该仓库为南京大学2022年秋季学期编译原理课程实验五代码框架, 需要同学们补全数据流分析求解器以及活跃变量分析, 复制传播, 可用表达式分析, 赋值传播四个数据流分析应用的具体实现, 以此来中间代码优化工作.
注意: 实验框架会随时更新注释和修补bug, 请定期从远程仓库执行pull, 最近一次代码更新时间为 2023 年 1 月 3 日
希望大家能够帮助补充相关注释. 发现bug, 提供建议, 可联系助教.
使用c语言实现面向对象编程请自行STFW
本实验用到的面向对象编程相关宏定义
// 返回已执行init构造函数的指针, 类似于C++的 new obj 语句
#define NEW(TYPE, ...) ({ \
TYPE *TMP = (TYPE*)malloc(sizeof(TYPE)); \
concat(TYPE, _init) (TMP, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
TMP; \
})
// 从虚函数表vTable中调用函数, 指针需要解引用
#define VCALL(obj, func, ...) \
(((obj).vTable)->func(&(obj), ##__VA_ARGS__))
// 执行teardown析构函数并free, 类似于C++的 delete obj 语句
#define DELETE(obj_ptr) \
do { VCALL(*obj_ptr, teardown); free(obj_ptr); } while(0)
// 虚函数表中没有teardown, 需要显式调用特定类型的析构函数
#define RDELETE(type, obj_ptr) \
do { concat(type, _teardown)(obj_ptr); free(obj_ptr); } while(0)#include <container/vector.h>定义模板类型
DEF_VECTOR(int) // 全局定义宏展开结果大致为
typedef struct Vec_int {
struct Vec_int_virtualTable {
void (*teardown)(Vec_int *vec);
void (*resize)(Vec_int *vec, vec_size_t new_size);
void (*push_back)(Vec_int *vec, int item);
void (*pop_back)(Vec_int *vec);
vec_size_t (*find)(Vec_int *vec, bool (*check)(int *arr_item, void *arg), void *arg);
vec_size_t (*lower_bound)(Vec_int *vec, bool (*check)(int *arr_item, void *arg), void *arg);
void (*insert)(Vec_int *vec, vec_size_t idx, int item);
void (*delete)(Vec_int *vec, vec_size_t idx);
} const *vTable;
vec_size_t len; // arr_len
int *arr;
...
} Vec_int;
void Vec_int_init(Vec_int *vec);迭代器 it 为 TYPE* 指针, 解引用 *it 为内容
for_vec(int, it, vec)宏展开为
for(int *it = vec.arr; it != vec.arr + vec.len; it ++)void func() {
Vec_int v;
Vec_int_init(&v);
// do somthing
Vec_int_teardown(&v);
// 或者
Vec_int *v = NEW(Vec_int);
// do somthing
// 例如需要调用虚函数表中的函数, 可使用宏定义
VCALL(v, pushback, 1);
// 等价于
v.vTable->push_back(&v, 1);
DELETE(v); // v->vTable->teardown(v); free(v);
}#include <container/list.h>定义模板类型
DEF_LIST(int) // 全局定义宏展开结果大致为
typedef struct ListNode_int {
struct ListNode_int *pre, *nxt;
int val;
} ListNode_int;
struct List_int {
struct List_int_virtualTable {
void (*teardown)(List_int *l);
void (*insert_front)(List_int *l, ListNode_int *x, int val);
void (*insert_back)(List_int *l, ListNode_int *x, int val);
void (*push_front)(List_int *l, int val);
void (*push_back)(List_int *l, int val);
ListNode_int *(*delete)(List_int *l, ListNode_int *x); // 返回nxt节点(迭代器)
void (*pop_front)(List_int *l);
void (*pop_back)(List_int *l);
} const *vTable;
struct ListNode_int *head, *tail; // 当 list 为空时, head 与 tail 均为 NULL
};
void List_int_init(List_int *l);迭代器 it 为 ListNode_TYPE* 链表节点指针, it->val 为内容
for_list(int, it, list)宏展开为
for(ListNode_int *it = list.head; it; it = it->nxt)#include <container/treap.h>定义模板类型
DEF_MAP(int, double) // 全局定义
DEF_MAP_CMP(int, double, CMP_FUNC)
// CMP_FUNC 为自定义比较函数, 返回值为 a == b ? -1 : a < b宏展开为
typedef struct MapNode_int_double {
...
int key;
double val;
} MapNode_int_double;
struct Map_int_double {
struct Map_int_double_virtualTable {
void (*teardown)(Map_int_double *t);
bool (*insert)(Map_int_double *t, int key, double val); // 若key已存在则不修改值, 并返回false
bool (*delete)(Map_int_double *t, int key); // 若key不存在则返回false
bool (*exist)(Map_int_double *t, int key);
double (*get)(Map_int_double *t, int key); // 需保证 key 已经存在
void (*set)(Map_int_double *t, int key, double val); // // 若key已存在则修改val值, 否则等价于insert
} const *vTable;
...
