Let's Learn for Free! Click Here
Book 1:1 Session here -> Click Here
- Kotlin
- Android
- Lifecycle
- Networking
- Webview
- Dependency Injection
- Jetpack Compose
- Thread
- Architecture
- Design Pattern
- System Design
- Libraries
- Common Question
- Questions from Company
- Kotlin Sheet 2024
- Jetpack Compose Sheet 2024
- What is the difference between
const valandval?- Both are used to define read-only properties, but
const valproperties should be initialized at compile-time whereasvalproperties can be initialized at runtime- If we decompile,
const valvariable will replace with its value butvalnot, because it can be initialized at runtime -
const val BASE_URL = "https://github.com" val githubHandle = "anandwana001" val repoName: String
- What is so interesting about
data class?- Uses to hold data
- Pre-functions like
toString,equals,copy, andcomponentN - Data classes cannot be abstract, open, sealed, or inner.
- Data classes cannot extend other classes
- Supports destructuring declaration
- Is singleton thread-safe? vs Object?
- What are the different types of scope functions?
- Let =
T.let { R }- lambda result (R) is the return type
- can be performed on any
Ttype object - lambda reference is
it - suitable for null check
- Run =
T.run { R }- same as
let, but mostly used in initializing an object - lambda reference is
this - suitable for null check
- same as
- With =
with(T) { R }- if T is nullable object use
runelse usewith(T) - lambda reference is
this - not suitable for null check
- if T is nullable object use
- Also =
T.also { T }- when need to perform multiple operations in chain use
also - lambda reference is
it
- when need to perform multiple operations in chain use
- Apply =
T.apply { T }- when need to perform the operation on the
Tobject and return the same useapply - lambda reference is
this - suitable for null check
- when need to perform the operation on the
- Let =
- What are the different Coroutine Scopes?
- How to manage series and parallel execution?
- Difference between Flow/SharedFlow/StateFlow and elaborate it.
- What happens if we call
.cancel()from a coroutine scope? - What is an Init block in Kotlin?
- How to choose between apply and with?
- What is inline function in Kotlin?
- Difference between Coroutine and Java Thread
- Why Coroutines are light weight?
- How does Coroutine switch context?
- When to use Kotlin sealed classes?
- Suspending vs Blocking in Kotlin Coroutines
- What are Dispatchers and Name all of them
- On which thread Dispatchers .Default execute the task or use which thread?
- Dispatchers .Default vs Dispatcher .IO
- What is SupervisorScope?
- Exception Handling in Coroutine
- Map vs FlatMap in kotlin
- Singleton Pattern in Kotlin with object keyword
- Collections API in Kotlin
- What is Unidirectional Flow
- StateFlow vs SharedFlow
- Builder Pattern in Kotlin
- Higher Order Functions in Kotlin
- Covariance in Kotlin
- Delay vs Thread.sleep? Answer
- How does Garbage collection works?
- What is a dangling pointer?
- Elaborate Memory Leak?
- Explain fragment Lifecycle when it comes to ViewPager and sliding between different fragments.
- Difference between FragmentStateAdapter and FragmentStatePagerAdapter.
- Difference between Serializable and Parcelable? What are the disadvantages of Serializable?
- How you could implement observable SharedPrefs or observable Databases i.e. Observe a certain key/table/query?
- How does layout inflation work from xml tags to view references in memory?
- What is a Thread, Handler, Looper, and Message Queue?
- What are the different methods of concurrency on Android? Can you explain the difference between ExecutorService vs CachedThreadPool vs FixedThreadPool vs AsyncTasks vs HandlerThreads?
- How does
ViewModelinstance provide to Activity and Fragment? How doesViewModelProviderStoredecide when to retain the instance? - How do you inspect and solve the Jank issue? here
- How does the OutOfMemory happen?
- How do you find memory leaks in Android applications?
- What is Doze? What about App Standby?
- What does
setContentViewdo? - Process of creating a custom view
- Deeplink understanding and architecture
- Notifications
- Difference between Fragment Lifecycle Observer and View Lifecycle Observer.
- When should you use a Fragment rather than an Activity?
- Explain the Android push notification system.
- How LiveData is different from ObservableField?
- What is the difference between setValue and postValue in LiveData?
- What is process death?
