Swag converts Go annotations to Swagger Documentation 2.0. We've created a variety of plugins for popular Go web frameworks. This allows you to quickly integrate with an existing Go project (using Swagger UI).
- Getting started
- Supported Web Frameworks
- How to use it with Gin
- The swag formatter
- Implementation Status
- Declarative Comments Format
- Examples
- Descriptions over multiple lines
- User defined structure with an array type
- Function scoped struct declaration
- Model composition in response
- Add a headers in response
- Use multiple path params
- Example value of struct
- SchemaExample of body
- Description of struct
- Use swaggertype tag to supported custom type
- Use global overrides to support a custom type
- Use swaggerignore tag to exclude a field
- Add extension info to struct field
- Rename model to display
- How to use security annotations
- Add a description for enum items
- Generate only specific docs file types
- About the Project
-
Add comments to your API source code, See Declarative Comments Format.
-
Download swag by using:
$ go get -u github.com/chaintraced/swag/cmd/swag
# 1.16 or newer
$ go install github.com/chaintraced/swag/cmd/swag@latestTo build from source you need Go (1.15 or newer).
Or download a pre-compiled binary from the release page.
- Run
swag initin the project's root folder which contains themain.gofile. This will parse your comments and generate the required files (docsfolder anddocs/docs.go).
$ swag initMake sure to import the generated docs/docs.go so that your specific configuration gets init'ed. If your General API annotations do not live in main.go, you can let swag know with -g flag.
swag init -g http/api.go- (optional) Use
swag fmtformat the SWAG comment. (Please upgrade to the latest version)
swag fmt$ swag init -h
NAME:
swag init - Create docs.go
USAGE:
swag init [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
--generalInfo value, -g value Go file path in which 'swagger general API Info' is written (default: "main.go")
--dir value, -d value Directories you want to parse,comma separated and general-info file must be in the first one (default: "./")
--exclude value Exclude directories and files when searching, comma separated
--propertyStrategy value, -p value Property Naming Strategy like snakecase,camelcase,pascalcase (default: "camelcase")
--output value, -o value Output directory for all the generated files(swagger.json, swagger.yaml and docs.go) (default: "./docs")
--outputTypes value, --ot value Output types of generated files (docs.go, swagger.json, swagger.yaml) like go,json,yaml (default: "go,json,yaml")
--parseVendor Parse go files in 'vendor' folder, disabled by default (default: false)
--parseDependency, --pd Parse go files inside dependency folder, disabled by default (default: false)
--markdownFiles value, --md value Parse folder containing markdown files to use as description, disabled by default
--codeExampleFiles value, --cef value Parse folder containing code example files to use for the x-codeSamples extension, disabled by default
--parseInternal Parse go files in internal packages, disabled by default (default: false)
--generatedTime Generate timestamp at the top of docs.go, disabled by default (default: false)
--requiredByDefault Set validation required for all fields by default (default: false)
--parseDepth value Dependency parse depth (default: 100)
--instanceName value This parameter can be used to name different swagger document instances. It is optional.
--overridesFile value File to read global type overrides from. (default: ".swaggo")
--help, -h show help (default: false)swag fmt -h
NAME:
swag fmt - format swag comments
USAGE:
swag fmt [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
--dir value, -d value Directories you want to parse,comma separated and general-info file must be in the first one (default: "./")
--exclude value Exclude directories and files when searching, comma separated
--generalInfo value, -g value Go file path in which 'swagger general API Info' is written (default: "main.go")
--help, -h show help (default: false)
Find the example source code here.
- After using
swag initto generate Swagger 2.0 docs, import the following packages:
import "github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger" // gin-swagger middleware
import "github.com/swaggo/files" // swagger embed files- Add General API annotations in
main.gocode:
// @title Swagger Example API
// @version 1.0
// @description This is a sample server celler server.
// @termsOfService http://swagger.io/terms/
// @contact.name API Support
// @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support
// @contact.email support@swagger.io
// @license.name Apache 2.0
// @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
// @host localhost:8080
// @BasePath /api/v1
// @securityDefinitions.basic BasicAuth
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
c := controller.NewController()
v1 := r.Group("/api/v1")
{
accounts := v1.Group("/accounts")
{
accounts.GET(":id", c.ShowAccount)
accounts.GET("", c.ListAccounts)
accounts.POST("", c.AddAccount)
accounts.DELETE(":id", c.DeleteAccount)
accounts.PATCH(":id", c.UpdateAccount)
accounts.POST(":id/images", c.UploadAccountImage)
}
//...
