-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 758
Duplicates
The Duplicates tool compares files by content and helps you delete extra copies while making sure you have at least one copy left.
The underlying routines use size and checksums (MD5) to determine which files are exactly the same, paired with lots of failsafes.
A lot of people ask which duplicates to delete and which to keep and there is no right or wrong answer to this question. At least none that an app could make, it's all up to preference.
Example:
Lets say you have two music albums called "Best running tracks of 2013" and "My favorite motorcycle music" and both obviously contain the track "Darken - Singing in the shower.mp3". You have the same file in two different locations. Now which one should be deleted, or none at all? I can't answer that and neither can SD Maid, only you can. In any case the DuplicateFinder will make sure you always have one copy left.
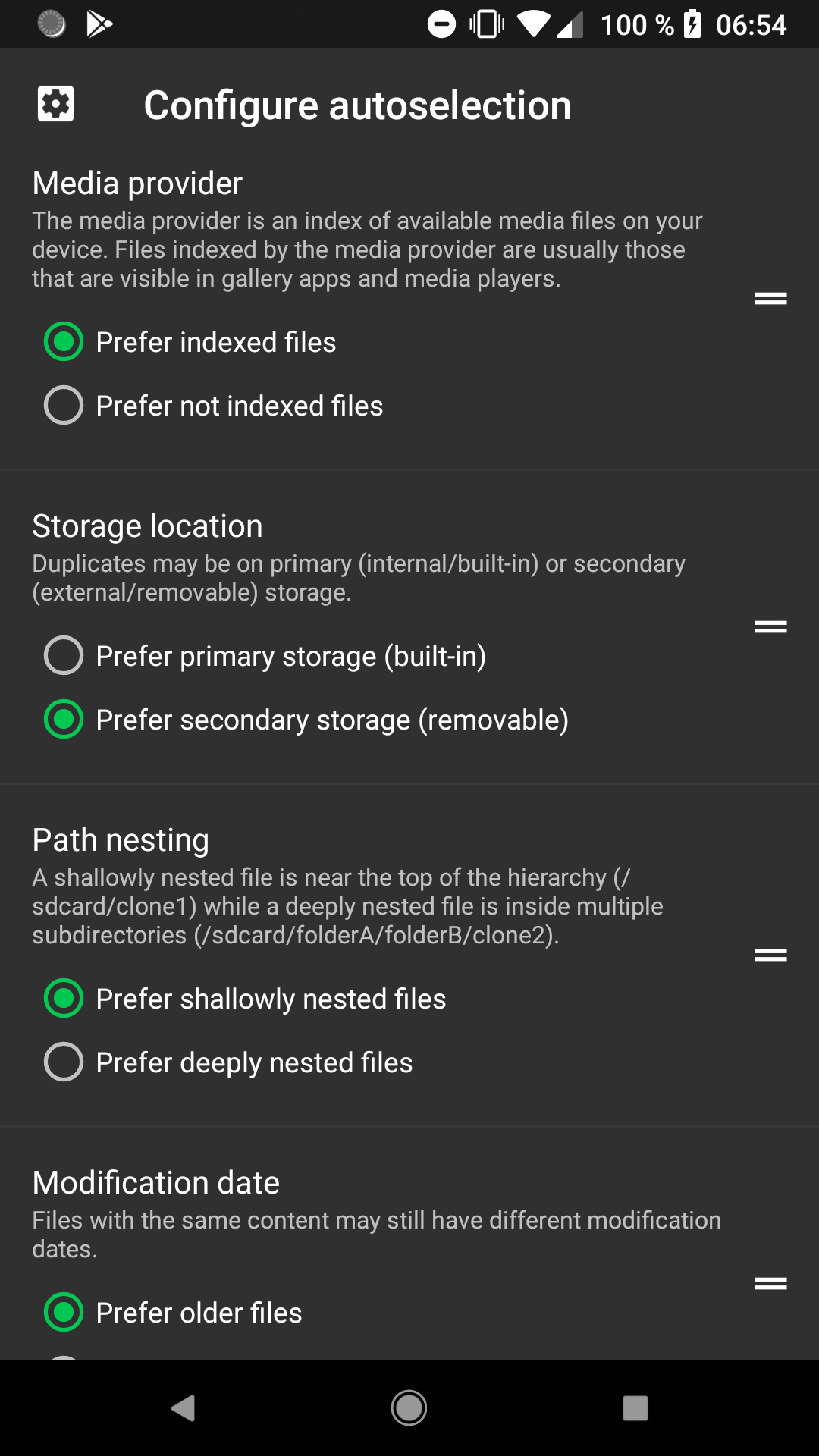
SD Maid determines which duplicates to keep through a list of Criteria (a list of tests/ a set of preferences). Each files in a set of duplicates will be compared and ordered based on these criteria, the most preferred file is kept while other duplicates are be deleted.
