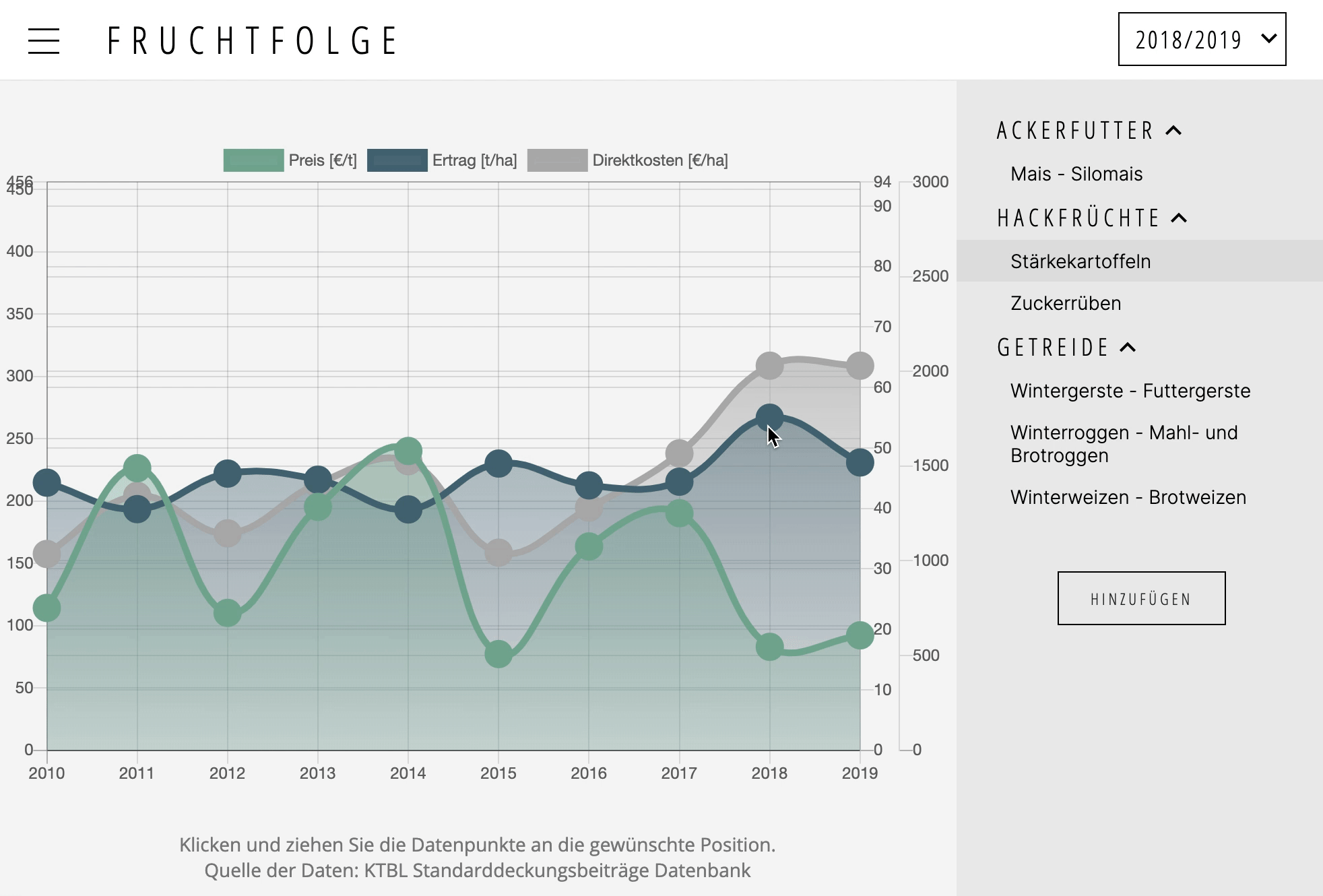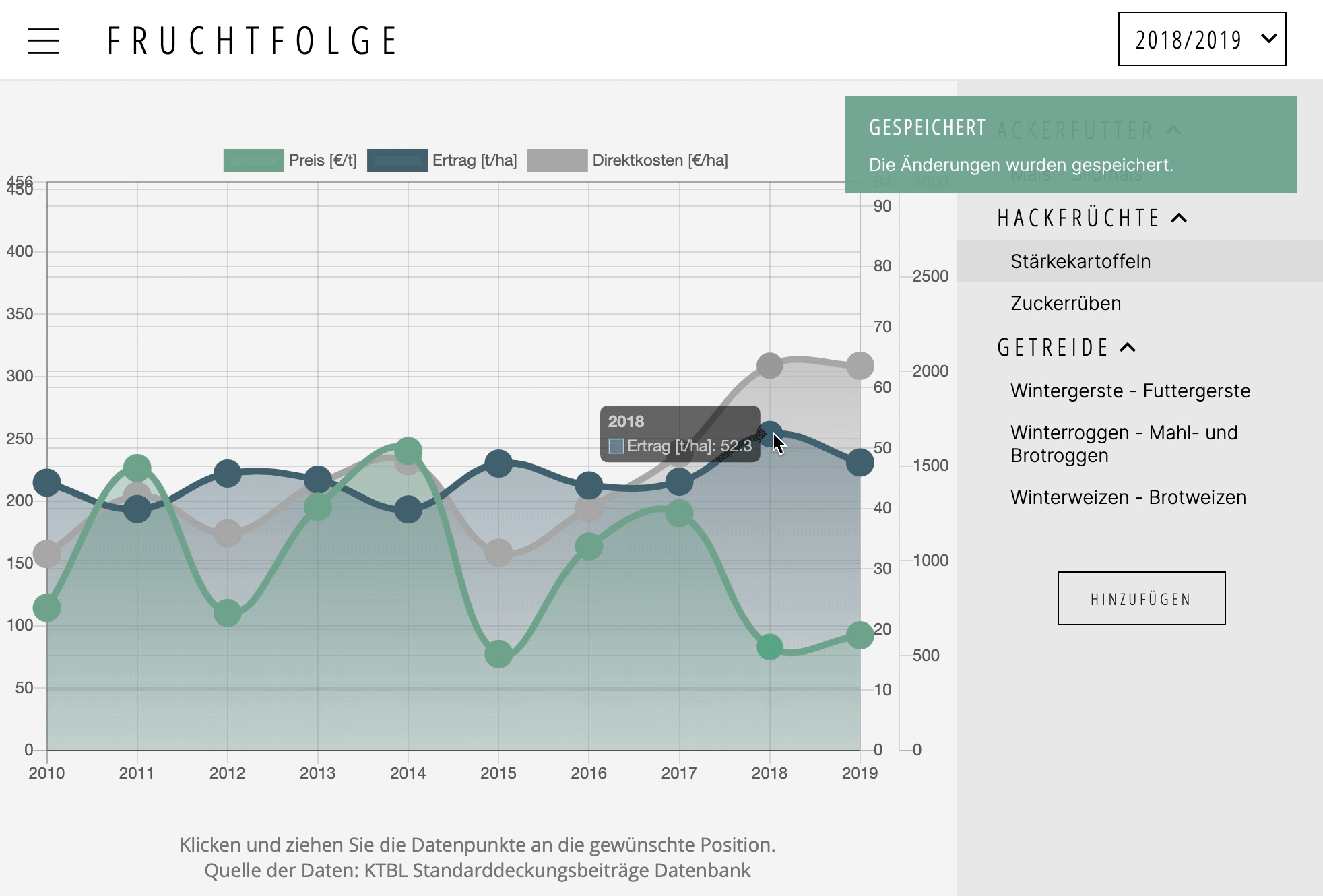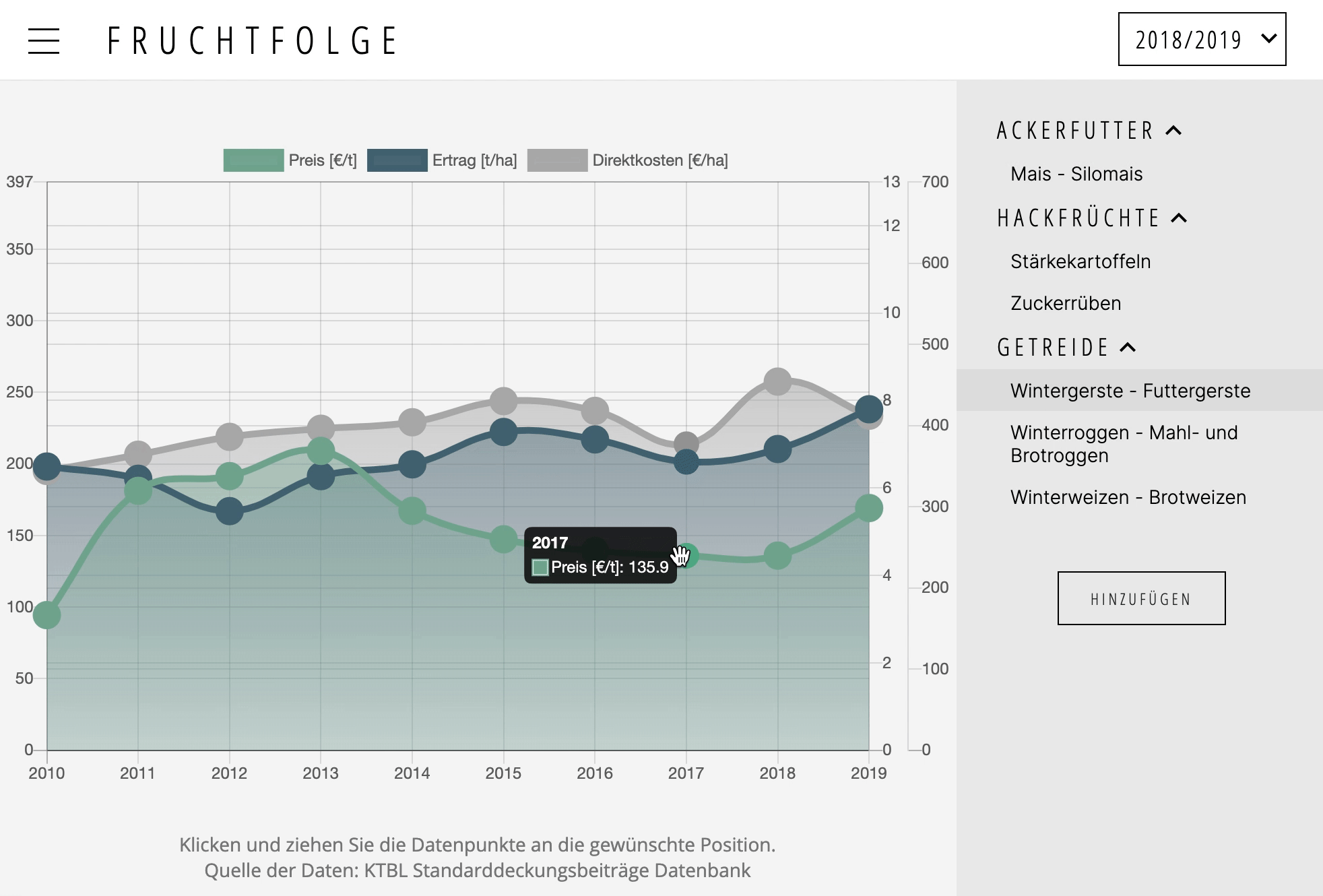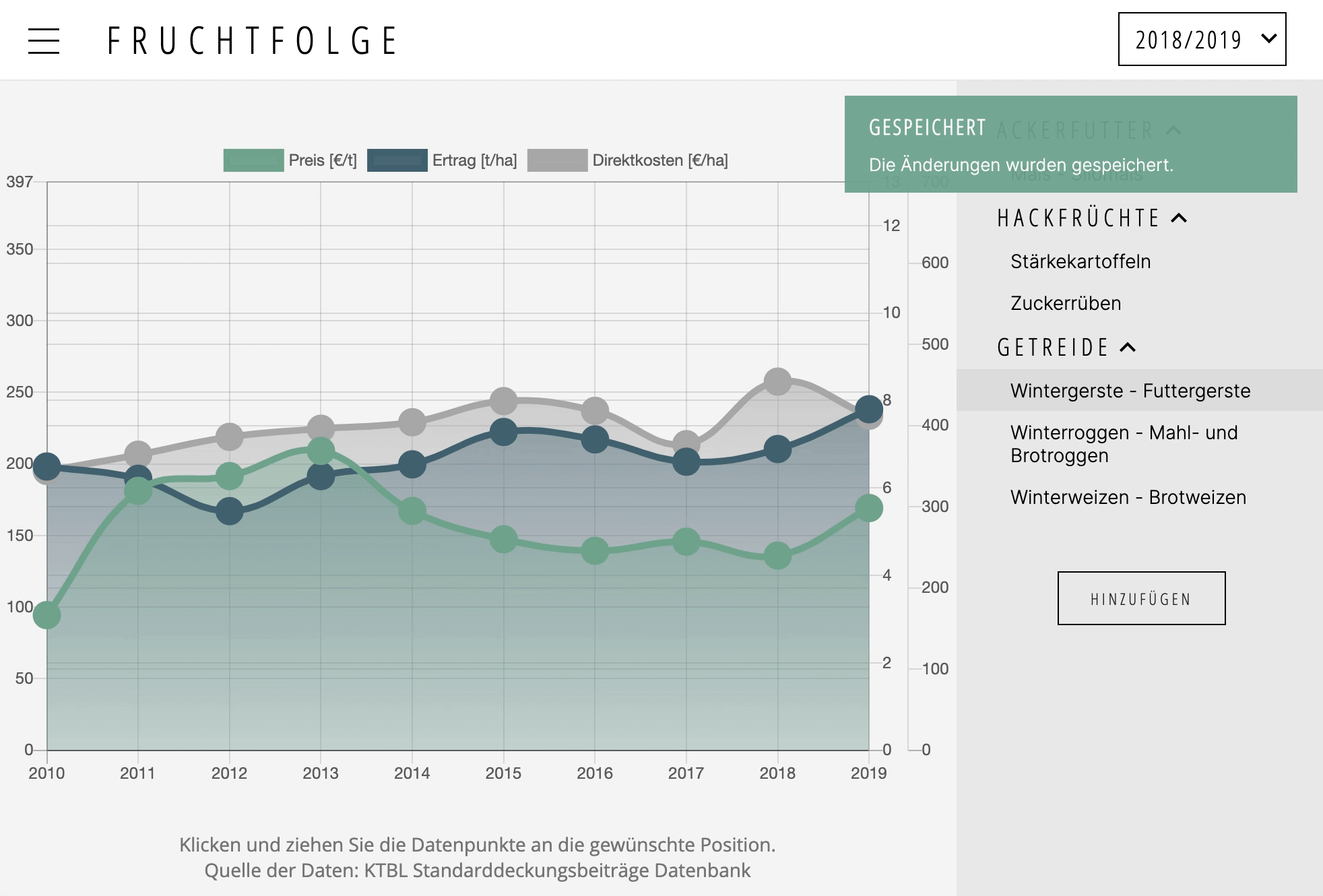
A plugin for Chart.js >= 2.4.0
Makes data points draggable. Supports touch events.
| Chart Type | Demo | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Bar - Simple Bar | demo | source |
| Bubble - Simple Bubble | demo | source |
| Horizontal Bar - Simple Horizontal Bar | demo | source |