}
r.GET("/swagger/*any", ginSwagger.WrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler))
r.Run(":8080")
}
//...Additionally some general API info can be set dynamically. The generated code package docs exports SwaggerInfo variable which we can use to set the title, description, version, host and base path programmatically. Example using Gin:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/swaggo/files"
"github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger"
"./docs" // docs is generated by Swag CLI, you have to import it.
)
// @contact.name API Support
// @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support
// @contact.email support@swagger.io
// @license.name Apache 2.0
// @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
func main() {
// programmatically set swagger info
docs.SwaggerInfo.Title = "Swagger Example API"
docs.SwaggerInfo.Description = "This is a sample server Petstore server."
docs.SwaggerInfo.Version = "1.0"
docs.SwaggerInfo.Host = "petstore.swagger.io"
docs.SwaggerInfo.BasePath = "/v2"
docs.SwaggerInfo.Schemes = []string{"http", "https"}
r := gin.New()
// use ginSwagger middleware to serve the API docs
r.GET("/swagger/*any", ginSwagger.WrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler))
r.Run()
}- Add API Operation annotations in
controllercode
package controller
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/chaintraced/swag/example/celler/httputil"
"github.com/chaintraced/swag/example/celler/model"
)
// ShowAccount godoc
// @Summary Show an account
// @Description get string by ID
// @Tags accounts
// @Accept json
// @Produce json
// @Param id path int true "Account ID"
// @Success 200 {object} model.Account
// @Failure 400 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Failure 404 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Failure 500 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Router /accounts/{id} [get]
func (c *Controller) ShowAccount(ctx *gin.Context) {
id := ctx.Param("id")
aid, err := strconv.Atoi(id)
if err != nil {
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusBadRequest, err)
return
}
account, err := model.AccountOne(aid)
if err != nil {
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusNotFound, err)
return
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, account)
}
// ListAccounts godoc
// @Summary List accounts
// @Description get accounts
// @Tags accounts
// @Accept json
// @Produce json
// @Param q query string false "name search by q" Format(email)
// @Success 200 {array} model.Account
// @Failure 400 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Failure 404 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Failure 500 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Router /accounts [get]
func (c *Controller) ListAccounts(ctx *gin.Context) {
q := ctx.Request.URL.Query().Get("q")
accounts, err := model.AccountsAll(q)
if err != nil {
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusNotFound, err)
return
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, accounts)
}
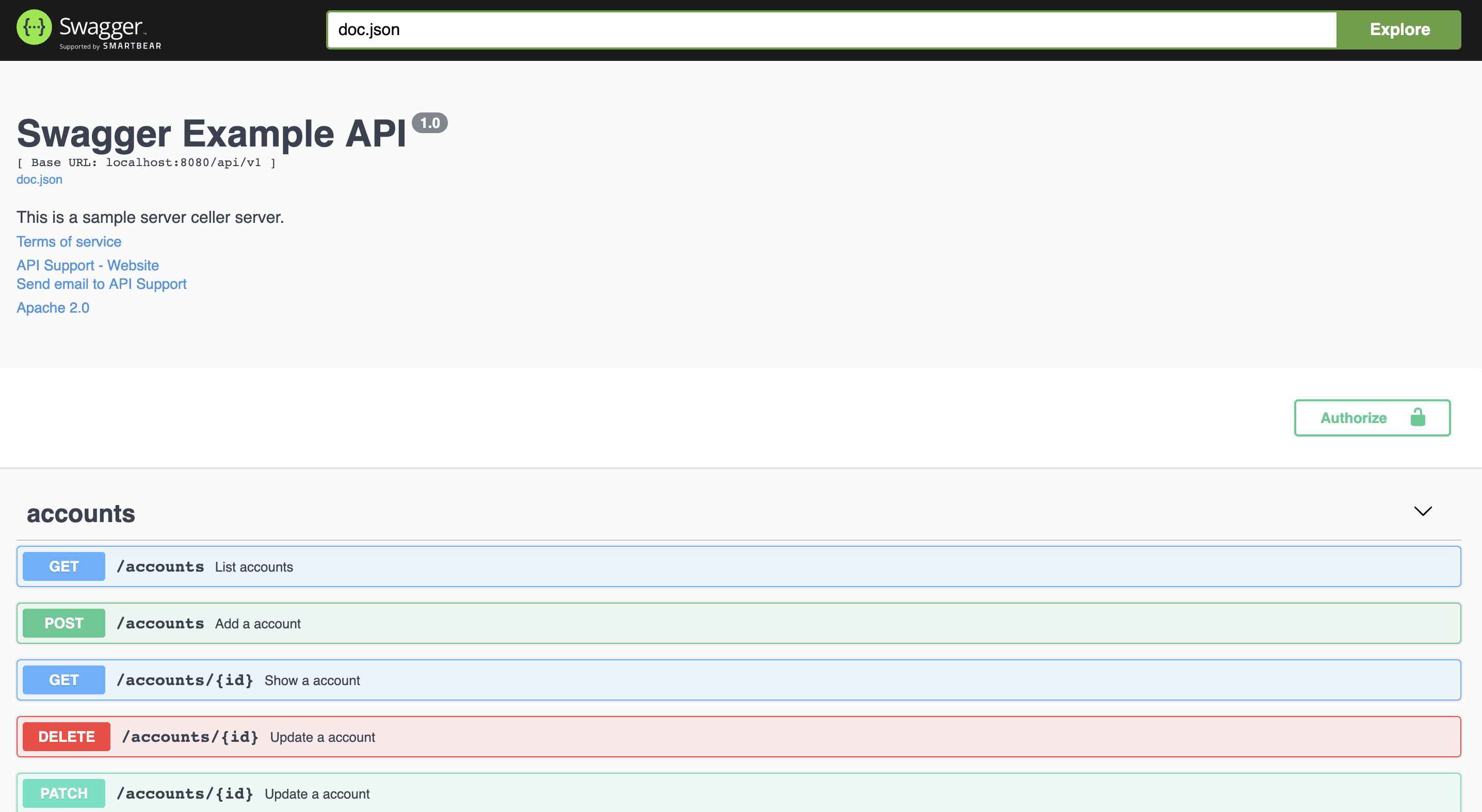
