideReferenceUnistrokes: [...],
);Straight lines are a special case in the default unistroke templates, in that they're best recognized by a different algorithm than the other shapes (i.e. not $1).
If you're using default$1Unistrokes (the default), you don't need to worry about this, and straight lines will be detected as DefaultUnistrokeNames.line.
But if you're using custom unistroke templates, ensure that your straight line unistroke template has exactly 2 points and that they're distinct.
referenceUnistrokes = <Unistroke<MyUnistrokeNames>>[
Unistroke(MyUnistrokeNames.line, [
// This template should have exactly 2 distinct points.
Offset(0, 0),
Offset(0, 100),
]),
// ...
];The $1 Unistroke Recognizer is a 2-D single-stroke recognizer designed for rapid prototyping of gesture-based user interfaces. In machine learning terms, $1 is an instance-based nearest-neighbor classifier with a 2-D Euclidean distance function, i.e., a geometric template matcher. $1 is a significant extension of the proportional shape matching approach used in SHARK2, which itself is an adaptation of Tappert's elastic matching approach with zero look-ahead. Despite its simplicity, $1 requires very few templates to perform well and is only about 100 lines of code, making it easy to deploy. An optional enhancement called Protractor improves $1's speed.
You can read more about the $1 Unistroke Recognizer at depts.washington.edu/acelab/proj/dollar.
On that link, you'll see a demo with 16 templates. This package uses a different set of templates by default, but you can use the original templates by setting referenceUnistrokes to example$1Unistrokes.
This Dart package is a port of the JavaScript version of the $1 Unistroke Recognizer, which you can find at depts.washington.edu/acelab/proj/dollar/dollar.js.