};
void Map_int_double_init(Map_int_double *t);迭代器 it 为 MapNode_KEY_TYPE_VAL_TYPE* 平衡树节点指针, {it->key, it->val} 为映射内容
for_map(int, double, it, map) ...宏展开为
for(
MapNode_KEY_TYPE_VAL_TYPE *it = TreapNode_first_iter(map.root);
it != NULL;
it = TreapNode_next_iter(it)
)#include <container/treap.h>定义模板类型
DEF_SET(int) // 全局定义
DEF_SET_CMP(int, CMP_FUNC) // 自定义比较函数宏展开为
typedef struct SetNode_int {
...
int key;
} SetNode_int;
struct Set_int {
struct Set_int_virtualTable {
void (*teardown)(Set_int *t);
bool (*insert)(Set_int *t, int key); // 已存在返回false
bool (*delete)(Set_int *t, int key); // 不存在返回false
bool (*exist)(Set_int *t, int key);
} const *vTable;
...
};
void Set_int_init(Set_int *t);迭代器 it 为 SetNode_KEY_TYPE* 平衡树节点指针, it->key 为内容
for_set(int, it, set) ...宏展开为
for(
MapNode_KEY_TYPE_VAL_TYPE *it = TreapNode_first_iter(set.root);
it != NULL;
it = TreapNode_next_iter(it)
)该实验框架已完成IR输入解析, 划分基本块, 建立控制流图等基本工作, 你只需要了解IR相关数据结构
- IR_program
- IR_function
- IR_block 基本快
- IR_stmt 基本语句
- def -> def变量
- use_vec -> use变量数组
- IR_stmt 基本语句
- IR_block 基本快
- IR_function
IR_op_stmt: rd := rs1 op rs2
IR_assign_stmt: rd := rs
IR_load_stmt: rd := *rs_addr
IR_store_stmt: *rd_addr = rs
IR_call_stmt: (ARGS argv[argc]{rs1,rs2,...})
rd := CALL func
IR_if_stmt: IF rs1 relop rs2 GOTO true_label ELSE false_label
IR_goto_stmt: GOTO label
IR_return_stmt: return rs
IR_read_stmt: READ rd
IR_write_stmt: WRITE rs
//// ================================== IR var & label ==================================
typedef unsigned IR_var; // 数字表示 v1, v2...
typedef unsigned IR_label; // 数字表示 L1, L2...
typedef unsigned IR_DEC_size_t;
enum {IR_VAR_NONE = 0};
enum {IR_LABEL_NONE = 0};
DEF_VECTOR(IR_var)
extern IR_var ir_var_generator(); // 获取新变量编号
extern IR_label ir_label_generator(); // 获取新label编号
//// ================================== IR ==================================
//// IR_val
typedef struct IR_val { // 常量或变量
bool is_const;
union {
IR_var var;
int const_val;
};
} IR_val;
//// IR_stmt
typedef enum {
IR_OP_STMT, IR_ASSIGN_STMT, IR_LOAD_STMT, IR_STORE_STMT, IR_IF_STMT, IR_GOTO_STMT, IR_CALL_STMT, IR_RETURN_STMT, IR_READ_STMT, IR_WRITE_STMT
} IR_stmt_type;
// use 数组, 需要手动忽略常量
typedef struct IR_use {
unsigned use_cnt; // use 个数
IR_val *use_vec; // use 数组
}IR_use;
struct IR_stmt_virtualTable {
void (*teardown) (IR_stmt *stmt);
void (*print) (IR_stmt *stmt, FILE *out);
IR_var (*get_def) (IR_stmt *stmt); // def 最多只有一个, 不存在则返回 IR_VAR_NONE
IR_use (*get_use_vec) (IR_stmt *stmt);
};
struct IR_stmt {
struct {
struct IR_stmt_virtualTable const *vTable;
IR_stmt_type stmt_type;
bool dead;
};
};
//// IR_block
typedef struct {
IR_label label;
bool dead;
List_IR_stmt_ptr stmts;
} IR_block, *IR_block_ptr;
//// IR_function
typedef struct {
