Dynamic communication flows between message based actors.
Babble makes it easy to code communication flows between actors. A conversation
is modeled as a control flow diagram containing blocks ask, tell, listen,
iif, decide, and then. Each block can link to a next block in the
control flow. Conversations are dynamic: a scenario is build programmatically,
and the blocks can dynamically determine the next block in the scenario.
During a conversation, a context is available to store the state of the
conversation.
Babblers communicate with each other via a message bus. Babble comes with built in support for a local message bus, and pubnub to connect actors distributed over multiple devices. Its easy to add support for other message buses.
Babble runs in node.js and in the browser.
Install babble via npm:
npm install babble
Load in node.js:
var babble = require('babble');Load in the browser:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- load pubnub, only needed when using pubnub -->
<script src="http://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/pubnub/3.5.4/pubnub.min.js"></script>
<!-- load babble -->
<script src="../../dist/babble.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Then, babble can be loaded and used:
var babble = require('babble');
var emma = babble.babbler('emma');
var jack = babble.babbler('jack');
// listen for messages containing either 'age' or 'how old'
emma.listen(/age|how old/)
.tell(function () {
return 25;
});
jack.ask('emma', 'what is your age?', function (age, context) {
console.log(context.from + ' is ' + age + ' years old');
});TODO: describe control flow blocks
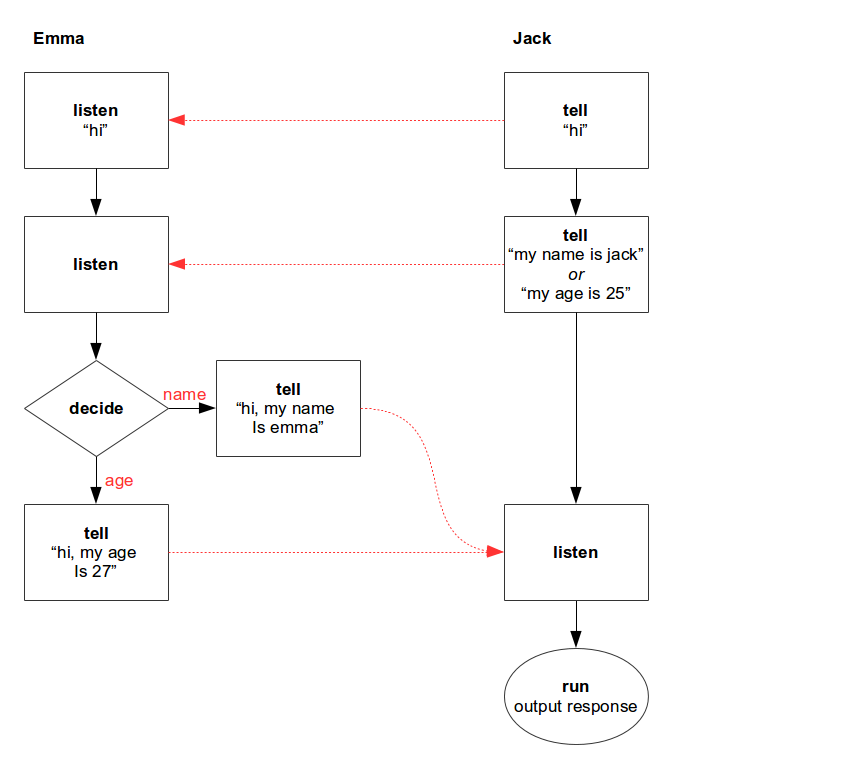
Babble can be used to listen for messages and send a reply. In the following example, emma listens for a message "hi", then she will listen to the next message. Depending on the contents of this second message, she determines how to respond. Jack says hi to emma, then tells his name or age, and awaits a response from emma.