| Line - Single Y-Axis | demo | source |
| Line - Dual Y-Axis | demo | source |
| Line - Drag multiple points | demo | source |
| Line - Small | demo | source |
| Line - React Fiddle | demo | source |
| Line - Drag x-, and y-axis (scatter chart) | demo | source |
| Line - Zoom, Pan, and drag data points (combination with chartjs-plugin-zoom | demo | source |
| Mixed - Bar, Bubble, and line Chart | demo | source |
| Radar - Simple Radar | demo | source |
| Stacked Bar - Simple Stacked Bar | demo | source |
| Stacked Horizontal Bar - Simple Stacked Horizontal Bar | demo | source |
npm install chartjs-plugin-dragdata
In browsers, you may use the following script tag:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/chartjs-plugin-dragdata@latest/dist/chartjs-plugin-dragdata.min.js"></script>
Or, download a release archive file from the dist folder.
To make (line, bubble, bar and radar chart) data points draggable, simply add dragData: true to the config section of the chart instance. If you (additionally to the y-axis) would like to drag data along the x-axis, you may also add dragX: true.
To round the values dragged to, simply add dragDataRound: 0 to the config section of the chart instance.
0will round to..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...1will round to..., -0.2, -0.1, 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, ...-1will round to..., -20, -10, 0, 10, 20, ...
