This is a simple hard coded example of the LSTM copy task as defined in the NTM paper by Graves et al. and was done to understand LSTMs in sequence generating conditions.
The code is written as simple as possible to understand working with LSTMs in TensorFlow.
To run the LSTM copy task run the following command in the terminal. This will train the network and run a prediction test on it.
python3 LSTM_copy_task.pyTraining was done up to 40 epochs which resulted in a final binary cross entropy loss of about ~0.0080. During this, random sequence lengths between 1 and 20 was used and each of the sequences contained random binary vectors of size 8. The input sequence contained two extra bits to signal the start and end of the sequence making the LSTM input vector size 10. All the extra bits are padded close to a zero value like 0.001.
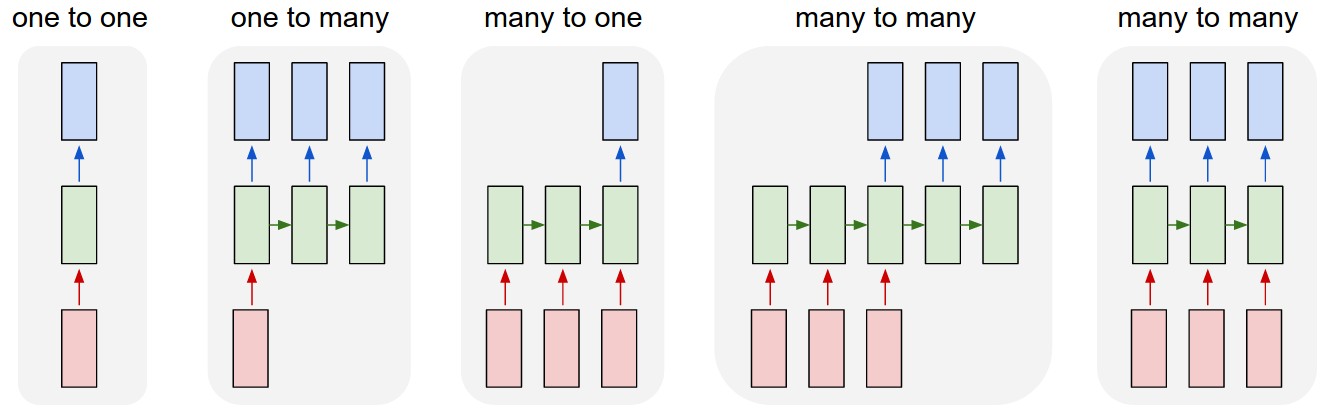
Target delay was used in which the target sequence is presented only after the input sequence is completely shown. The 3-layer LSTM network implemented is a many to many (5) as shown below.
Different types of RNN implementations (Andrej Karpathy)
The following are the sequence copy attempts done by the LSTM network at sequence lengths of 10, 20, 40 and 120. Both target (top) and prediction (bottom) is shown.
As it can be seen from the above figure, the 3-layer LSTM network was able to copy the sequence length of 10 extremely well but for sequence length of 20, errors are showing up even though the network was trained for copying sequences up to a length of 20. The errors are small and concentrated in the middle for most cases. The network does not generalise well for sequence lengths beyond 20 without training and this is inline with what the authors have observed.