-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 778
Building Tasks
Ryan Cobb edited this page Aug 4, 2020
·
2 revisions
Tasks, or "modules", are built-in functions that can be assigned to active grunts. Tasks should be written to complete common functionality to be run on grunts.
To view a list of previously created and built-in tasks, navigate to the "Tasks" page:
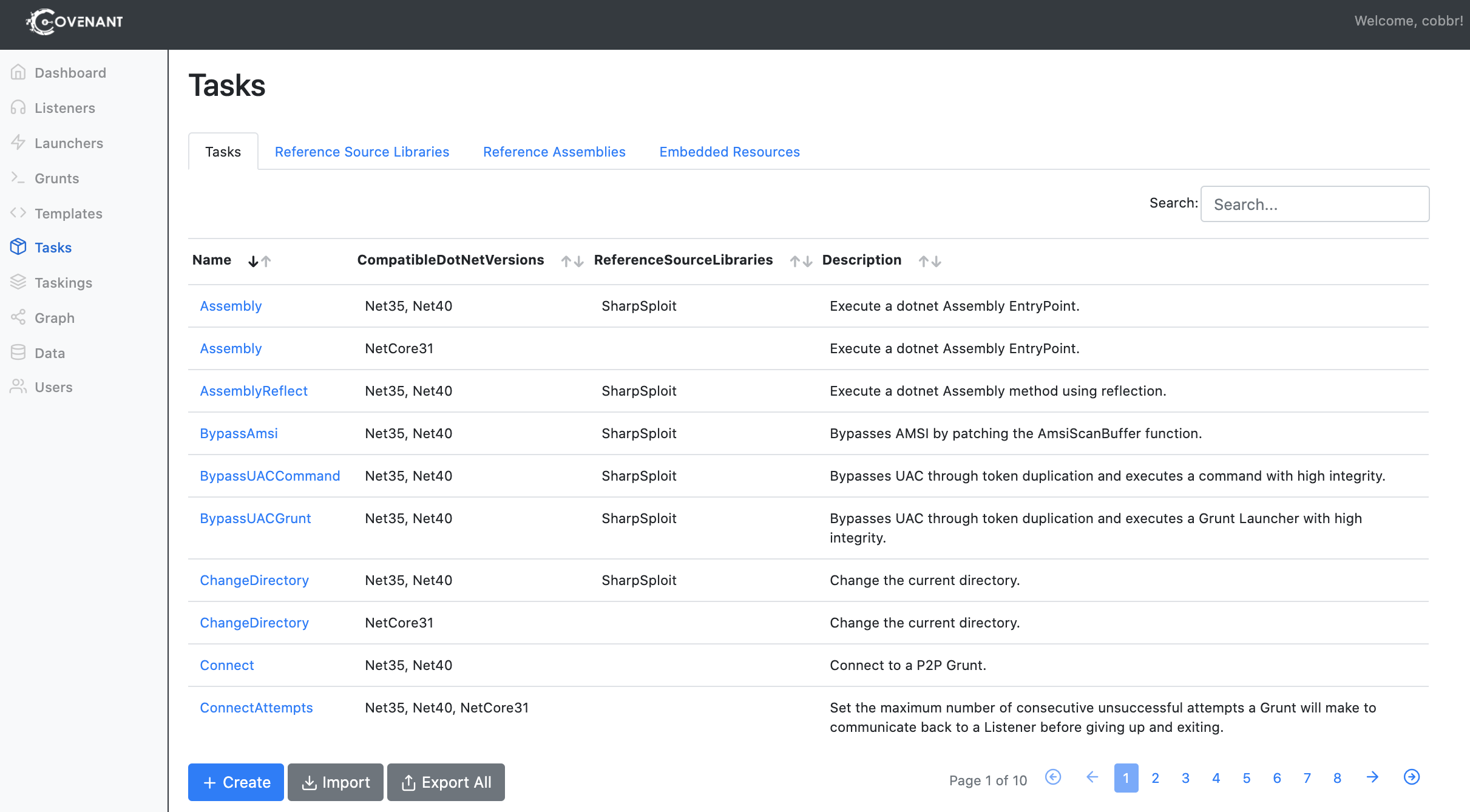
Covenant provides a rich dataset for creating and configuring Tasks that includes:
-
Reference Assemblies - Reference Assemblies are .NET assemblies, usually a DLL file, that can be referenced by a Reference Source Library or Task. When a Reference Assembly is applied to a Task, it will be included in the task's compilation. For .NET Framework tasks, at a minimum the
mscorlib.dll,System.Core.dll, andSystem.dllReference Assemblies will need to be applied. - Embedded Resources - Embedded Resources are any data files that will be needed by a task. When an Embedded Resource is applied to a Task, it will be included as a resource in the task's compilation.
