University projects using OpenMP, MPI (C & Python), CUDA
- gcc & g++ compilers
- MPI, CUDA libraries
2 Threads running in parallel, one starting from the initial start point of the line (red line), the other starting from the end point (green line).
In order to run & see output in your cmd (Windows) or command line (Linux) you need Borland Graphics Interface (if running on Windows) or SDL graphics library if running on Linux system. See instructions for Windows & Linux.
g++ dda_seq.c -lbgi -lgdi32 -lcomdlg32 -luuid -loleaut32 -lole32 -o dda
dda
./ddag++ dda_parallel_midpoint.c -lbgi -lgdi32 -lcomdlg32 -luuid -loleaut32 -lole32 -fopenmp -o dda_p
dda_p./dda_pUsed omp parallel for in draw triangle's for loop. Parallel point drawing. See more about Chaos Game
In order to run & see output in your cmd (Windows) or command line (Linux) you need Borland Graphics Interface (if running on Windows) or SDL graphics library if running on Linux system. See instructions for Windows & Linux.
g++ chaos_seq.c -lbgi -lgdi32 -lcomdlg32 -luuid -loleaut32 -lole32 -fopenmp -o chaos
chaos./chaosg++ chaos_parallel.c -lbgi -lgdi32 -lcomdlg32 -luuid -loleaut32 -lole32 -fopenmp -o chaos_p
chaos_p./chaos_pCounts the frequency of each ASCII character in a txt file (as input). Parallelized with 7 different ways
- Using Global Array of Locks
- Using Local Array of Locks
- Using Atomic Operation (Global)
- Using Atomic Operation (Local)
- Using Critical Operation (Global)
- Using Critical Operation (Local)
- Using Reduction
gcc -fopenmp char_freq_parallel_<method>.c -o char_freq_p
char_freq_p./char_freq_pUsing as input the bible.txt file.
Parallelized count sort algorithm (enumeration sort), using omp parallel for. Change the N macro inside the code.
gcc -fopenmp count_sort_parallel.c -o cs_p
cs_p./cs_pTested both with random array, size 90000.
Parallelized insertion sort algorithm, using omp parallel and critical block (lock). Change the N macro inside the code. Sequential calculaton is even faster.
gcc -fopenmp insertion_sort_parallel.c -o is_p
is_p./is_pTested both with random array, size 500000.
As you can see, no real difference in time. This is most likely due to critical block, each thread waits every time to get the lock.
Parallelized calculation of epsilon (in mathematics). Used omp parallel reduction.
gcc -fopenmp epsilon_parallel.c -o epsilon_p
epsilon_parallel./epsilon_parallelAs you can see, no real difference in time. Sequential calculaton is even faster.
Every thread writes to different element of a global array. When all threads are finished (barrier), add all elements' values to variable.
gcc -fopenmp pi_parallel_array.c -o pi_parallel_array
pi_parallel_array./pi_parallel_arrayEach thread writes to global variable (protected with atomic operation).
gcc -fopenmp pi_parallel_atomic.c -o pi_parallel_atomic
pi_parallel_atomic./pi_parallel_atomicEach thread writes to global variable (protected with critical section).
gcc -fopenmp pi_parallel_critical.c -o pi_parallel_critical
pi_parallel_critical./pi_parallel_criticalEach thread writes to local variable and then adds its result to global variable (pi).
gcc -fopenmp pi_parallel_local.c -o pi_parallel_local
pi_parallel_local./pi_parallel_localEach thread writes to global variable (using OpenMP's reduction operation).
gcc -fopenmp pi_parallel_reduction.c -o pi_parallel_reduction
pi_parallel_reduction./pi_parallel_reductionAs we can observe, reduction works better compared to other methods (pi_parallel_local is reduction, pi_parallel_reduction uses OpenMP's reduction operation).
SPMD: Each thread takes a specific slice of the file of characters and stores the character frequency to local array (each process has its own frequency array).
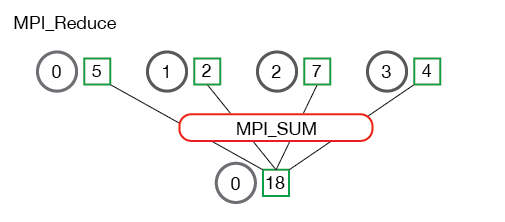
Using the MPI_Reduce function (with MPI_SUM operation), all local frequency arrays sums to root's (process 0) total frequency array.
/* Make the reduce */
MPI_Reduce(freq, total_freq, N, MPI_INT, MPI_SUM, ROOT, MPI_COMM_WORLD);Source: https://mpitutorial.com/tutorials/mpi-reduce-and-allreduce/
mpicc char_freq_parallel_Reduce.c -o char_freqmpirun -np 4 char_freq // 4 coresSPMD: Each process is aware of the whole array and sorts a specific part of the array (start, stop). Using the MPI_Reduce function (with MPI_SUM operation), each process returns its results to sorted_array.
mpicc count_sort_parallel_Reduce.c -o cs_rmpirun -np 4 cs_r // 4 coresEach process has a local array which contains indexes on where the ith element (i=0,1,...,N) should be put, in order the final array to be sorted. For example, if local_locations[2] == 0, then the element in position 2 of the initial array should be put in position zero.
mpicc count_sort_parallel_Locations.c -o cs_lmpirun -np 4 cs_l // 4 coresAll tests with N = 400000.
Parallelized insertion sort algorithm, using pipeline. N is standard (the number of processors).
mpicc insertion_sort_parallel_Pipeline.c -o ismpirun -np 4 is // 4 coresParallelized shell sort algorithm, using the method of Computer Science and Engineering, University at Buffalo.
mpicc shell_sort_parallel_Reduce.c -o shellmpirun -np 4 shell // 4 coresParallelized Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm for finding prime numbers in specific range. Used Pipeline (2 alternatives, first is slow, for big N it actually never ends), global array (bitmap alike) and MPI_Scan directive.
mpicc sieve_parallel_Pipeline.c -o sieve_pipempirun -np 4 sieve_pipe // 4 coresmpicc sieve_parallel_Pipeline_2.c -o sieve_pipe_2mpirun -np 4 sieve_pipe_2 // 4 coresmpicc sieve_parallel_Locations_Global.c -o sieve_gmpirun -np 4 sieve_g // 4 coresmpicc sieve_parallel_Locations_MPI_Scan.c -o sieve_scanmpirun -np 4 sieve_scan // 4 coresTested for N = 200 (below).
All code from MPI is written in Python, too, using mpi4py lib.
python <name_of_py_file>