The criteria are configured in a list of descending priority. You can drag and rearrange this list. The criterion at the top is the most important one. If two files are equal in regards to the top criterion, then they are compared based on the second criterion.
The configured preferences will also be used when the Duplicates tool is used through the Scheduler, QuickAccess or Widget.
Currently these criteria are supported:
The media provider is an app that holds a database of most media files (including their metadata) on your device. Other apps such as galleries use this information to know which files to display. My default it suggests to keep indexed files and to delete not not indexed files. Meaning we keep the duplicate files we can actually see in an gallery app while we delete other duplicate version of that file that are likely not directly visible to us.
The storage location refers to the physical storage device the files reside on. You can choose between primary storage, which is usually the built-in storage and secondary storage which usually refers to removable sdcards. By default this criterion prefers files on secondary storage by assuming that it is more likely the user wants to free space on internal storage.
Path nesting refers to the amount of subdirectories a file is in. The default setting prefers shallowly nested files as those are more accessible to the user. When you look at your storage you are more likely to look in /sdcard/Pictures than in /sdcard/Android/data/some.app/pictures.
Even if two files have different modification dates, they can still have the same content. This criterion prefers older files by default as the newer file is likely an unwanted copy.
Example: You take a picture with your camera and at a later point in time you send that picture to someone with another app. That other app creates a copy of the picture in its own folder. It's likely that you want to keep the file at it's original location (in your camera folder) as this is where you expect it.
Where the tool will search. By default SD Maid will search all public storages. You can modify this and remove locations but be careful when adding locations to not ask SD Maid to search the same storage twice. SD Maid has a lot of failsafes against this, but Androids filesystem is quite complicated.
The Media Storage app is a database/ an index of all media files (and their meta data) on your device. Othernames for this you will find are: Apps (e.g. galleries) use it to know what to display. The Media Storage app can get out of sync causing issues like gallery apps displaying black squares (thumbnails). If this option is enabled and the Duplicates tool deletes a file then SD Maid will also check the media index for references to the now deleted file and if one is found delete it. This keeps the media index directly in sync. If you disable this option you may see stale references to images until you reboot the device or otherwise force the Media Storage app to syncronize.
Deleting an entry from the media index does not delete the file it references, and vice versa, deleting a media file from your device does not always delete it's references in the media index.
This is known under multiple names: Media Storage, Media Index, MediaProvider, MediaStore.
Your gallery app is just not showing the picture because the remaining copy of the image is in a location that's not searched by the gallery app.
- Make sure the autoselection criterion Media Storage is at the top and that you have selected Prefer indexed files
- In some cases a device reboot can help as it often forces the devices to reindex media on your device.
- Some gallery app have options to change the search pathes or move the image into a folder which the gallery app indexes.
The list of images the gallery app gets from the Media Provider likely contains stale references. Make sure Prune Media Storage is enabled in the settings.
This error happens when SD Maid encounters an unexpected error while trying to calculate checksums. Possible reasons:
- You manually changed the search pathes and now SD Maid is trying to search a location that is not readable with the available permission. By default SD Maid will correctly choose the pathes to scan all public storage (internal & external sdcard). You can reset the search pathes by removing them all. If no custom search pathes are defined, SD Maid will use the default search pathes.
- The sdcard SD Maid is trying to read is faulty and/or has a corrupt file system. Remove the sdcard and try again. If the error no longer happens, try a different sdcard. If the error is still gone than the original sdcard was faulty. Backup any important data from it ASAP. You may try fixing and/or formatting it from a desktop computer which can fix corrupt filesystems but if the card itself is faulty, it will corrupt itself again.