This repository is the accumulation of the following works:
- [P1]: Predicting slice-to-volume transformation in presence of arbitrary subject motion (Springer | ArXiv)
- [P2]: 3D Reconstruction in Canonical Co-ordinate Space from Arbitrarily Oriented 2D Images (IEEE Xplore)
- [P3]: Computing CNN Loss and Gradients for Pose Estimation with Riemannian Geometry (Springer | ArXiv)
The original experiments were conducted using Caffe deep learning framework. Code and original experiments have now been updated for Tensorflow v1.13.1.
Experiments in [P2] uses the original King's College dataset by Kendall et al. This dataset consists of 3 channel RGB images; 1220 training and 342 testing. Original images are 1920x1080 and further downsampled by a factor of 4 to 480x270. Ground truth labels consists of quaternion, se(3) rotation vector and xyz translation.
To create TFRecords of the dataset, download the King's College then run:
python make_dataset_kingscollege.py \
--root_dir path/to/KingsCollege \
--dataset dataset_train.txt \
--out_file dataset_train.tfrecord
This dataset was used in [P1], [P2] and [P3]. [P1] introduced Anchor Points as an alternative loss function, with experiments and evaluation conducted using the CaffeNet architecture. [P2] further explored methods of generating data; iterating using euler angles or a fibonacci sphere sampling sequence. It was found that with enough data, the sampling methodology has less effect on the prediction accuracy. [P2] also explored different network architectures, as well as monte-carlo sampling for uncertainty prediction.
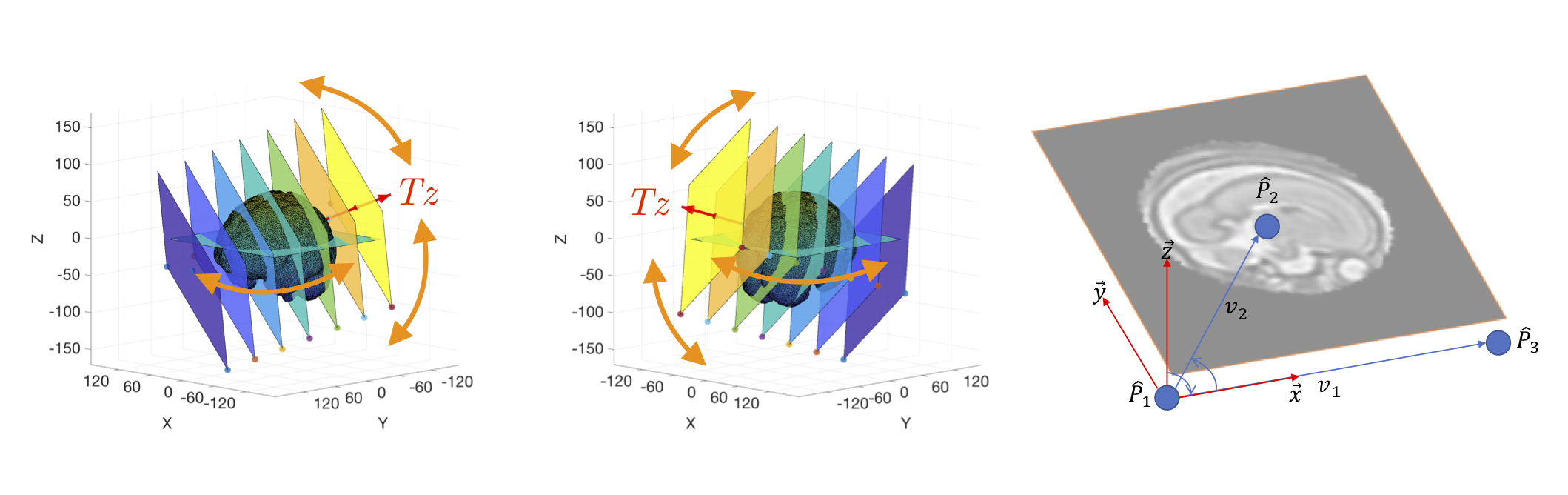
The iFIND Fetal Brain dataset used here follows the same generation method as [P1], [P2] and [P3], where the 2D slices are extracted from high resolution 3D volumes. The high resolution 3D volumes were reconstructed from motion free scans using Fast Volume Reconstruction From Motion Corrupted Stacks of 2D Slices, with isotropic spacing of 0.75mm x 0.75mm x 0.75mm.
A stack of 120px x 120px sampling planes is first center aligned with the brain. Instead of using the euler or fibonacci sampling schemes, random sampling was used instead. The entire stack is rotated randomly w.r.t. the fetal brains' isocenter, with Tz offsets also sampled randomly.
2000 random rotations were made between -90 and +90 degrees in xyz axis, with 16 random z-offsets per rotation spanning between +40 and -40. This samples approximately the middle 66% of the brain volume. Nearest Neighbour was used as the interpolation method due to speed, any other interpolation method (e.g. Linear, BSpline, Gaussian, etc) should also be applicable. 28 volumes was used for training, 5 volumes for testing. Each volume generates 32K images.
