This repository focuses on converting static functional safety (FuSa) requirements into runtime FuSa supervision using behavior trees.
The inputs are the ISO 26262 fault tree analysis (FTA), represented as a draw.io diagram XML file, and the hazard analysis and risk assessment (HARA), provided in a CSV file.
The outputs consist of behavior tree XML files (one per HARA item) compatible with BehaviorTree.CPP and Groot. This facilitates integration with systems using the ROS framework for managing complex behaviors and enables real-time visualization of the supervision status. Additionally, these supervisors can be formally verified using the NuSMV tool.
The tool is designed to convert fault trees from draw.io diagram XML files into behavior tree XML files compatible with the BehaviorTree.CPP library. Here's how to use it:
- Create or Open Your Fault Tree Diagram in Draw.io:
- First, visit draw.io to create or edit your fault tree diagram. You may refer to their documentation for guidance on using the tool.
- Diagram Structure & Symbols:
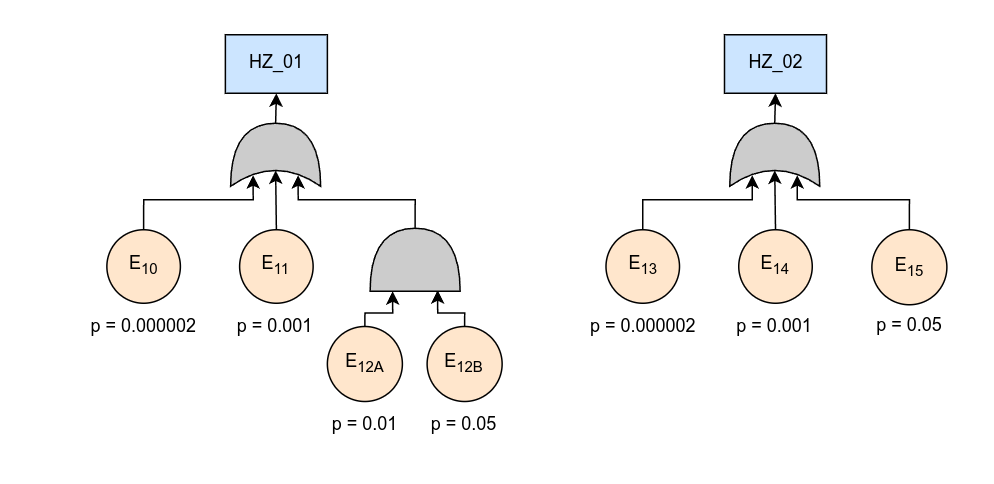
- Hazards: Represent hazards using rectangles. This is a required element in your diagram.
- Events: Depict events using circles. These are also required elements.
- AND/OR Gates: Use the respective symbols for AND/OR gates in your diagram. These are required for depicting logical relationships in the fault tree.
- Probabilities: Use text below the events to indicate the correspondent probability. Example:
p = 0.1. These elements are not required.
- Exporting the Diagram as XML:
- Once your fault tree diagram is ready, you need to export it in XML format. In draw.io, go to
File>Export as>XMLto save your diagram as an XML file.
- Once your fault tree diagram is ready, you need to export it in XML format. In draw.io, go to
Warning!: All fault tree elements, with the exception of text probabilities, should be connected by directional arrows. Ensure that each arrow is physically attached to its corresponding elements to maintain clarity and accuracy in the diagram.
