Apache ActiveMQ is an open-source message broker written in Java, which supports a variety of messaging protocols. It is designed to facilitate communication between different applications and systems, allowing them to exchange information asynchronously and reliably. ActiveMQ is known for its robustness, flexibility, and performance, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from simple message queuing to complex enterprise-level messaging solutions.
- GO: activemq, to wrap and simplify go-stomp. Example is at go-active-mq-sample
- nodejs: activemq, to wrap and simplify activemq. Example is at activemq-sample
- The libraries to implement this flow are:
- mq for GOLANG. Example is at go-active-mq-sample
- mq-one for nodejs. Example is at activemq-sample
- Supports several messaging protocols including AMQP, STOMP, MQTT, OpenWire, and WebSockets.
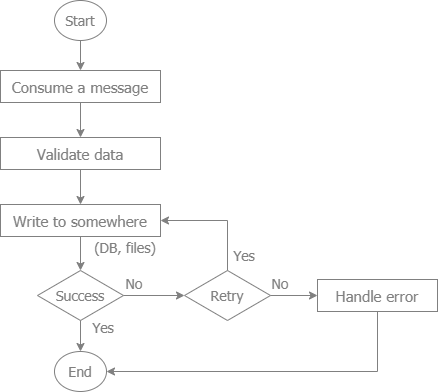
- Ensures message durability by supporting message persistence to databases, file systems, and other storage mechanisms.
- Supports clustering and network of brokers for load balancing and fault tolerance, ensuring high availability and reliability.
- Can be deployed as a standalone server, embedded within applications, or in a cloud environment.
- Fully compliant with the Java Message Service (JMS) API, making it easy to integrate with Java applications.
- Supports a wide range of messaging patterns including point-to-point (queues), publish-subscribe (topics), request-reply, and more.
- Provides robust security features including SSL/TLS encryption, authentication, and authorization.
- Includes a web-based administration console and supports JMX for management and monitoring.
- Allows customization and extension through plugins and integration with other systems.
- Implements event-driven patterns, allowing applications to react to events and changes asynchronously.
- Supports real-time data streaming and processing, integrating with big data and analytics platforms.
- Facilitates communication and data exchange between disparate enterprise applications and systems.
- Handles messaging between IoT devices and backend systems, supporting protocols like MQTT for IoT communication.
- In an order processing system, ActiveMQ can be used to integrate various components such as order entry, inventory management, payment processing, and shipping services.
- The order entry system sends an order message to a queue.
- An inventory service consumes the order message, updates stock levels, and sends a message to the payment queue.
- A payment service processes the payment and sends a confirmation message to a shipping queue.
- A shipping service schedules shipment based on the confirmation message and updates the order status.
Throughout this process, ActiveMQ ensures reliable and asynchronous communication between the different services, improving scalability and fault tolerance.
ActiveMQ operates using the following core concepts:
- The central server component that routes messages between producers and consumers. A broker manages one or more queues and topics.
- Used in point-to-point messaging. Messages sent to a queue are delivered to one consumer.
- Used in publish-subscribe messaging. Messages sent to a topic are delivered to all subscribed consumers.
- The data or payload that is exchanged between producers and consumers. Messages can include headers, properties, and the body.
- Components or applications that send messages to queues or topics.
- Components or applications that receive and process messages from queues or topics.
- Persistent messages are stored to ensure they are not lost in case of broker failure.
- Non-persistent messages are faster but can be lost if the broker crashes.
- Supports multiple protocols and can be extended to meet specific requirements through plugins.
- Being open-source, it offers cost advantages and the ability to customize and contribute to its development.
- Seamlessly integrates with various enterprise systems, including Java applications, web applications, and other messaging systems.
- Supports clustering and distributed configurations, allowing it to scale horizontally to handle increasing load.
- Backed by a large community and extensive documentation, providing ample resources for learning and troubleshooting.
- Offers a wide range of features and capabilities, from basic queuing to advanced messaging patterns and high availability.
- The extensive feature set can introduce complexity, especially for small-scale or simple use cases.
- May require significant resources (CPU, memory) to handle large volumes of messages and complex configurations.
- The flexibility and pluggability can introduce performance overhead compared to more lightweight brokers.
Apache ActiveMQ is a versatile and powerful message broker that supports a wide range of messaging protocols and patterns. Its flexibility, robustness, and extensive feature set make it suitable for a variety of use cases, from simple message queuing to complex enterprise-level messaging solutions. While it introduces some complexity and resource overhead, its benefits in terms of reliability, scalability, and integration capabilities make it a valuable tool for modern software architectures.
Please make sure to initialize a Go module before installing core-go/activemq:
go get -u github.com/core-go/activemqImport:
import "github.com/core-go/activemq"