//...$ swag init- Run your app, and browse to http://localhost:8080/swagger/index.html. You will see Swagger 2.0 Api documents as shown below:
The Swag Comments can be automatically formatted, just like 'go fmt'. Find the result of formatting here.
Usage:
swag fmtExclude folder:
swag fmt -d ./ --exclude ./internal- Basic Structure
- API Host and Base Path
- Paths and Operations
- Describing Parameters
- Describing Request Body
- Describing Responses
- MIME Types
- Authentication
- Basic Authentication
- API Keys
- Adding Examples
- File Upload
- Enums
- Grouping Operations With Tags
- Swagger Extensions
Example celler/main.go
| annotation | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| title | Required. The title of the application. | // @title Swagger Example API |
| version | Required. Provides the version of the application API. | // @version 1.0 |
| description | A short description of the application. | // @description This is a sample server celler server. |
| tag.name | Name of a tag. | // @tag.name This is the name of the tag |
| tag.description | Description of the tag | // @tag.description Cool Description |
| tag.docs.url | Url of the external Documentation of the tag | // @tag.docs.url https://example.com |
| tag.docs.description | Description of the external Documentation of the tag | // @tag.docs.description Best example documentation |
| termsOfService | The Terms of Service for the API. | // @termsOfService http://swagger.io/terms/ |
| contact.name | The contact information for the exposed API. | // @contact.name API Support |
| contact.url | The URL pointing to the contact information. MUST be in the format of a URL. | // @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support |
| contact.email | The email address of the contact person/organization. MUST be in the format of an email address. | // @contact.email support@swagger.io |
| license.name | Required. The license name used for the API. | // @license.name Apache 2.0 |
| license.url | A URL to the license used for the API. MUST be in the format of a URL. | // @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html |
| host | The host (name or ip) serving the API. | // @host localhost:8080 |
| BasePath | The base path on which the API is served. | // @BasePath /api/v1 |
| accept | A list of MIME types the APIs can consume. Note that Accept only affects operations with a request body, such as POST, PUT and PATCH. Value MUST be as described under Mime Types. | // @accept json |
| produce | A list of MIME types the APIs can produce. Value MUST be as described under Mime Types. | // @produce json |
| query.collection.format | The default collection(array) param format in query,enums:csv,multi,pipes,tsv,ssv. If not set, csv is the default. | // @query.collection.format multi |
| schemes | The transfer protocol for the operation that separated by spaces. | // @schemes http https |
| x-name | The extension key, must be start by x- and take only json value | // @x-example-key {"key": "value"} |
When a short string in your documentation is insufficient, or you need images, code examples and things like that you may want to use markdown descriptions. In order to use markdown descriptions use the following annotations.