The following example configuration shows how individual event listeners (callbacks) can be configured.
const myChartOptions = {
type: 'line', // or radar, bar, horizontalBar, bubble
data: {...},
options: {
... // the rest of your chart options, e.g. axis configuration
dragData: true,
dragX: false,
dragDataRound: 0, // round to full integers (0 decimals)
dragOptions: {
// magnet: { // enable to stop dragging after a certain value
// to: Math.round
// },
showTooltip: true // Recommended. This will show the tooltip while the user
// drags the datapoint
},
onDragStart: function (e, element) {
// where e = event
},
onDrag: function (e, datasetIndex, index, value) {
// change cursor style to grabbing during drag action
e.target.style.cursor = 'grabbing'
// where e = event
},
onDragEnd: function (e, datasetIndex, index, value) {
// restore default cursor style upon drag release
e.target.style.cursor = 'default'
// where e = event
},
hover: {
onHover: function(e) {
// indicate that a datapoint is draggable by showing the 'grab' cursor when hovered
const point = this.getElementAtEvent(e)
if (point.length) e.target.style.cursor = 'grab'
else e.target.style.cursor = 'default'
}
}
}
}Minimum and maximum allowed data values can be specified through the min and max ticks settings in the scales options. By setting these values accordingly, unexpected (fast) changes to the scales, that may occur when dragging data points towards the outer boundaries of the y-axis, can be prohibited.
const myChartOptions = {
type: 'line', // or radar, bar, horizontalBar, bubble
data: {...},
options: {
dragData: true,
scales: {
yAxes: [{
ticks: {
max: 25,
min: 0
}
}]
},
... // the remainder of your chart options, e.g. dragData: true etc.
}To avoid dragging specific datasets, you can set dragData to false within the dataset options.
const myChartOptions = {
type: 'line', // or radar, bar, horizontalBar, bubble
data: {
datasets: [
{
label: "Data Label",
fill: false,
data: dataPoints,
yAxisID: 'B',
dragData: false
}, {
...
},
options: {
dragData: true,
... // the remainder of your chart options
}
}To avoid dragging specific scales, you can set dragData to false within the axis scale options.
const myChartOptions = {
type: 'line', // or radar, bar, horizontalBar, bubble
data: {...},
options: {
dragData: true,
scales: {
yAxes: [{
dragData: false
}]
},
... // the remainder of your chart options
}To avoid dragging specific data points inside a draggable dataset, you can return false to function onDragStart.
To disable the automatic update of the data, you can return false to function onDrag. Nothing will happen to the points without you changing the data attribute somewhere else. This is useful for frameworks like emberjs who us the data down action up paradigm.
When you drag a point you might want to stop dragging at the closest (rounded) value, or at a fixed value.
In order to do that, specify magnet options you can easily do it:
const myChartOptions = {
type: 'line', // or radar, bar, horizontalBar, bubble
data: {...},
options: {
dragOptions: {
magnet: {
to: Math.round // to: (value) => value + 5
}
},
... // the remainder of your chart options
},In order to support touch events, the pointHitRadius option should be set to a value greater than 25. You can find working example configurations in the docs/*.html files. Also note, that mobile devices (and thus touch events) can be simulated with the device mode in the Chrome DevTools.
When working with a module bundler (e.g. Webpack) and a framework (e.g. Vue.js/React/Angular), you still need to import the plugin library after installing. Here's a small example for a Vue.js component
<template>
<div>
<canvas id="chart"></canvas>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Chart from 'chart.js'
// load the options file externally for better readability of the component.
// In the chartOptions object, make sure to add "dragData: true" etc.
import chartOptions from '~/assets/js/labour.js'
import 'chartjs-plugin-dragdata'
export default {
data() {
return {
chartOptions
}
},
mounted() {
this.createChart('chart', this.chartOptions)
},
methods: {
createChart(chartId, chartData) {
const ctx = document.getElementById(chartId)
const myChart = new Chart(ctx, {
type: chartData.type,
data: chartData.data,
options: chartData.options,
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>Please feel free to submit an issue or a pull request!
If you make changes to the src/index.js file, don't forget to npm run build and
manually test your changes against all demos in the docs folder.
chartjs-plugin-dragdata.js is available under the MIT license.