IR_var dec_addr;
IR_DEC_size_t dec_size;
} IR_Dec;
typedef List_IR_block_ptr *List_ptr_IR_block_ptr;
typedef struct IR_function{
char *func_name;
Vec_IR_var params;
Map_IR_var_IR_Dec map_dec; // dec_var => (addr_var, size)
List_IR_block_ptr blocks;
// Control Flow Graph
IR_block *entry, *exit;
Map_IR_label_IR_block_ptr map_blk_label; // Label -> Block 指针
Map_IR_block_ptr_List_ptr_IR_block_ptr blk_pred, blk_succ; // Block 指针 -> List<前驱后继Block> 的指针
} IR_function, *IR_function_ptr;
//// IR_program
typedef struct IR_program {
Vec_IR_function_ptr functions;
} IR_program;
//// ================================== Stmt ==================================
typedef enum {
IR_OP_ADD, IR_OP_SUB, IR_OP_MUL, IR_OP_DIV
} IR_OP_TYPE;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_OP_TYPE op;
IR_var rd;
union {
IR_val use_vec[2];
struct { IR_val rs1, rs2; };
};
} IR_op_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_var rd;
union {
IR_val use_vec[1];
struct { IR_val rs; };
};
} IR_assign_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_var rd;
union {
IR_val use_vec[1];
struct { IR_val rs_addr; };
};
} IR_load_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
union {
IR_val use_vec[2];
struct { IR_val rd_addr, rs; };
};
} IR_store_stmt;
typedef enum {
IR_RELOP_EQ, IR_RELOP_NE, IR_RELOP_GT, IR_RELOP_GE, IR_RELOP_LT, IR_RELOP_LE
} IR_RELOP_TYPE;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_RELOP_TYPE relop;
union {
IR_val use_vec[2];
struct { IR_val rs1, rs2; };
};
IR_label true_label, false_label;
IR_block *true_blk, *false_blk;
} IR_if_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_label label;
IR_block *blk;
} IR_goto_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
union {
IR_val use_vec[1];
struct { IR_val rs; };
};
} IR_return_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_var rd;
char *func_name;
unsigned argc;
IR_val *argv;
} IR_call_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
IR_var rd;
} IR_read_stmt;
typedef struct {
CLASS_IR_stmt
union {
IR_val use_vec[1];
struct { IR_val rs; };
};
} IR_write_stmt;以下内容参考软件分析课程与实验讲义
Static Program Analysis | Tai-e (pascal-lab.net)
可简要阅读实验 1 2 3 获得更多信息
框架代码将每个数据流分析抽象成了对应的子类, 并使用统一的求解器进行求解
以活跃变量分析为例, 其主要提供的方法为
typedef struct LiveVariableAnalysis {
struct LiveVariableAnalysis_virtualTable {
bool (*isForward) (LiveVariableAnalysis *t); // 前向/后向数据流分析?
Set_IR_var *(*newBoundaryFact) (LiveVariableAnalysis *t, IR_function *func);
Set_IR_var *(*newInitialFact) (LiveVariableAnalysis *t);
bool (*meetInto) (LiveVariableAnalysis *t, Set_IR_var *fact, Set_IR_var *target);
bool (*transferBlock) (LiveVariableAnalysis *t, IR_block *block, Set_IR_var *in_fact, Set_IR_var *out_fact);
// 若结果发生改变则返回true
...