| annotation | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| title | Required. The title of the application. | // @title Swagger Example API |
| version | Required. Provides the version of the application API. | // @version 1.0 |
| description.markdown | A short description of the application. Parsed from the api.md file. This is an alternative to @description | // @description.markdown No value needed, this parses the description from api.md |
| tag.name | Name of a tag. | // @tag.name This is the name of the tag |
| tag.description.markdown | Description of the tag this is an alternative to tag.description. The description will be read from a file named like tagname.md | // @tag.description.markdown |
Example celler/controller
| annotation | description |
|---|---|
| description | A verbose explanation of the operation behavior. |
| description.markdown | A short description of the application. The description will be read from a file. E.g. @description.markdown details will load details.md |
| id | A unique string used to identify the operation. Must be unique among all API operations. |
| tags | A list of tags to each API operation that separated by commas. |
| summary | A short summary of what the operation does. |
| accept | A list of MIME types the APIs can consume. Note that Accept only affects operations with a request body, such as POST, PUT and PATCH. Value MUST be as described under Mime Types. |
| produce | A list of MIME types the APIs can produce. Value MUST be as described under Mime Types. |
| param | Parameters that separated by spaces. param name,param type,data type,is mandatory?,comment attribute(optional) |
| security | Security to each API operation. |
| success | Success response that separated by spaces. return code or default,{param type},data type,comment |
| failure | Failure response that separated by spaces. return code or default,{param type},data type,comment |
| response | As same as success and failure |
| header | Header in response that separated by spaces. return code,{param type},data type,comment |
| router | Path definition that separated by spaces. path,[httpMethod] |
| x-name | The extension key, must be start by x- and take only json value. |
| x-codeSample | Optional Markdown usage. take file as parameter. This will then search for a file named like the summary in the given folder. |
| deprecated | Mark endpoint as deprecated. |
swag accepts all MIME Types which are in the correct format, that is, match */*.
Besides that, swag also accepts aliases for some MIME Types as follows:
| Alias | MIME Type |
|---|---|
| json | application/json |
| xml | text/xml |
| plain | text/plain |
| html | text/html |
| mpfd | multipart/form-data |
| x-www-form-urlencoded | application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| json-api | application/vnd.api+json |
| json-stream | application/x-json-stream |
| octet-stream | application/octet-stream |
| png | image/png |
| jpeg | image/jpeg |
| gif | image/gif |
- query
- path
- header
- body
- formData
- string (string)
- integer (int, uint, uint32, uint64)
- number (float32)
- boolean (bool)
- user defined struct
| annotation | description | parameters | example |
|---|---|---|---|
| securitydefinitions.basic | Basic auth. | // @securityDefinitions.basic BasicAuth | |
| securitydefinitions.apikey | API key auth. | in, name, description | // @securityDefinitions.apikey ApiKeyAuth |
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.application | OAuth2 application auth. | tokenUrl, scope, description | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.application OAuth2Application |
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit | OAuth2 implicit auth. | authorizationUrl, scope, description | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit OAuth2Implicit |
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.password | OAuth2 password auth. | tokenUrl, scope, description | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.password OAuth2Password |
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.accessCode | OAuth2 access code auth. | tokenUrl, authorizationUrl, scope, description | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.accessCode OAuth2AccessCode |
| parameters annotation | example |
|---|---|
| in | // @in header |
| name | // @name Authorization |
| tokenUrl | // @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token |
| authorizationurl | // @authorizationurl https://example.com/oauth/authorize |
| scope.hoge | // @scope.write Grants write access |
| description | // @description OAuth protects our entity endpoints |
// @Param enumstring query string false "string enums" Enums(A, B, C)
// @Param enumint query int false "int enums" Enums(1, 2, 3)
// @Param enumnumber query number false "int enums" Enums(1.1, 1.2, 1.3)
// @Param string query string false "string valid" minlength(5) maxlength(10)
// @Param int query int false "int valid" minimum(1) maximum(10)
// @Param default query string false "string default" default(A)
// @Param example query string false "string example" example(string)
// @Param collection query []string false "string collection" collectionFormat(multi)
