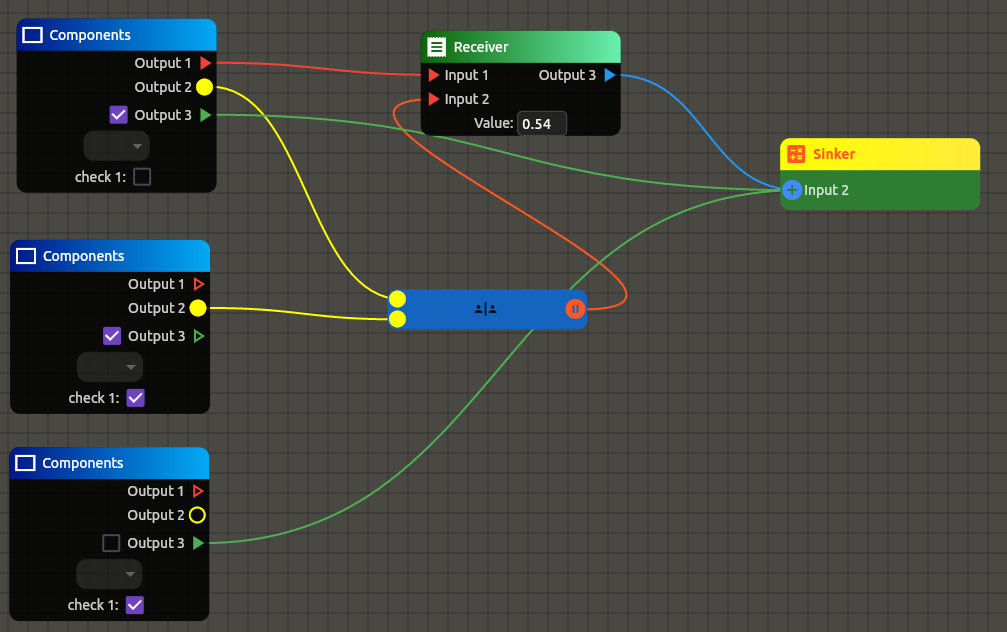
A highly customizable node editor for Flutter
- Flutter Widgets for Nodes & Ports: Customize nodes and ports with any Flutter widget, offering unparalleled UI flexibility.
- Interactive Node Elements: Embed interactive widgets like text fields and checkboxes directly in nodes for dynamic user input.
- Customizable Connections & Backgrounds: Tailor connections and backgrounds with extensive styling options for visual coherence.
- Dynamic Port Logic: Advanced logic for port connections, including customizable verification and unlimited connection capacities.
- Extensible Design: Easily add new node and port types with your custom widgets, ensuring scalability.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Build once, deploy everywhere with Flutter’s cross-platform capabilities.
To use the package you just need to add the dependency in your pubspec.yaml file.
dependencies:
node_editor: ^0.0.5or use the command:
flutter pub add node_editorTo instantiate a NodeEditor object and start using the package, you just need to instantiate a focus node and a controller.
// (...)
final NodeEditorController _controller = NodeEditorController();
final FocusNode _focusNode = FocusNode();
// (...)
NodeEditor(
focusNode: _focusNode,
controller: _controller,
background: const GridBackground(),
)
// (...)To add nodes in the NodeEditor, you just need to add any widget that inherits from NodeWidgetBasec. In this case, we add a ContainerNodeWidget, which functions as a traditional Flutter container. However, it is a node, meaning you can add input and output ports as child widgets, in addition to implementing operations like selection and movement within the NodeEditor.
To actually add the node, just call the addNode method of the controller object, and pass the node object to be added, as well as the initial position where it should appear in the NodeEditor.
// (...)
NodeWidgetBase exampleNode(String name) {
return ContainerNodeWidget(
name: name,
typeName: 'node_3',
backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade800,
radius: 10,
width: 200,
contentPadding: const EdgeInsets.all(4),
selectedBorder: Border.all(color: Colors.white),
child: // (...)