-
Reference Source Libraries - A Reference Source Library is a complete .NET Framework project that can be referenced by a Task, built-in examples include
SharpSploit,Rubeus, and other GhostPack projects. A Reference Source Library includes any C# code included in the project, a list of Reference Assemblies, and a list of Embedded Resources. When a Reference Source Library is applied to a Task, the entire project and associated assemblies and resources will be included in the task's compilation. - Tasks - A Task is a function that can be assigned to active Grunts and will be available to execute by all operators. A task can use 0 or many Reference Source Libraries, Reference Assemblies, and Embedded Resources. It should be noted that it will also inherit any Reference Assemblies or Embedded Resources associated with any Reference Source Library that the Task utilizes.
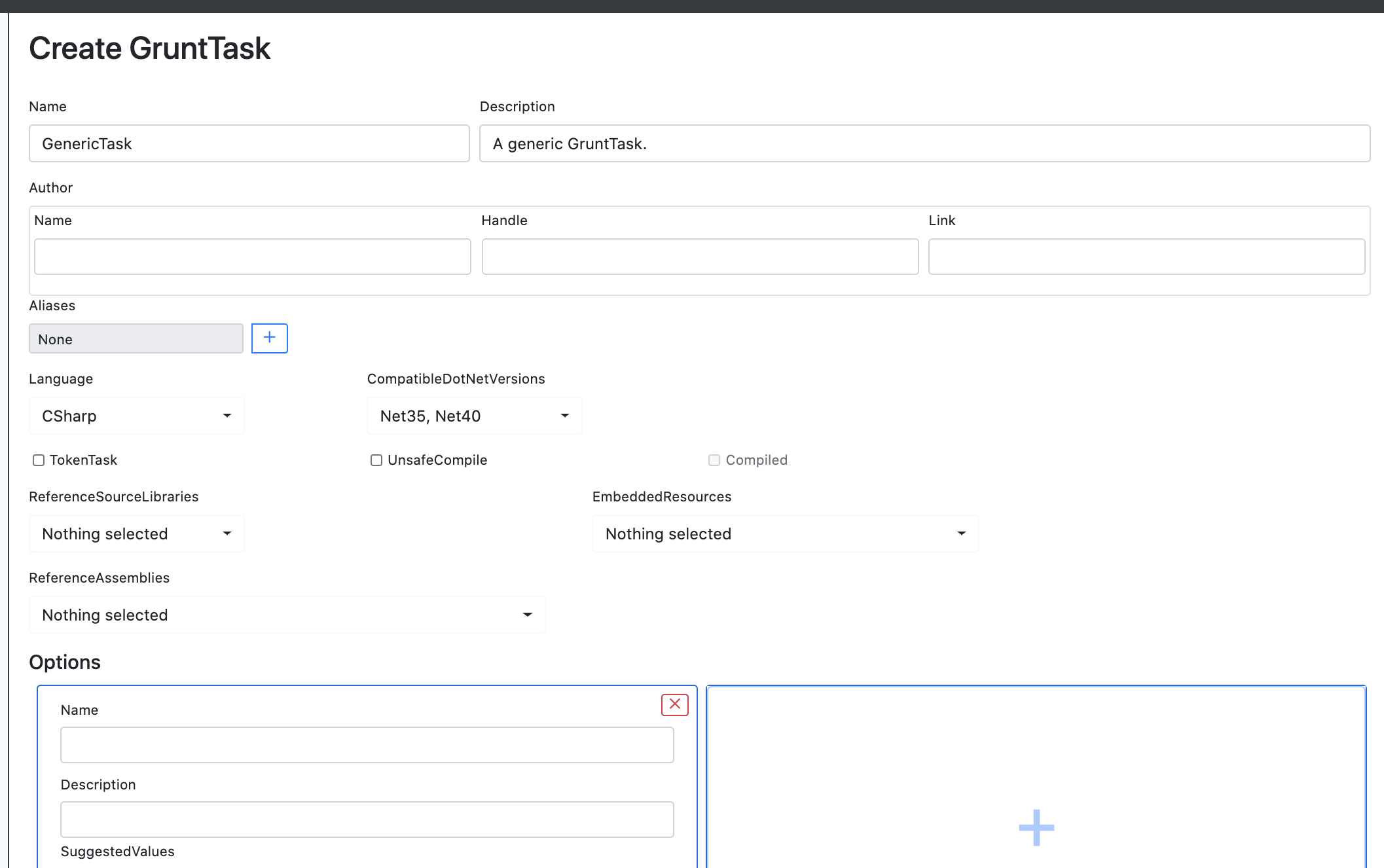
To create a new task, click the "Create" button at the bottom of the "Tasks" tab. The following options will need to be configured when creating a new Task:
-
Name - The
Nameof the task that will be used throughout the interface. Pick something recognizable! This name will also be tab-completable from the Grunt interaction tab. -
Description - The
Descriptionof the task. This should be a thorough description of the task that operators can read and easily understand how the task works, and the use cases for which it would be appropriate to use the task. -
Author - The
Authorof the task, so you can get credit for your hard work! TheAuthorincludes fields for aName,Handle, andLinkto external information about the Task's author. -
Aliases -
Aliasesare alternative names for Tasks so you can reference them byNameor by alias. -
Language - The programming
Languagethat the Task is written in. - CompatibleDotNetVersions - A list of the DotNetVersions the Task is compatible with.
-
TokenTask - The
TokenTaskoption is used for some particular tasks that handle token manipulation, since threading has to be handled differently for these sorts of tasks. Most tasks should not require this option to be enabled. -
