-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Graph Data Model
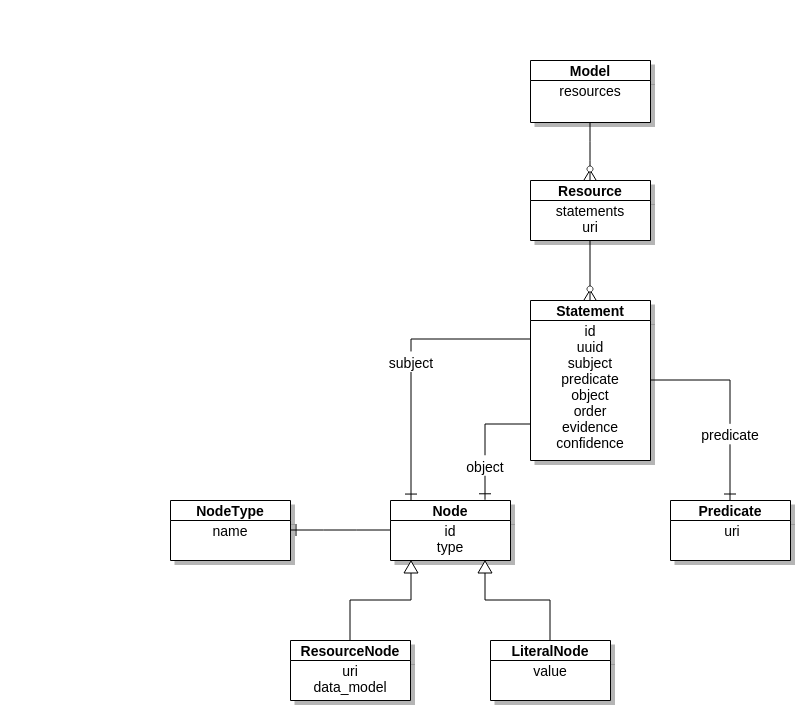
A graph data model consists of a set of resources. A resource has an identifier, e.g., an URI, and is a bunch of statements that describe this resource. A statement follows the simple sentence structure: subject - predicate - object. Whereby,
- a subject can be a reference (by identifier, i.e., URI) to a resource, i.e., it is a resource node, or a blank node
- a predicate is a reference (by identifier, i.e., URI) to a property
- an object can be a reference (by identifier, i.e., URI) to a resource, or a blank node or a literal.
So a node can be of the following types: resource, blank node or literal. A Statement can have an arbitrary number of qualified attributes, e.g., order, evidence or confidence. A resource node can refer to an arbitrary resource in a specific data model. This opens the possibility to connect to resources between different data models.
For those familiar to RDF, we offer a comparison table for RDF and the GDM model.
A graph data model implies the notion of nodes and edges. In the graph data model, statements are represented as directed binary graphs – they always consist of a subject node, a predicate edge and an object node.
Nodes can be
- a resource or the entry point of a resource,
- part of a resource (blank node), i.e. a subelement of a hierarchical description of a resources, e.g. a field in a MARCXML recordset (record), or
- simple value nodes, i.e. literals.
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| uri | if node has label RESOURCE |
| value | if node has label LITERAL |
| datatype | if node has label LITERAL and the literal is a typed literal, i.e., of a certain data type, e.g., integer |
| datamodel | if node has label RESOURCE; indicates the data model the resource belongs to |
| resource | indicates the resource the node belongs to (in case it is a literal node or a blank node) |
A record is always a resource so one of the labels of the record’s entry node is RESOURCE. Resources or parts of resources can be typed. The types of resources are used as node labels in the graph:
- a MABXML record, for instance, is of the type ‘Datensatz’ (record, http://www.ddb.de/professionell/mabxml/mabxml-1.xsd#datensatzType) and
- a field within the MABXML record is of the type ‘Feld’ (field, http://www.ddb.de/professionell/mabxml/mabxml-1.xsd#feldType).
URIs are utilised as identifiers for resources, types and attributes (predicates) of statements. All resource nodes have a data model attribute (datamodel). It refers to the data model the resource belongs to. All edges hava a resource attribute (resource). It refers to the resource the statement belongs to. Resource identifiers are assigned to resource nodes by the attribute uri. Values of literals are assigned to literal nodes by the attribute value.
Edges are always attributes of resources or resource parts, e.g. mabxml:nr (http://www.ddb.de/professionell/mabxml/mabxml-1.xsd#nr).
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| resource | Indicates the resource the edge belongs to |
| order | Signifies the “element” order of values of a certain type, e.g. “mixed XML elements” |
| index | Signifies the statement index of a resource (i.e. of the original element order as occurs in XML files) |
| uuid | Identifies a statement uniquely (in a data model) |
| valid_from | The version number upon this statement is valid |
| valid_to | The version number until this statement was valid (i.e. upon this version number the statement is invalid) |
- Overview
- misc
- Graph Data Model
- Server-Installation (Productive Environment)
- Maintenance
- HowTos
- Use Cases