// @Param extensions query []string false "string collection" extensions(x-example=test,x-nullable)It also works for the struct fields:
type Foo struct {
Bar string `minLength:"4" maxLength:"16" example:"random string"`
Baz int `minimum:"10" maximum:"20" default:"15"`
Qux []string `enums:"foo,bar,baz"`
}| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| validate | string |
Determines the validation for the parameter. Possible values are: required,optional. |
| default | * | Declares the value of the parameter that the server will use if none is provided, for example a "count" to control the number of results per page might default to 100 if not supplied by the client in the request. (Note: "default" has no meaning for required parameters.) See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-6.2. Unlike JSON Schema this value MUST conform to the defined type for this parameter. |
| maximum | number |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.1.2. |
| minimum | number |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.1.3. |
| multipleOf | number |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.1.1. |
| maxLength | integer |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.2.1. |
| minLength | integer |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.2.2. |
| enums | [*] | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.5.1. |
| format | string |
The extending format for the previously mentioned type. See Data Type Formats for further details. |
| collectionFormat | string |
Determines the format of the array if type array is used. Possible values are:
csv. |
| example | * | Declares the example for the parameter value |
| extensions | string |
Add extension to parameters. |
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| pattern | string |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.2.3. |
| maxItems | integer |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.3.2. |
| minItems | integer |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.3.3. |
| uniqueItems | boolean |
See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.3.4. |
You can add descriptions spanning multiple lines in either the general api description or routes definitions like so:
// @description This is the first line
// @description This is the second line
// @description And so forth.// @Success 200 {array} model.Account <-- This is a user defined struct.package model
type Account struct {
ID int `json:"id" example:"1"`
Name string `json:"name" example:"account name"`
}You can declare your request response structs inside a function body.
You must have to follow the naming convention <package-name>.<function-name>.<struct-name> .
package main
// @Param request body main.MyHandler.request true "query params"
// @Success 200 {object} main.MyHandler.response
// @Router /test [post]
func MyHandler() {
type request struct {
RequestField string
}
type response struct {
ResponseField string
}
}// JSONResult's data field will be overridden by the specific type proto.Order
@success 200 {object} jsonresult.JSONResult{data=proto.Order} "desc"type JSONResult struct {
Code int `json:"code" `
Message string `json:"message"`
Data interface{} `json:"data"`
}
type Order struct { //in `proto` package
Id uint `json:"id"`
Data interface{} `json:"data"`
}- also support array of objects and primitive types as nested response
@success 200 {object} jsonresult.JSONResult{data=[]proto.Order} "desc"
@success 200 {object} jsonresult.JSONResult{data=string} "desc"
@success 200 {object} jsonresult.JSONResult{data=[]string} "desc"- overriding multiple fields. field will be added if not exists
@success 200 {object} jsonresult.JSONResult{data1=string,data2=[]string,data3=proto.Order,data4=[]proto.Order} "desc"- overriding deep-level fields
type DeepObject struct { //in `proto` package
...
}
@success 200 {object} jsonresult.JSONResult{data1=proto.Order{data=proto.DeepObject},data2=[]proto.Order{data=[]proto.DeepObject}} "desc"// @Success 200 {string} string "ok"
// @failure 400 {string} string "error"
// @response default {string} string "other error"
// @Header 200 {string} Location "/entity/1"
// @Header 200,400,default {string} Token "token"
// @Header all {string} Token2 "token2"/// ...
// @Param group_id path int true "Group ID"
// @Param account_id path int true "Account ID"
// ...
// @Router /examples/groups/{group_id}/accounts/{account_id} [get]/// ...
// @Param group_id path int true "Group ID"
// @Param user_id path int true "User ID"
// ...
// @Router /examples/groups/{group_id}/user/{user_id}/address [put]
// @Router /examples/user/{user_id}/address [put]type Account struct {
ID int `json:"id" example:"1"`
Name string `json:"name" example:"account name"`
PhotoUrls []string `json:"photo_urls" example:"http://test/image/1.jpg,http://test/image/2.jpg"`
}// @Param email body string true "message/rfc822" SchemaExample(Subject: Testmail\r\n\r\nBody Message\r\n)// Account model info
// @Description User account information
// @Description with user id and username
type Account struct {
// ID this is userid
ID int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"` // This is Name
}#708 The parser handles only struct comments starting with @Description attribute.
But it writes all struct field comments as is.