- What is ViewModelScope and How does it work internally?
- How to keep a video maintain a playing state when we rotate the screen?
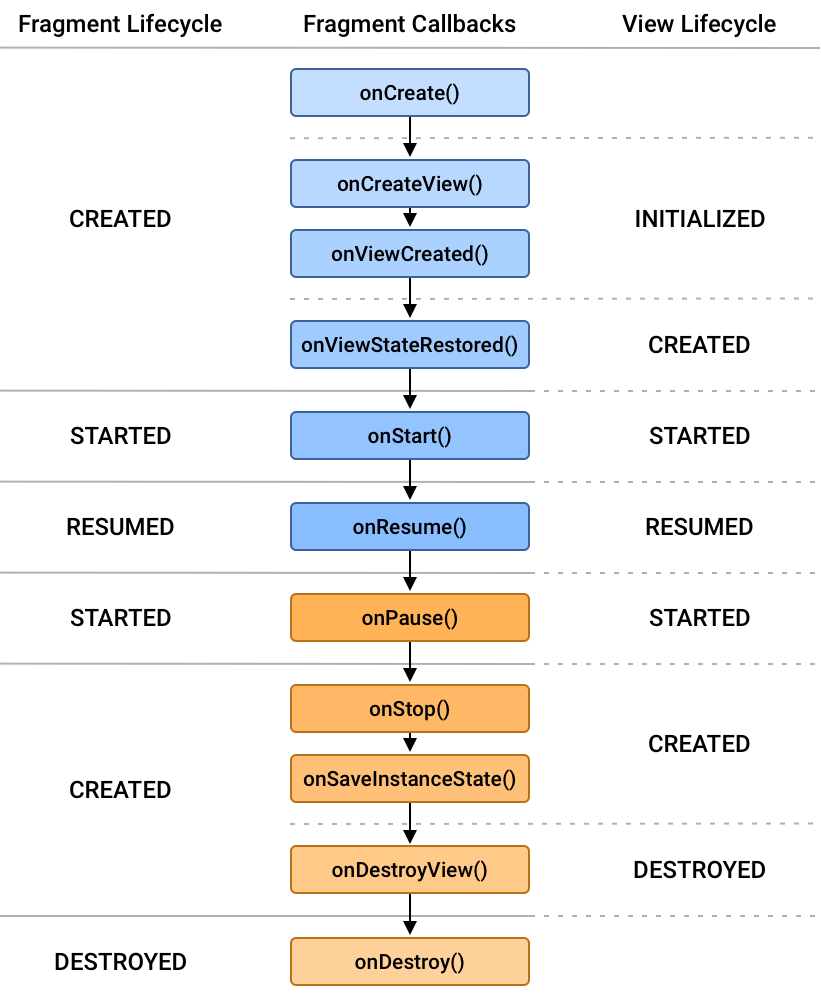
- How many callbacks are in Fragments?
- What could be the reasons why
onPausedidn't get triggered? - What kind of events trigger
onPause()to run? - In what scenario does the "onDestory" get called directly after "onCreate"?
- Which callback gets called on Activity when an AlertDialog is shown?
- What's the lifecycle in PIP (Picture-in-Picture)?
- What happens if you rotate the device?
- Inside a viewpager (Fragment state pager adapter) what will be the lifecycle of the fragments when you swap from one tab to another?
- Why onActivityCreated is now depreciated in Fragment?
- Which callback should I use if I want to know when my activity came to the foreground?
- When is onActivityResult called?
- What does setRetainInstance do and how you can avoid it?
- What callbacks trigger when a Dialog opens up? In both cases, the dialog is attached from the same activity/fragment and another activity/fragment.
- What do
launchWhenCreated,launchWhenStarted, andlaunchWhenResumedfunctions do? - Fragment Callbacks when moving from one fragment to another and coming back to prev one?
- Does onCreateView get called after coming to a fragment from top fragment?