UnsafeCompile - The
UnsafeCompileoption is used for tasks that need to be compiled with theUnsafeCompilecopmilation option. Most tasks should not require this option to be enabled. -
ReferenceSourceLibraries - The
ReferenceSourceLibrariesare the libraries that this task will need to reference to complete the task. This allows a task to use namespaces and functions exposed by the library. The task will also inherit any ReferenceAssemblies and EmbeddedResources used by the library. -
ReferenceAssemblies - The
ReferenceAssembliesare the additional assemblies to be included in the compilation. If not including a library, be sure to selectmscorlib.dll,System.Core.dll, andSystem.dllat a minimum. -
EmbeddedResources - The
EmbeddedResourcesare the additional resources to be included in the compilation. -
Options - The
Optionsare parameters that are accepted by the Task. You can use 0 or many Options within a task. Each Option should correlate with a parameter accepted by the Task function. Each Option will have aName,Description,SuggestedValues,Optional, andDisplayInCommandvalue. The name should correlate with the name of the parameter accepted by the Task function, the description should describe the use of the Option, the suggested values will be filled as tab completion options for operators, the displayincommand determines whether the option will be displayed in command history, the Optional flag should be set only if a value is not required. If the Optional flag is set, the corresponding parameter of the Task function should have a default value. -
Help - The
Helpoption is an additional help message that will be displayed to an operator when they request help for the Task. A help message will be interpreted based on options and descriptions, but an additionalHelpmessage may be useful to an operator. -
Code - The
Codeis the actual C# code that is executed by the Task. The code must include a staticTaskclass that exposes a public function that returns a string calledExecute. TheExecutefunction should accept parameters that correlate with theOptionsof the Task.