AfrikaBurn is a community of participants who come together to create art, burning structures, costume, performance, theme camps, music, mutant vehicles and much, much more. All of this is created through the volunteer culture of the citizens of Tankwa Town in the Karoo once a year. It is roughly based on the Burning Man event in the USA.
It is recommended that the Kotlin programming language was used, since Kotlin is Google's preferred programming language for Android Developers. Furthermore, Google have taken a "Kotlin first" approach whereby features will be released for Kotlin prior to release for Java.
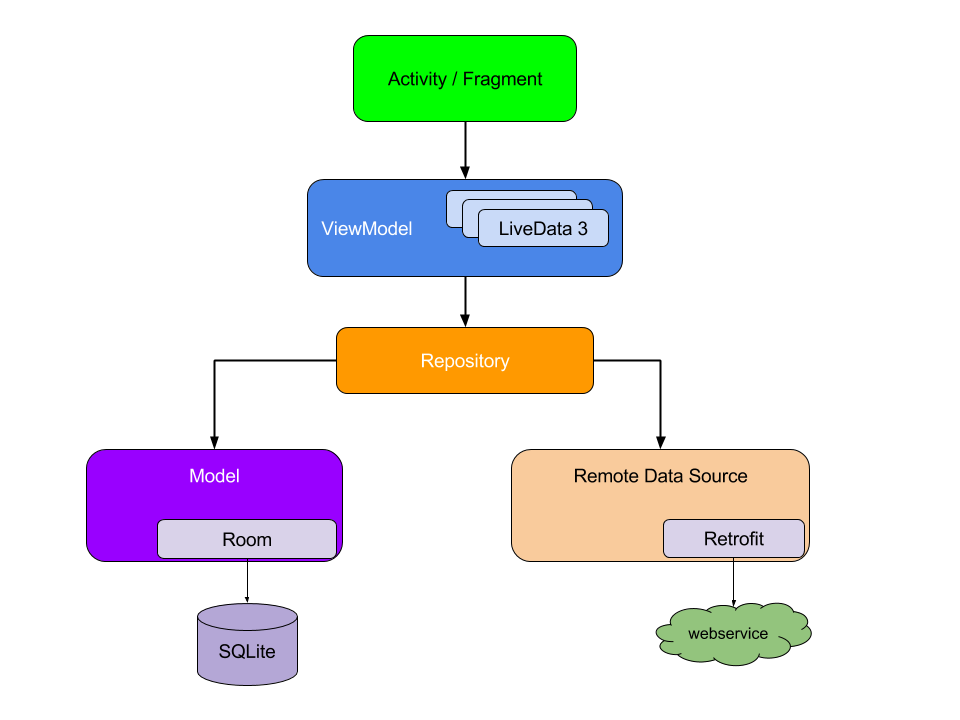
The Google Recommended App Architecture was also followed. Broadly speaking, this mandates a MVVM (Model, View, ViewModel) and single Activity architecture.
Furthermore, Android Jetpack components were used whenever feasible. The Jetpack libraries will help by placing the Android OS fragmentation burden largely upon Google. Additionally, the Jetpack libraries facilitate adherance to the Architectural practices described in this document.
The modular programming software design technique is utilized within this app. Modular programming emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent modules. Each module then contains everything necessary to execute only one aspect of the desired functionality. These libraries would provide the required functionality in an independent and encapsulated, loosely coupled manner.
The Afrikaburn app can therefore be viewed as a collection of modules delivering the required functionality.
A number of advantages of the architecture outlined above have been identified, including:
- Reduced build times. This is due to changes requiring module rebuilds, rather than app rebuilds.
- Enforced separation of concerns due to a module encapsulating a limited set of functionality.
- Adoption of an API orientated mindset
- Improved ability to write Unit Tests due to limited object scope
- Code reuse by means of libraries which can be used by multiple other libraries.
- Enhanced scope for refactoring due to library module code base being smaller than application code base.
The following disadvantages with the proposed approach are noted:
- Dependency management - each library module will have a unique Gradle file declaring dependencies. These Gradle files will have to be kept in sync on a continual basis.
- Versioning of library modules must be carefully managed and documented, since the library modules will be developed separately. Compatibility of these different library module versions in client apps would need to be carefully managed.
- The transfer of information and navigation between library modules introduces more developer friction than in a monolithic application.
- Increased QE load due to testing of the interaction between library modules.
Risks associated with this approach:
- Library modules may need to be split into further sub-modules at a later stage, which could entail extensive refactoring.
- Both Kotlin and the Jetpack libraries are production ready, however they are a recent addition to the Android ecosystem. As a result, both Entersekt and the Android development community at large relatively unfamiliar with aforementioned technologies.
The map tiles are downloaded on first launch for offline capability, thanks to Mapbox
You will need to provide the following or contact me:
- API keys have been hidden from source control
- Get your Mapbox API key
- google-services.json
- Jitpack
Offline capability is provided by Firebase
Policy generated with this awesome privacy policy generator