This scenario can be represented by the following control flow diagram:
The scenario can be programmed as:
var babble = require('babble');
var emma = babble.babbler('emma');
var jack = babble.babbler('jack');
emma.listen('hi')
.listen(function (message, context) {
console.log(context.from + ': ' + message);
return message;
})
.decide(function (message, context) {
return (message.indexOf('age') != -1) ? 'age' : 'name';
}, {
'name': babble.tell('hi, my name is emma'),
'age': babble.tell('hi, my age is 27')
});
jack.tell('emma', 'hi')
.tell(function (message, context) {
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
return 'my name is jack'
} else {
return 'my age is 25';
}
})
.listen(function (message, context) {
console.log(context.from + ': ' + message);
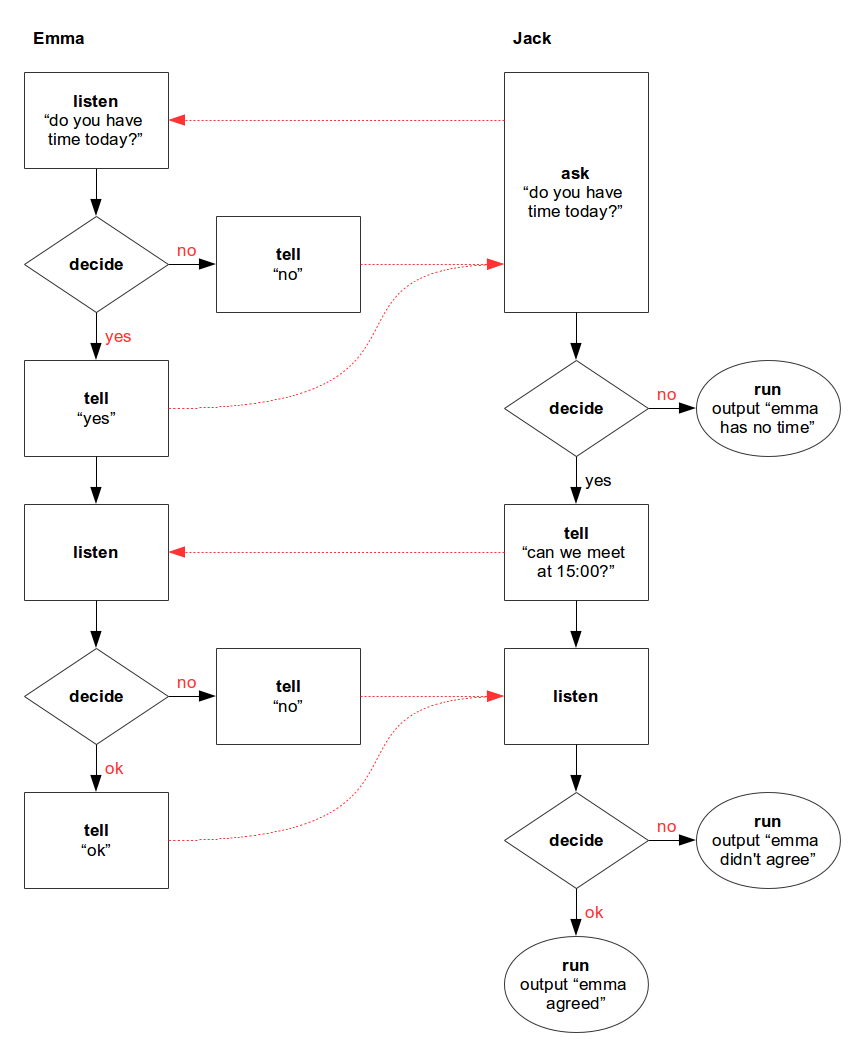
});The following scenario describes two peers planning a meeting in two steps: First jack asks whether emma has time for a meeting, and if so, jack will propose to meet, and await emma's response.
This scenario can be represented by the following control flow diagram:
The scenario can be coded as follows. Note that the implementations of the control flow blocks are separated from the flow itself.
var babble = require('babble');
var emma = babble.babbler('emma');
var jack = babble.babbler('jack');
function decideIfAvailable () {
return (Math.random() > 0.4) ? 'yes' : 'no';
}
function decideToAgree (response) {
if (response == 'can we meet at 15:00?' && Math.random() > 0.5) {
return 'ok';
}
else {
return 'no';
}
}
emma.listen('do you have time today?')
.decide(decideIfAvailable, {
yes: babble.tell('yes')
.listen()
.decide(decideToAgree, {
ok: babble.tell('ok'),
no: babble.tell('no')
}),
no: babble.tell('no')
});
function noTime () {
console.log('emma has no time');
}
function agreesToMeet (response) {
return (response == 'ok') ? 'ok': 'no';
}
function agreement () {
console.log('emma agreed');
}
function noAgreement () {
console.log('emma didn\'t agree');
}
jack.ask('emma', 'do you have time today?')