);
}
// (...)
controller.addNode(
binaryNode('node_3_1'),
NodePosition.afterLast,
);A node used in real-world practice should have at least one input or output port. Often, a node has several input and output ports, in addition to various properties. An input or output port can be added anywhere below the node in the Flutter widget tree, as the ports use a Flutter mechanism to check which node is directly above them in the widget tree. Thus, ports can be added inside any other widgets such as Row, Column, among others. Another thing are some mandatory arguments, such as name and typeName, each node must have a unique name, while the typeName is a more useful parameter for performing checks, something that will be explained further ahead.
NodeWidgetBase exampleNode(String name) {
return ContainerNodeWidget(
name: name,
typeName: 'node_3',
backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade800,
radius: 10,
width: 200,
contentPadding: const EdgeInsets.all(4),
selectedBorder: Border.all(color: Colors.white),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
InPortWidget(
name: 'PortIn1',
onConnect: (String name, String port) => true,
icon: Icon(
Icons.circle_outlined,
color: Colors.yellowAccent,
size: 20,
),
iconConnected: Icon(
Icons.circle,
color: Colors.yellowAccent,
size: 20,
),
multiConnections: false,
connectionTheme:
ConnectionTheme(color: Colors.yellowAccent, strokeWidth: 2),
),
],
),
Icon(Icons.safety_divider),
OutPortWidget(
name: 'PortOut1',
icon: Icon(
Icons.pause_circle_outline,
color: Colors.deepOrange,
size: 24,
),
iconConnected: Icon(
Icons.pause_circle,
color: Colors.deepOrange,
size: 24,
),
multiConnections: false,
connectionTheme:
ConnectionTheme(color: Colors.deepOrange, strokeWidth: 2),
),
],
),
);
}The NodeEditor has two main types of nodes, however, it's very easy to create your own custom node by simply creating a new class that inherits from NodeWidgetBase.
Provides a flexible and visually distinct way to represent nodes in a graphical editor, offering extensive customization options to fit the design needs of various applications. It is ideal for creating nodes that need a clear separation between their title area and content, making them easily identifiable and interactive within a node graph.
Properties:
child: A Widget that represents the main content of the node. This is where you place the interactive or display elements of your node.
icon: A Widget (typically an Icon) displayed in the title bar, providing a visual representation of the node's purpose.
title: A Widget that displays the title of the node in the title bar. It is typically a Text widget.
width: The width of the node. It defaults to 150 if not specified.
titleBarColor: The background color of the title bar. It can be used to differentiate node types or states.
backgroundColor: The background color of the node's content area.
radius: The border radius for the corners of the node, applied to both the title bar and the content area.
boxShadow: A list of BoxShadow objects that define the shadow cast by the node.
border: The border of the node when it is not selected.
selectedBorder: The border of the node when it is selected, allowing for visual emphasis.
gradient: An optional Gradient applied to the background color of the node, allowing for complex color transitions.
backgroundBlendMode: The blend mode applied to the background gradient or color.
image: An optional background image for the node.
titleBarBorder: The border of the title bar, allowing for custom styling separate from the node's main border.
titleBarGradient: An optional Gradient applied to the title bar's background.
titleBarBackgroundBlendMode: The blend mode applied to the title bar's background gradient or color.
titleBarImage: An optional background image for the title bar.
iconTileSpacing: The space between the icon and the title text in the title bar.
titleBarPadding: The padding inside the title bar, allowing for adjustment of the title text and icon positioning.
contentPadding: The padding inside the node's content area, allowing for spacing adjustments around the child widget.
Functionality:
Interactivity: The title bar is interactive, supporting drag operations to move the node within the editor. Additionally, tapping the icon in the title bar selects the node, enabling further interaction or modification.
Customization: Through its properties, TitleBarNodeWidget offers extensive customization of both the title bar and content area, including colors, borders, shadows, and background images or gradients. This allows for a high degree of visual customization to fit the aesthetics of any node editor.
Layout: The class uses a Column widget to vertically arrange the title bar and content area, ensuring a clear visual hierarchy and separation of concerns within the node.
Offers a streamlined and flexible approach to crafting nodes within a graphical editor or a node-based UI framework. It supports a broad spectrum of visual customization options, including background colors, gradients, images, and more, making it suitable for a variety of application themes and purposes.