So, generated swagger doc as follows:
"Account": {
"type":"object",
"description": "User account information with user id and username"
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "ID this is userid"
},
"name": {
"type":"string",
"description": "This is Name"
}
}
}type TimestampTime struct {
time.Time
}
///implement encoding.JSON.Marshaler interface
func (t *TimestampTime) MarshalJSON() ([]byte, error) {
bin := make([]byte, 16)
bin = strconv.AppendInt(bin[:0], t.Time.Unix(), 10)
return bin, nil
}
func (t *TimestampTime) UnmarshalJSON(bin []byte) error {
v, err := strconv.ParseInt(string(bin), 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return err
}
t.Time = time.Unix(v, 0)
return nil
}
///
type Account struct {
// Override primitive type by simply specifying it via `swaggertype` tag
ID sql.NullInt64 `json:"id" swaggertype:"integer"`
// Override struct type to a primitive type 'integer' by specifying it via `swaggertype` tag
RegisterTime TimestampTime `json:"register_time" swaggertype:"primitive,integer"`
// Array types can be overridden using "array,<prim_type>" format
Coeffs []big.Float `json:"coeffs" swaggertype:"array,number"`
}type CerticateKeyPair struct {
Crt []byte `json:"crt" swaggertype:"string" format:"base64" example:"U3dhZ2dlciByb2Nrcw=="`
Key []byte `json:"key" swaggertype:"string" format:"base64" example:"U3dhZ2dlciByb2Nrcw=="`
}generated swagger doc as follows:
"api.MyBinding": {
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"crt":{
"type":"string",
"format":"base64",
"example":"U3dhZ2dlciByb2Nrcw=="
},
"key":{
"type":"string",
"format":"base64",
"example":"U3dhZ2dlciByb2Nrcw=="
}
}
}If you are using generated files, the swaggertype or swaggerignore tags may not be possible.
By passing a mapping to swag with --overridesFile you can tell swag to use one type in place of another wherever it appears. By default, if a .swaggo file is present in the current directory it will be used.
Go code:
type MyStruct struct {
ID sql.NullInt64 `json:"id"`
Name sql.NullString `json:"name"`
}.swaggo:
// Replace all NullInt64 with int
replace database/sql.NullInt64 int
// Don't include any fields of type database/sql.NullString in the swagger docs
skip database/sql.NullString
Possible directives are comments (beginning with //), replace path/to/a.type path/to/b.type, and skip path/to/a.type.
(Note that the full paths to any named types must be provided to prevent problems when multiple packages define a type with the same name)
Rendered:
"types.MyStruct": {
"id": "integer"
}type Account struct {
ID string `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Ignored int `swaggerignore:"true"`
}type Account struct {
ID string `json:"id" extensions:"x-nullable,x-abc=def,!x-omitempty"` // extensions fields must start with "x-"
}generate swagger doc as follows:
"Account": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "string",
"x-nullable": true,
"x-abc": "def",
"x-omitempty": false
}
}
}type Resp struct {
Code int
}//@name ResponseGeneral API info.
// @securityDefinitions.basic BasicAuth
// @securitydefinitions.oauth2.application OAuth2Application
// @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token
// @scope.write Grants write access
// @scope.admin Grants read and write access to administrative informationEach API operation.
// @Security ApiKeyAuthMake it AND condition
// @Security ApiKeyAuth
// @Security OAuth2Application[write, admin]Make it OR condition
// @Security ApiKeyAuth || firebase
// @Security OAuth2Application[write, admin] || APIKeyAuthtype Example struct {
// Sort order:
// * asc - Ascending, from A to Z.
// * desc - Descending, from Z to A.
Order string `enums:"asc,desc"`
}By default swag command generates Swagger specification in three different files/file types:
- docs.go
- swagger.json
- swagger.yaml
If you would like to limit a set of file types which should be generated you can use --outputTypes (short -ot) flag. Default value is go,json,yaml - output types separated with comma. To limit output only to go and yaml files, you would write go,yaml. With complete command that would be swag init --outputTypes go,yaml.
This project was inspired by yvasiyarov/swagger but we simplified the usage and added support a variety of web frameworks. Gopher image source is tenntenn/gopher-stickers. It has licenses creative commons licensing.
This project exists thanks to all the people who contribute. [Contribute].
Thank you to all our backers! 🙏 [Become a backer]
Support this project by becoming a sponsor. Your logo will show up here with a link to your website. [Become a sponsor]