-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Home
See the README for details on the initial setup and how to use blambda from the command-line.
First, create a development environment:
./ve_setup.sh # this uses pyenv to create a virtualenv and install all requirementsInstall blambda to that environment in editable/develop mode. Using the -e/--editable flag means that the package will be installed from your dev directory so that running blambda will use your latest updates.
pip install -e {path-to-your-repo}
# e.g.
# pip install -e . # relative paths are fine
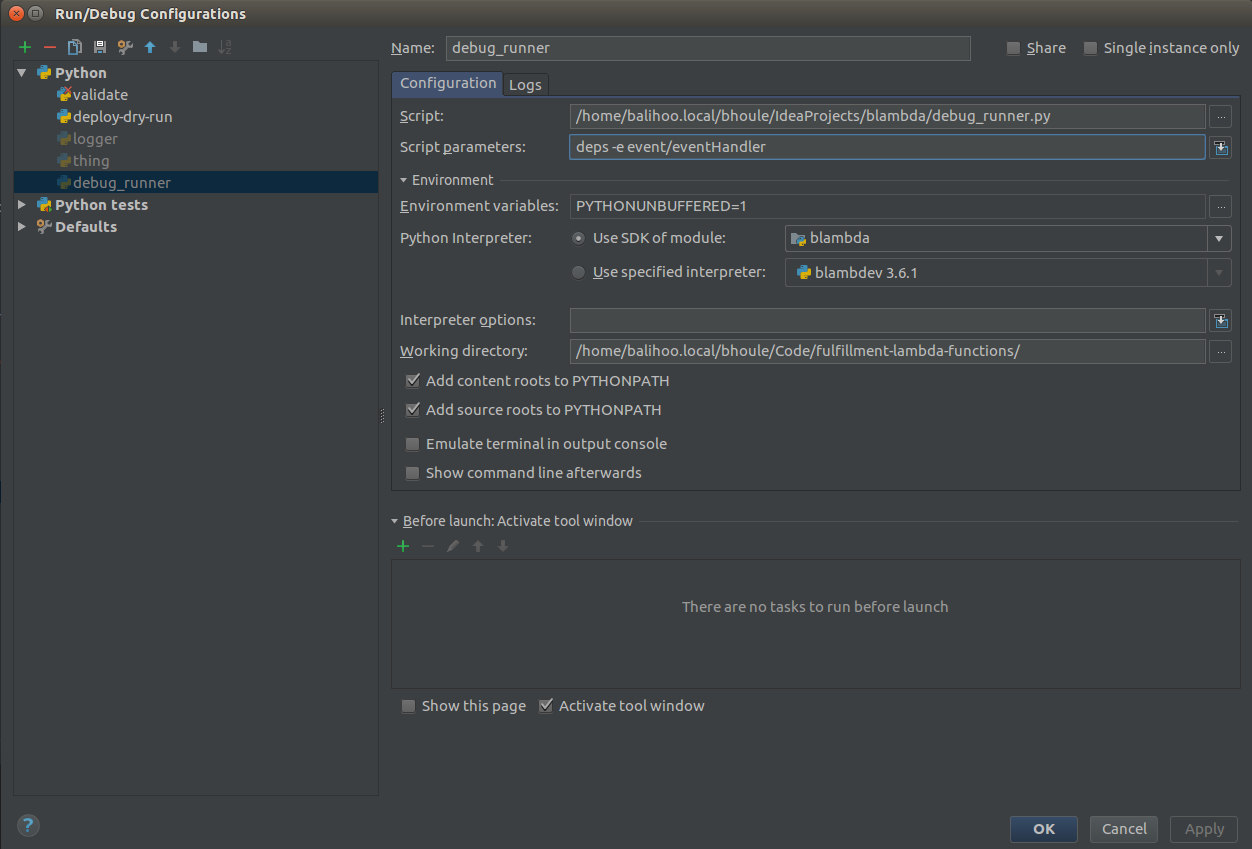
# pip install -e ~/Code/blambda # so are absoluteTo use the intellij debugger, set up a run configuration using
debug_runner.py. The cmd-line arguments can be passed in using the Script parameters option:
blambda uses Sub-commands for distinct
sets of functionality -- see blambda/__main__.py for the mapping of subcommands to code.
See findfunc.py for details on how blambda searches a directory tree for lambda function code, and lambda_manifest.py to see how blambda parses a manifest and uses the path to name and group functions.
The required manifest {function_name}.json file contains all the lambda function metadata. Any json with the { "blambda": "manifest" } key-value pair will be recognized as a manifest file. A rough example json is shown below.
{
"blambda": "manifest",
"dependencies": {
"dependency_name": "dependency_version",
"dep2": "1.0.a"
},
"options": {
"Description": "what it does",
"Timeout": 300,
"Runtime": "node or python"
},
"permissions": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:DescribeLogGroups",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams",
"logs:FilterLogEvents",
"logs:GetLogEvents"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
]
}
],
"source files": [
"filename.py",
["../shared_lib/shared_code.py", "shared_code.py"]
]
}See test_lambda_manifest.py and test_findfunc.py for more detailed examples on how lambda functions should be named / searched for.
The directory and filename of the manifest json file are used to create a lambda function name. For example, given the following directory tree:
bundle
├── config.py
├── html.json
├── html.py
└── test_html.py
The function will be deployed as fulfillment_bundle_html_{env_name} (e.g. fulfillment_bundle_html_dev).
From the blambda cmd-line, the lambda function can be accessed using bundle/html, e.g.:
blambda deps bundle/htmlIf the function name and directory name are collapsed if they match, e.g.
rest
├── restclient.py
├── rest.json
└── rest.py
Would produce fulfillment_rest_dev. Both short and long forms work from the cmd-line:
blambda deps rest/rest
blambda deps restWhen a "Lambda Functions" build in Bamboo errors out you'll want to look at the logs kfirst (here is an example).
There are a few possibilities when blambda can't find a specific lambda function:
-
New/Unreleased Lambda function?
- New functions won't be automatically built in dev bamboo jobs
-- you need to run an explicit build (using
this.package).
- New functions won't be automatically built in dev bamboo jobs
-- you need to run an explicit build (using
-
Typo in the name?
If neither of these is the case, you'll probably want to look at
findfunc.py.
Each lambda function has its own dependencies (managed from manifest.json) - we've seen a few cases where dependencies can get in a bad state (e.g. python/node.js import errors). In this case, the easiest thing to try is a clean reinstall of all the lambda function's dependencies:
blambda deps {function_name} --clean