- When does ViewModel not survive
Code
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentA())
.commit()
Callbacks
| MainActivity | onCreate |
| FragmentA | onAttach |
| FragmentA | onCreate |
| FragmentA | onCreateView |
| FragmentA | onViewCreated |
| FragmentA | CREATED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentA | onViewStateRestored |
| FragmentA | onStart |
| FragmentA | STARTED == Lifecycle.State |
| MainActivity | onStart |
| MainActivity | onResume |
| FragmentA | onResume |
| FragmentA | RESUMED == Lifecycle.State |
| MainActivity | onAttachedToWindow |
Code
parentFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentB())
.commit()
parentFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentB())
.addToBackStack(null)
.commit()
Callbacks
| FragmentB | onAttach |
| FragmentB | onCreate |
| FragmentB | onCreateView |
| FragmentB | onViewCreated |
| FragmentB | CREATED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentB | onViewStateRestored |
| FragmentB | onStart |
| FragmentB | STARTED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentB | onResume |
| FragmentB | RESUMED == Lifecycle.State |
Code
parentFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentB())
.addToBackStack(null)
.commit()
Callbacks
| FragmentA | onPause |
| FragmentA | onStop |
| FragmentB | onAttach |
| FragmentB | onCreate |
| FragmentB | onCreateView |
| FragmentB | onViewCreated |
| FragmentB | CREATED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentB | onViewStateRestored |
| FragmentB | onStart |
| FragmentB | STARTED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentA | onDestroyView |
| FragmentB | onResume |
| FragmentB | RESUMED == Lifecycle.State |
Code
parentFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentB())
.commit()
Callbacks
| FragmentA | onPause |
| FragmentA | onStop |
| FragmentB | onAttach |
| FragmentB | onCreate |
| FragmentB | onCreateView |
| FragmentB | onViewCreated |
| FragmentB | CREATED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentB | onViewStateRestored |
| FragmentB | onStart |
| FragmentB | STARTED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentA | onDestroyView |
| FragmentA | onDestroy |
| FragmentA | onDetach |
| FragmentB | onResume |
| FragmentB | RESUMED == Lifecycle.State |
Note: If addToBackStack is not used, and back stack is empty, nothing will happen when calling popBackStack() function
Code
// FragmentA
parentFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentB())
.addToBackStack(null)
.commit()
// FragmentB
parentFragmentManager.popBackStack()
Callbacks
| FragmentB | onPause |
| FragmentB | onStop |
| FragmentB | onDestroyView |
| FragmentB | onDestroy |
| FragmentB | onDetach |
FragmentA is visible. No FragmentA callbacks as FragmentA is always there, neither the view nor the lifecycle get affected.
Note: If addToBackStack is not used, and back stack is empty, nothing will happen when calling popBackStack() function
Code
// FragmentA
parentFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, FragmentB())
.addToBackStack(null)
.commit()
// FragmentB
parentFragmentManager.popBackStack()
Callbacks
| FragmentB | onPause |
| FragmentB | onStop |
| FragmentA | onCreateView |
| FragmentA | onViewCreated |
| FragmentA | CREATED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentA | onViewStateRestored |
| FragmentA | onStart |
| FragmentA | STARTED == Lifecycle.State |
| FragmentB | onDestroyView |
| FragmentB | onDestroy |
| FragmentB | onDetach |
| FragmentA | onResume |
| FragmentA | RESUMED == Lifecycle.State |
FragmentA view is created again. When replacing, the FragmentA view gets destroyed, onDestroyView gets called so when coming back it calls onCreateView to initialise the view again.
Though, onCreate will not get called again.
There are 5 States:
- DESTROYED
- INITIALIZED
- CREATED
- STARTED
- RESUMED
States are based on Context/Scope you are using in. Example:
viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.CREATED) {
//...
}
}
// viewLifecycleOwner => Lifecycle of the View
// should be used between onCreateView() and onDestroyView()
this.lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.CREATED) {
//...
}
}
// this => Lifecycle of Fragment or Activity
| CREATED | - listen in onDestroyView (if not View lifecycle) and in onStop, onSavedInstance too |
| STARTED | - listen in onStart, onPause |
| RESUMED | - listen in onResume |
| DESTROYED | - listen in onDestroyView (if View lifecycle) and in onDestroy |
| CREATED | - listen in onViewStateRestored (if View lifecycle) |
| CREATED | - listen in onCreate, onCreateView, onViewCreated, onViewStateRestored (if not View lifecycle) |
- if state CREATED and app moves to background, it will listen. Hence, Avoid UI work here
- use state CREATED if need to complete action even after Fragment View destroy
- What is the role of OkHttp and Retrofit?