.decide({
yes: babble.tell('can we meet at 15:00?')
.listen()
.decide(agreesToMeet, {
ok: babble.then(agreement),
no: babble.then(noAgreement)
}),
no: babble.then(noTime)
});Babble has the following factory functions:
-
babble.ask(message: String | Function [, callback: Function]) : Block
Send a question and listen for a reply. This is equivalent of doingtell(message).listen([callback]). -
babble.babbler(id: String) : Babbler
Factory function to create a new Babbler. -
babble.babblify(actor: Object, params: Object) : Object
Babblify an actor. The babblified actor will be extended with functionsask,tell,listen, andlistenOnce.Babble expects that messages sent via
actor.send(to, message)will be delivered by the recipient on a functionactor.receive(from, message). Babble replaces the originalreceivewith a new one, which is used to listen for all incoming messages. Messages ignored by babble are propagated to the originalreceivefunction.The function accepts the following parameters:
-
actor: Object
The actor to be babblified. Must be an Object containing functionssend(to, message)andreceive(from, message). -
[params: Object]
Optional parameters. Can contain properties:id: stringThe id for the babblersend: stringThe name of an alternative send function available on the actor.receive: stringThe name of an alternative receive function available on the actor.
The function returns the babblified actor. A babblified actor can be restored in its original state using
unbabblify(actor). -
-
babble.decide([decision: Function, ] choices: Object<String, Block>) : Block
Create a flow starting with aDecisionblock. When adecisionfunction is provided, the function is invoked asdecision(response, context). The function must return the id for the next block in the control flow, which must be available in the providedoptions. The functiondecisioncan also return a Promise resolving with an id for the next block. Whendecisionis not provided, the next block will be mapped directly from theresponse, which should be a string in that case.Parameter
choicesis a map with the possible next blocks in the flow. The next block is selected by the id returned by thedecisionfunction. The returned block is used as next block in the control flow.When there is no matching choice, the choice
'default'will be selected when available. -
babble.iif(condition: function | RegExp | * [, trueBlock : Block] [, falseBlock : Block]) : Block
Create a control flow starting with anIIfblock. When the condition is a function, it can either return a boolean or a Promise resolving with a boolean value. When the condition evaluatestrue,trueBlockis executed. If notrueBlockis provided, the next block in the chain will be executed. When the condition evaluatestrue,falseBlockis executed. -
babble.listen([callback: Function])
Wait for a message. The provided callback function is called ascallback(response, context), whereresponseis the just received message. When the callback returns a promise, babble will wait with execution of the next block until the promise is resolved. The result returned by the callback is passed to the next block in the chain. Providing a callback function is equivalent of doingbabble.listen().then(callback). -
babble.tell(message: Function | *) : Block
Create a flow starting with aTellblock. Message can be a static value, or a callback function returning a message dynamically. The callback function is called ascallback(response, context), whereresponseis the latest received message, and must return a result. The returned result is send to the connected peer. When the callback returns a Promise, the value returned when the promise resolves will be send to the connected peer. -
babble.then(next: Block | function) : Block
Create a flow starting with given block. When a callback function is provided, the function is wrapped into aThenblock. The provided callback function is called ascallback(response, context), whereresponseis the latest received message, and must return a result. When the callback returns a promise, babble will wait with execution of the next block until the promise is resolved. The result returned by the callback is passed to the next block in the chain. -
babble.unbabblify(actor: Object) : Object
Unbabblify an actor. Returns the unbabblified actor.
Babble contains the following prototypes. These prototypes are normally instantiated via the above mentioned factory functions.
babble.Babblerbabble.block.Blockbabble.block.Decisionbabble.block.IIfbabble.block.Listenbabble.block.Tellbabble.block.Then
A babbler is created via the factory function babble.babbler(id: String).
After creation, a babbler is automatically connected to the default (local)
message bus. The connection can replaced with another message bus using the
function Babbler.connect(bus).
A babbler has the following functions:
-
ask(to: String, message: * | Function [, callback: Function]) : Block
This is equivalent of doingtell(to, message).listen([callback]). Other blocks can be chained to the returned block. -
connect([bus: Object]) : Promise.<Babbler>
Connect to a message bus. Babble comes with interfaces to support various message buses:pubnub,pubsub-js, anddefault. These interfaces are available in thebabble.messagebusnamespace. If parameterbusis not provided, babble uses thedefaultmessage bus, which works locally. A specific message bus interface can be specified like:babbler.connect(babble.messagebus['pubnub']) .then(function (babbler) { // connected });
The connect function returns a promise which resolves with the babbler itself when the connection is ready.
