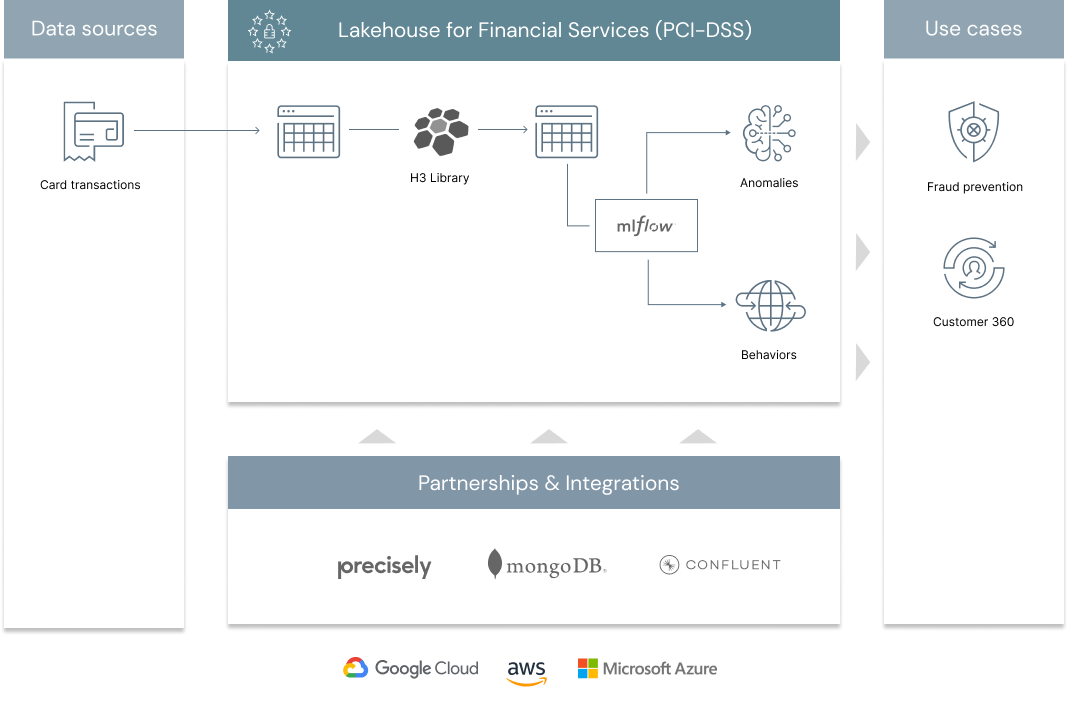
A large scale fraud prevention system is usually a complex ecosystem made of various controls (all with critical SLAs), a mix of traditional rules and AI and a patchwork of technologies between proprietary on-premises systems and open source cloud technologies. In a previous solution accelerator, we addressed the problem of blending rules with AI in a common orchestration layer powered by MLFlow. In this series of notebooks centered around geospatial analytics, we demonstrate how Lakehouse enables organizations to better understand customers behaviours, no longer based on who they are, but how they bank, no longer using a one-size-fits-all rule but a truly personalized AI. After all, identifying abnormal patterns can only be made possible if one first understands what a normal behaviour is, and doing so for millions of customers becomes a challenge that requires both data and AI combined into one platform. As part of this solution, we are releasing a new open source geospatial library, GEOSCAN, to detect geospatial behaviours at massive scale, track customers patterns over time and detect anomalous card transactions
© 2021 Databricks, Inc. All rights reserved. The source in this notebook is provided subject to the Databricks License [https://databricks.com/db-license-source]. All included or referenced third party libraries are subject to the licenses set forth below.
| library | description | license | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| h3 | Uber geospatial library | Apache2 | https://github.com/uber/h3-py |
| geoscan | Geoscan algorithm | Databricks | https://github.com/databrickslabs/geoscan |
| folium | Geospatial visualization | MIT | https://github.com/python-visualization/folium |
| pybloomfiltermmap3 | Bloom filter | MIT | https://github.com/prashnts/pybloomfiltermmap3 |
| PyYAML | Reading Yaml files | MIT | https://github.com/yaml/pyyaml |
To run this accelerator, clone this repo into a Databricks workspace. Switch to the web-sync branch if you would like to run the version of notebooks currently published on the Databricks website. Attach the RUNME notebook to any cluster running a DBR 11.0 or later runtime, and execute the notebook via Run-All. A multi-step-job describing the accelerator pipeline will be created, and the link will be provided. Execute the multi-step-job to see how the pipeline runs. The job configuration is written in the RUNME notebook in json format. The cost associated with running the accelerator is the user's responsibility.