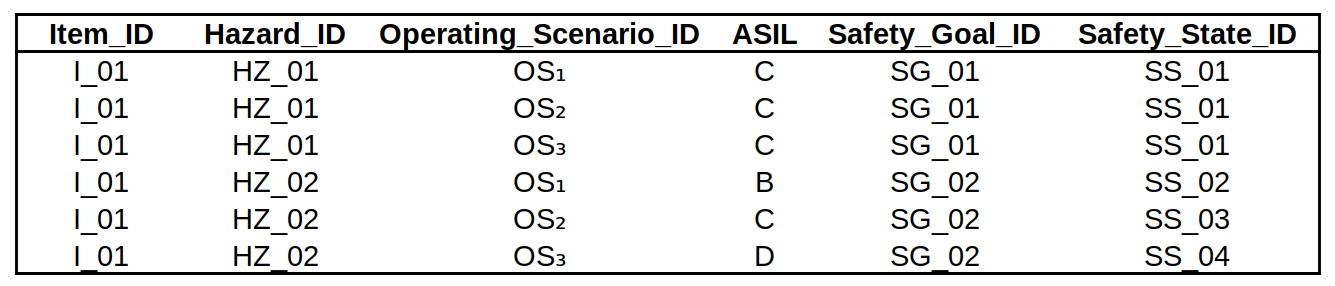
Create a *.csv file with some required column names:
- Item_ID: Identificator of the Item analyzed.
- Hazard_ID: Identificator of the possible Hazard. The ID must match with the name of the correspondent Hazard in the Fault Tree.
- Operating_Scenario_ID: Identificator of the Operating Scenario.
- ASIL: Automotive Safety Integrity Level. Options: A, B, C, D.
- Safety_Goal_ID: Identificator of the Safety Goal.
- Safety_State_ID: Identificator of the Safety State action.
Run the conversion command:
ft2bt -f FTA_FILEPATH [-o OUTPUT_FOLDER] [-H HARA_FILEPATH] [-ctl] [-v]Where:
- -f: (Required, str) Specifies the XML global filepath name of the draw.io diagram.
- -o: (Optional, str) Specifies the global folder path, where the behavior tree XML diagram is saved.
- -H: (Optional, str) Specifies the CSV global file name of the Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA).
- -ctl: (Optional, bool) Formally verifies the BT FuSa supervisor with CTL formulation, using NuSMV 2.6.0.
- -v: (Optional, bool) Automatically shows and saves the renders.
Below is an example of the behavior tree diagrams generated from the fault tree and HARA examples. The command used for the generation is:
ft2bt -ctl -f $FT2BT_PATH/test/fault_trees/fta_example.xml -H $FT2BT_PATH/test/hara/hara_example.csv -o $FT2BT_PATH/test/behavior_treesThe order of the events is sorted by probability of occurrence (-p option). The operational situations (OS) are added from the HARA information (-os option).Finally, CTL automotive functional safety formal verification is performed to ensure that the FuSa Supervisor is meeting the ISO 26262 requirements (-ctl option).
The output XML file that represents the supervisor can be loaded using Groot:
Install the ft2bt PyPI package:
pip install ft2bt
echo 'export FT2BT_PATH=$(python3 -c "import ft2bt; import os; print(os.path.dirname(ft2bt.__file__))")' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrcThis project requires NuSMV version 2.6.0 to be installed, only in the case that the formal verification is required. Follow the steps below to install it:
- Go to the NuSMV Downloads Page.
- Download the NuSMV 2.6.0 archive file for your operating system.
After downloading, extract the contents of the archive file:
tar -xvzf NuSMV-2.6.0.tar.gz
cd NuSMV-2.6.0
./configure
make
sudo make install
NuSMV -versionYou can refer to the NuSMV Documentation for more details.
The repository has been proven in an Ubuntu 20.04 environment.
- Behavior Trees for the Application of ISO 26262 in Field Monitoring Processes for Autonomous Vehicles (Conference Article, IEEE ITSC 2024)
- Behavior Trees in Functional Safety Supervisors for Autonomous Vehicles (Preprint Article, IEEE ITS)
For further information regarding this project, please feel free to reach out to Carlos Conejo carlos.conejo@upc.edu.
This project was mainly developed at the Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial (IRI), a joint university research center of the Polytechnic University of Catalonia (UPC) and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC). The automatized formal verification process was developed in collaboration with the Cyber Physical Systems Group (TUM).
Research partially funded by the Spanish State Research Agency (AEI) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERFD) through the SaCoAV project (ref. PID2020-114244RB-I00). Also funded by Renault Group through the Industrial Doctorate "Safety of Autonomous Vehicles" (ref. C12507).