[TODO]
[P3] introduces a general Riemannian formulation of the pose estimation problem, where CNNs were trained directly on SE(3) equipped with a left-invariant Riemannian metric. The loss between the ground truth and predicted pose (elements of the manifold) is calculated as the Riemannian geodesic distance, which couples together the translation and rotation components.
Training weights for each se(3) component can be intrinsically calculated from the dataset. During evaluation, error weights can be calculated using the formula:
Err_i = compose(inverse((y_true_i)^(-1)), y_pred_i)
err_weights = diagonal((covariance(Err_i.Transposed))^(-1))
This experiment uses code from the following repositories:
[P2] tested 6 networks; CaffeNet, GoogLeNet (Inception-v1), Inception-v4, ResNet-152, Vgg-16, Network-in-Network. Results showed that CaffeNet is ideal for speed, where as Vgg-16 is ideal for accuracy. Conversely, CaffeNet does not perform the best in terms of accuracy and Vgg-16 takes very long to train. It has been found that GoogLeNet (Inception_v1) is the ideal compromise between training speed vs accuracy.
This repository uses Inception_v3 as the base network from the Tensorflow Slim library, although any off-the-shelf network should be applicable in its place. Network were trained on a GPU cluster of Titan Xp's, training speed may vary depending on shared network load and host CPU utilisation. All experiments were trained using the Adam optimiser for 200K iterations, with an initial learning rate of 1e-4 and batch size 36.
# iFIND Data on Anchor Points:
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/ifind --dataset ifind --loss AP --model_dir models/ifind_ap
# iFIND Data on Quaternion + Translation
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/ifind --dataset ifind --loss PoseNet --model_dir models/ifind_posenet
# iFIND Data on SE3 Points (no weights)
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/ifind --dataset ifind --loss SE3 --model_dir models/ifind_se3
# iFIND Data on SE3 Points (with weights)
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/ifind --dataset ifind --loss SE3 --model_dir models/ifind_se3_with_weights
# Kings College on Quaternion + Translation
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/kingscollege --dataset kingscollege --loss PoseNet --model_dir models/kingscollege_posenet
# Kings College on SE3 Points
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/kingscollege --dataset kingscollege --loss SE3 --model_dir models/kingscollege_se3
# Kings College on SE3 Points (with weights)
python train_svrnet.py --data_dir data/kingscollege --dataset kingscollege --loss SE3 --model_dir models/kingscollege_se3_with_weights
| CC | MSE | PSNR | SSIM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternion + Translation | 0.747 | 1510 | 16.6 | 0.414 |
| Anchor Points | 0.851 | 877 | 19.2 | 0.573 |
| SE3 (no weights) | 0.831 | 1010 | 18.6 | 0.536 |
| SE3 (with weights) | 0.834 | 976 | 18.7 | 0.545 |
Original Quaternion + Translation Loss:
Error XYZ (m): 1.849 Error Q (degrees): 2.799
SE3 Geodesic Loss (no weights):
Error XYZ (m): 2.006 Error Q (degrees): 3.788
# From the evaluation set:
err_weights = [0.77848401, 0.61488583, 0.12600517, 0.00018093, 0.00020279, 0.00082466]
SE3 Geodesic Loss (with training weights):
Error XYZ (m): 1.580 Error Q (degrees): 1.910
[TODO]
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/miccai/HouAMDRHRGK17,
author = {Benjamin Hou and Amir Alansary and Steven G. McDonagh and Alice Davidson and
Mary A. Rutherford and Joseph V. Hajnal and Daniel Rueckert and Ben Glocker and
Bernhard Kainz},
title = {Predicting Slice-to-Volume Transformation in Presence of Arbitrary
Subject Motion},
booktitle = {{MICCAI} {(2)}},
series = {Lecture Notes in Computer Science},
volume = {10434},
pages = {296--304},
publisher = {Springer},
year = {2017}
}
@article{DBLP:journals/tmi/HouKAMDRHRGK18,
author = {Benjamin Hou and Bishesh Khanal and Amir Alansary and Steven G. McDonagh and
Alice Davidson and Mary A. Rutherford and Joseph V. Hajnal and Daniel Rueckert and
Ben Glocker and Bernhard Kainz},
title = {3-D Reconstruction in Canonical Co-Ordinate Space From Arbitrarily
Oriented 2-D Images},
journal = {{IEEE} Trans. Med. Imaging},
volume = {37},
number = {8},
pages = {1737--1750},
year = {2018}
}
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/miccai/HouMKLAMHRGK18,
author = {Benjamin Hou and Nina Miolane and Bishesh Khanal and Matthew C. H. Lee and
Amir Alansary and Steven G. McDonagh and Joseph V. Hajnal and Daniel Rueckert and
Ben Glocker and Bernhard Kainz},
title = {Computing {CNN} Loss and Gradients for Pose Estimation with
Riemannian Geometry},
booktitle = {{MICCAI} {(1)}},
series = {Lecture Notes in Computer Science},
volume = {11070},
pages = {756--764},
publisher = {Springer},
year = {2018}
}
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md for details