- What design pattern does Retrofit use?
- How would optimize the handling of access token expiration? How would you handle a retry network call when the API fails? (Custom Interceptor response)
- What are the problems around security when dealing with
WebView? - How to interact or make connections with JavaScript?
- Provides vs binds
- Subcomponent vs. component dependency, what is the difference under the hood
- What is a subcomponent and what is its use? How do you use qualifiers or how would you provide different instances of a class with the same data type? Constructor Injection V/s Method Injection? What is the scope? Singleton Annotation?
- What is Circular dependency in dagger? and how to resolve it
- What's interesting about Hilt?
- Did you use Koin? What are your thoughts on it?
- How to launch a coroutine from a composable function? - LaunchedEffect
- How to launch a coroutine from a non-composable function, but tied to composition? - rememberCoroutineScope()
- What is recomposition? Recomposition
- What is
rememberin compose?- A composable function to remember the value produced by a calculation only at the time of composition. It will not calculate again in recomposition.
- Recomposition will always return the value produced by composition.
- Whole Compose is based on the concept of
Positional Memoization - At the time of recomposition,
rememberinternally calls a function calledrememberedValue()whose work is to look into theslotTableand compare if the previous value and the new value have any difference, if not return, else update the value
- Why and when to use
remember {}? - Difference between
LazyColumnandRecyclerView? - What is AndroidView in compose?
- What is the lifecycle of composeables? Lifecycle
- How to avoid recomposition of any composable, if the state is not changed? Smart Recomposition
- What are stable types that can skip recomposition?
- What is State?
- What is MutableState and how does recomposition happen?
- How to retain State across recomposition and configuration changes?
- Difference between Stateless and Stateful composeables?
- What are your thoughts on flat hierarchy, constraint Layout in compose vs. the older view hierarchy in xml
- Difference b/w remember and LaunchedEffect
- Does re-composition of
ComposeItem1bring any effect onComposeItem2? If yes, then how?ComposeParent() { ComposeItem1 {} ComposeItem2() {...} }- What is
CompositionLocal?
- Custom views in compose
- Canvas in Compose
- What are the benefits of Jetpack Compose?
- How does Jetpack Compose integrate with existing Android frameworks and libraries?
- What are the best practices for performance optimization in Jetpack Compose?
- How is navigation handled in Jetpack Compose?
- What is Strong Skipping Mode? Answer
- Different types of threads?
- Difference between different types of thread?
- Thread <-> Handler <-> looper
- UI vs Background Thread
- How do you know when some process if blocking a UI thread?
- What are SOLID principles?
- What is MVVM?
- Brief about Android Architecture.
- MVP vs MVVM?
- Is there any issue in the Presenter in the MVP?
- Clean Architecture
- MVVM vs MVI
- What is Clean Architecture in MVVM
- What are Provides and Binds in your Dagger library
- What is SOLID principle?
- What are different design patterns you know about?
- What is a creational pattern?
- What is a structural pattern?
- What is a behavioral pattern?
- Create Singleton Pattern without Kotlin default implementation
- Create Observer Pattern
- Create Adapter Pattern
- How to make a Singleton Pattern Thread Safe?
- What is Dependency Inversion
- Write a real-life example of Dependency Injection without using any library
- Explain how Android Architecture components (ViewModel, LiveData, etc.) utilize design patterns behind the scenes
- Design Image Loading Library
- Design Image Downloading Library
- Design LRU Cache
- Design a real-time Twitter feed timeline. How will you structure the backend? Will you use WebSocket or REST for this use case? Justify.
- Design Networking Library
- Design Checkout Screen
- Design Error handling Structure
- REST <-> Web Sockets
- Implement caching mechanism
- Build an offline-first app
- Design Analytics Library
- How does Glide internally work?
- How does retrofit work internally?
- ViewModel internal working
- How will you choose between Dagger 2 and Dagger-Hilt?
StringvsStringBuilder==vs.equals?===vs==?- Java OOP concepts
| Company | Questions |
|---|---|
| Booking.com |
|
| Spotify |
|
| PhonePe |
|
| Paytm |
|
| Meesho |
|
What interesting questions do you face while giving an interview for an Android Engineer role (any level)? Let's open a PR.