Properties:
child: The primary content of the node, accepting a Widget. This allows for a diverse range of content to be displayed within the node, from simple texts to complex structured layouts.
width: Specifies the node's width, defaulting to 150. This width can be adjusted to accommodate the contained child widget's size requirements.
backgroundColor: Defines the node's background color, enhancing the node's visual distinctiveness or thematic alignment with the application.
radius: The border radius for the node's corners, allowing for rounded corner designs that can match or enhance the application's aesthetic.
boxShadow: A list of BoxShadow objects that enable the node to cast a shadow, adding depth and prominence within the UI.
border: Defines the border of the node when it is not selected, allowing for visual differentiation or emphasis.
selectedBorder: Specifies the border of the node when it is selected, providing visual feedback and focus to users.
gradient: An optional Gradient for the node's background, offering sophisticated visual effects through color transitions.
backgroundBlendMode: The blend mode applied to the background's color or gradient, allowing for complex visual effects in combination with background images.
image: An optional background image, providing additional opportunities for thematic or informational customization.
contentPadding: The padding within the node, surrounding the child widget. This property ensures that content is appropriately spaced from the node's edges.
Functionality:
Interactivity: Incorporates gesture detection to facilitate node interaction, such as moving the node within the editor through drag gestures and selecting the node via double-tap actions.
Visual Customization: Through its extensive range of properties, ContainerNodeWidget enables significant visual customization, allowing nodes to be tailored to fit the design requirements of various applications.
Content Flexibility: Designed to encapsulate a child widget, it supports a wide variety of content types and layouts, making it versatile for different use cases within a node-based UI.
InPortWidget provides a graphical representation of an input port on a node, allowing users to create connections between nodes. It supports both single and multiple connections, with customization options for appearance and behavior.
Properties
multiConnections: A bool indicating whether the port can accept multiple connections. If false, the port is limited to a single connection.
maxConnections: An optional int that specifies the maximum number of connections the port can accept. This is only relevant if multiConnections is true.
name: A String that uniquely identifies the input port within its node. This is crucial for managing connections programmatically.
icon: A Widget (typically an Icon) that visually represents the input port when not connected.
iconConnected: An optional Widget that represents the input port when it is connected. If not provided, icon is used for both connected and disconnected states.
connectionTheme: An optional ConnectionTheme that defines the visual properties of the connection line, such as color and stroke width.
onConnect: An optional callback function that is invoked when a connection to this port is made. It allows for custom logic to be executed upon connection, such as validation.
Functionality:
Connection Management: InPortWidget integrates with NodeEditorController to manage connections. It supports interactive connection creation by tapping the port, leveraging the addConnectionByTap method of the controller.
Customization: It offers customization through connectionTheme for styling connections and allows different icons for connected and disconnected states, providing visual feedback to the user.
Dynamic State Handling: The widget uses an AnimatedBuilder to reactively update its appearance based on the connection state, ensuring the UI reflects the current state accurately.
OutPortWidget provides a graphical representation of an output port on a node, allowing users to create connections between nodes. It supports both single and multiple connections, with customization options for appearance and behavior.
Properties
multiConnections: A bool indicating whether the port can accept multiple connections. If false, the port is limited to a single connection.
maxConnections: An optional int that specifies the maximum number of connections the port can accept. This is only relevant if multiConnections is true.
name: A String that uniquely identifies the input port within its node. This is crucial for managing connections programmatically.
icon: A Widget (typically an Icon) that visually represents the input port when not connected.
iconConnected: An optional Widget that represents the input port when it is connected. If not provided, icon is used for both connected and disconnected states.
connectionTheme: An optional ConnectionTheme that defines the visual properties of the connection line, such as color and stroke width.
onConnect: An optional callback function that is invoked when a connection to this port is made. It allows for custom logic to be executed upon connection, such as validation.\
Functionality:
Connection Management: InPortWidget integrates with NodeEditorController to manage connections. It supports interactive connection creation by tapping the port, leveraging the addConnectionByTap method of the controller.
Customization: It offers customization through connectionTheme for styling connections and allows different icons for connected and disconnected states, providing visual feedback to the user.
Dynamic State Handling: The widget uses an AnimatedBuilder to reactively update its appearance based on the connection state, ensuring the UI reflects the current state accurately.\