See section Message bus for documentation on the interface of a message bus.
-
disconnect()
Disconnect from the connected message bus. -
listen([condition: Function | RegExp | * [, callback: Function]]) : Block
Listen for incoming messages and start the conversation flow. Other blocks can be chained to the returned block.Providing a condition will only start the flow when condition is met, this is equivalent of doing
listen().iif(condition).Providing a callback function is equivalent of doing either
listen(message).then(callback)orlisten().iif(message).then(callback). The callback is invoked ascallback(message, context), and must return either a result or a Promise resolving with a result. The result will be passed to the next block in the chain. -
listenOnce([condition: Function | RegExp | * [, callback: Function]]) : Block
Equal tolisten, except that the listener is removed as soon as a message is received matching listeners condition, i.e. the listener is executed only once. -
send(to: String, message: *)
Send a message to another peer. -
tell(to: String, message: Function | *)
Send a notification to another peer.messagecan be a static value or a callback function. Whenmessageis a function, it is invoked ascallback(message, context), and must return either a result or a Promise resolving with a result. The result will be sent to the other peer, and will be passed to the next block in the chain.
Blocks can be created via the factory functions available in babble
(tell, iif, decide, then, listen), or in a Babbler (listen, tell,
ask). Blocks can be chained together, resulting in a control flow. The results
returned by blocks are used as input argument for the next block in the chain.
A Block has the following functions:
-
ask(message: * [, callback]) : Block
Append aTellandListenblock to the control flow. Parametermessagecan be a callback function or an object or value. -
decide([decision: function, ] choices: Object<String, Block>) : Block
Append aDecisionblock to the control flow. -
iif(condition: function | RegExp | * [, trueBlock : Block] [, falseBlock : Block]) : Block
Append anIIfblock to the control flow. When the condition evaluatestrue,trueBlockis executed. If notrueBlockis provided, the next block in the chain will be executed. When the condition evaluatestrue,falseBlockis executed. -
listen([callback: Function]) : Block
Append aListenblock to the control flow. Providing a callback function is equivalent of doinglisten().then(callback). -
tell(message: * | Function) : Block
Append aTellblock to the control flow. Parametermessagecan be callback function or an object or value. -
then(block : Block | function) : Block
Append an arbitrary block to the control flow. When a callback function is provided, it is wrapped into aThenblock and added to the chain.
Babblers talk to each other via a message bus. This can be any message bus implementation. Babble comes with support for two message buses: a local message bus and pubnub.
The function Babbler.connect(bus) accepts a message bus interface. This
interface must be an Object with the following functions:
-
connect(params: Object) : string
The functionconnectwill be called by the Babbler with an object having the following parameters:idthe id of the babbler itself.messagethe callback function to deliver messages for this babbler. This function must be invoked asmessage(msg : *).callbackan optional callback function which is invoked when the connection is established.
The
connectfunction must return a token which can be used to disconnect again. -
disconnect(token: string)
Disconnect from a message bus.tokenis the token returned by theconnectfunction. -
send(id: string, message: *)
Send a message to a babbler.
The messages sent between babblers are JSON objects having the following properties:
id: string
A unique identifier for the conversation, typically a uuid. This id is generated by the initiator of a conversation, and is sent with every message between the two babblers during the conversation.from: string
The id of the sender.to: string
The id of the receiver.message: *
The message contents. This is a (serializable) JSON object (often a string).
Example:
{
"id": "547d1840-2142-11e4-8c21-0800200c9a66",
"from": "babbler1",
"to": "babbler2",
"message": "Hello babbler!"
}Babble can be build for use in the browser. This is done using the tools browserify and uglify. First install all project dependencies:
npm install
To build the library, run:
npm run build
This generates the files ./dist/babble.js, ./dist/babble.min.js, and
./dist/babble.min.map.
To execute tests for the library, install the project dependencies once:
npm install
Then, the tests can be executed:
npm test
- Implement error handling and timeout conditions.
- Store message history in the context.
- Implement conversations with multiple peers at the same time.