} const *vTable;
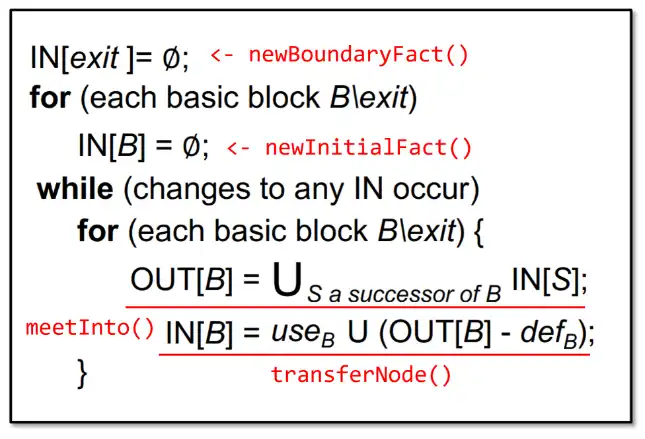
} LiveVariableAnalysis;若使用迭代求解器求解, 求解器算法如下
此处 meetInto() 的设计可能与你设想的稍有差别:它接受 fact 和 target 两个参数并把 fact 集合并入 target 集合。这个函数有什么用呢?考虑一下上图中 meetInto() 附近的那行伪代码,它会取出 B 的所有后继,然后把它们 IN facts 的并集赋给 OUT[B]。如果这行代码用 meetInto() 来实现,那么我们就可以根据下图所示,用 meetInto(IN[S], OUT[B]) 把 B 的每个后继 S 的 IN fact 直接并入到 OUT[B] 中:
这样设计 meetInto() 是出于效率考量。首先,在一个控制流合并节点多次调用 meetInto() 时,我们都在改写同一个对象。这样,我们可以避免像伪代码 OUT[S] = U… 所描述的那样,每次合并两个集合就会创建出一个新的 SetFact 对象保存结果。当然,为了实现上面所说的 meet 策略,你需要在初始化阶段给每条语句的 OUT[S] 赋上和 IN[S] 一样的初值。
在 src/IR_optimze/solver.c 中, 前向分析的迭代求解器与worklist求解器代码已给出实现. 请实现后向分析的 TODO 内容
建议完成活跃变量分析和常量传播的数据流分析应用实现. 同时, 每个数据流分析都提供了结果输出函数用来进行debug
请根据实验指导完成 src/IR_optimze/available_expressions_analysis.c 中的 TODO 内容
请根据实验指导实现 src/IR_optimze/constant_propogation.c 中的 TODO 内容
本框架对可用表达式分析采用了以下做法
-
对相同的表达式使用相同的变量重新赋值, 例如
v := v1 + v2 => expr1 := v1 + v2 v := expr2 -
对所有的expr对应的变量构造 e_kill 与 e_gen, 针对所有expr对应的变量进行数据流分析
具体优化流程见下文
如果需要实现该部分内容, 请实现 src/IR_optimze/available_expressions_analysis.c 中的 TODO 内容
复制传播的数据流分析方程见下
Data-flow analysis: copy propagation. (uwo.ca)
如果需要实现该部分内容, 请实现 src/IR_optimze/copy_propogation.c 中的 TODO 内容
FUNCTION main :
READ v1
READ v2
v3 := v1 + v2
v4 := v1 + v2
IF v1 < v2 GOTO L1
v5 := v1 - v2
GOTO L2
LABEL L1 :
v6 := v1 - v2
LABEL L2 :
v7 := v1 - v2
WRITE v4
WRITE v7
RETURN #0
合并公共子表达式
FUNCTION main :
READ v1
READ v2
expr1 := v1 + v2
v3 := expr1
expr1 := v1 + v2
v4 := expr1
IF v1 < v2 GOTO L1
expr2 := v1 - v2
v5 := expr2
GOTO L2
LABEL L1 :
expr2 := v1 - v2
v6 := expr2
LABEL L2 :
expr2 := v1 - v2
v7 := expr2
WRITE v4
WRITE v7
RETURN #0
消除可用表达式
FUNCTION main :
READ v1
READ v2
expr1 := v1 + v2
v3 := expr1
v4 := expr1
IF v1 < v2 GOTO L1
expr2 := v1 - v2
v5 := expr2
GOTO L2
LABEL L1 :
expr2 := v1 - v2
v6 := expr2
LABEL L2 :
v7 := expr2
WRITE v4
WRITE v7
RETURN #0
复制传播
FUNCTION main :
READ v1
READ v2
expr1 := v1 + v2
v3 := expr1
v4 := expr1
IF v1 < v2 GOTO L1
expr2 := v1 - v2
v5 := expr2
GOTO L2
LABEL L1 :
expr2 := v1 - v2
v6 := expr2
LABEL L2 :
v7 := expr2
WRITE expr1
WRITE expr2
RETURN #0
死代码消除
FUNCTION main :
READ v1
READ v2
expr1 := v1 + v2
IF v1 < v2 GOTO L1
expr2 := v1 - v2
GOTO L2
LABEL L1 :
expr2 := v1 - v2
LABEL L2 :
WRITE expr1
WRITE expr2
RETURN #0
请根据实验指导, 通过迭代执行活跃变量分析, 完成死代码消除
事实上, 可以根据常量传播的结果分析IF语句的跳转关系, 标记不可达基本块, 从而进一步完成死代码消除
目前实验框架的 gen/kill, use/def 关系是以 Stmt 为单位进行转移, 效率较低, 事实上可用将 Block 内所有 Stmt 的 gen/kill, use/def 进行合并以提高 transferBlock 的效率, 从而得到龙书课本上真正的算法实现. 如果你选择实现改进, 你需要建立从 block 到 gen/kill, use/def 的映射, 当然会遇到很多具体细节和难点.