This project features methods to use simple classic and quantum neural networks to try their efficiency when it comes to decipher a database. Using various libraries such as Tensorflow and Pennylane, it showcases how far a neural network can learn a decryption method based on ciphered and clear data assumed leaked from a database.
The different classes : You'll find 4 classes in this simulator :
-
main.py : The main class where examples are computed and evaluated, please refer to the part "How to use the simulator" to understand how to use the solution.
-
functions.py : Also named "toolkit", you'll find all the functions called for binary encryption/decryption or dataset's generation. You can choose any encryption key you want by modifying the variable "key_array" in the "encrypt" function. this class currently has a XOR binary encryption method.
-
NeuralNetwork.py : The file where is initialized the neural network. You can modify few parameters to adjust the network and optimize its training efficiency.
-
QuantumNeuralNetwork.py : The quantum counterpart of the previous class. It inherits the Neural Network's core functions called for the simulation in the main. The constructor is overridden to implement a specific quantum structure with variable depth (change the number of layers). It currently features basic and strong entanglement between qubits.
How to use the simulator : To run the simulator, just launch the file "main.py" in any environment supporting Python3. You might need to install many libraries in your environment such as Tensorflow or Pennylane, please refer to their respective tutorials to prepare your setup. You'll be asked several parameters before running the simulation :
-
Number of neural networks : You can either create one or several neural networks if you want to compare them on a specific dataset. You can modify their parameters (learning rate, loss function...) in their respective files "NeuralNetwork.py" and "QuantumNeuralNetwork.py" in the constructor of each class.
-
Size of a batch's sample : The size/length of one sample of your training dataset. Datasets must have the same length. If you want to try the decryption on a dataset of 4-bits arrays, you'll enter 4.
-
Number of training samples : The number of samples you want to use for training. For binary encryption/decryption, you can use a built-in function to generate your binary arrays at random, specific arrays or use built-in datasets and see whereas your dataset contains too much data or not enough for your networks.
-
Type of neural network : This is where your choose which neural network you want to simulate. It can either be a classic or quantum neural network and, in the case of a classic neural network, a regular one with a Dense layer only or a Convolutional network.
This project can currently simulates up to 8-bits XOR decryption for any type of neural network featured (see #Results). You can also push further the simulation by choosing random datasets with binary arrays of up to 32 bits for classic and convolutional networks only. Quantum neural networks can decipher up to 10-bits long datasets but the training time is abysmal (almost 2 hours). Since those quantum networks can only rely on entanglement their performances are still quite underwhelming as compared to their classic counterparts (reaching almost 100% accuracy on lengthy datasets, convolutional networks will require more filters).
You'll find published here the current results for n-bits binary decryption with the parameters required to achieve such results.
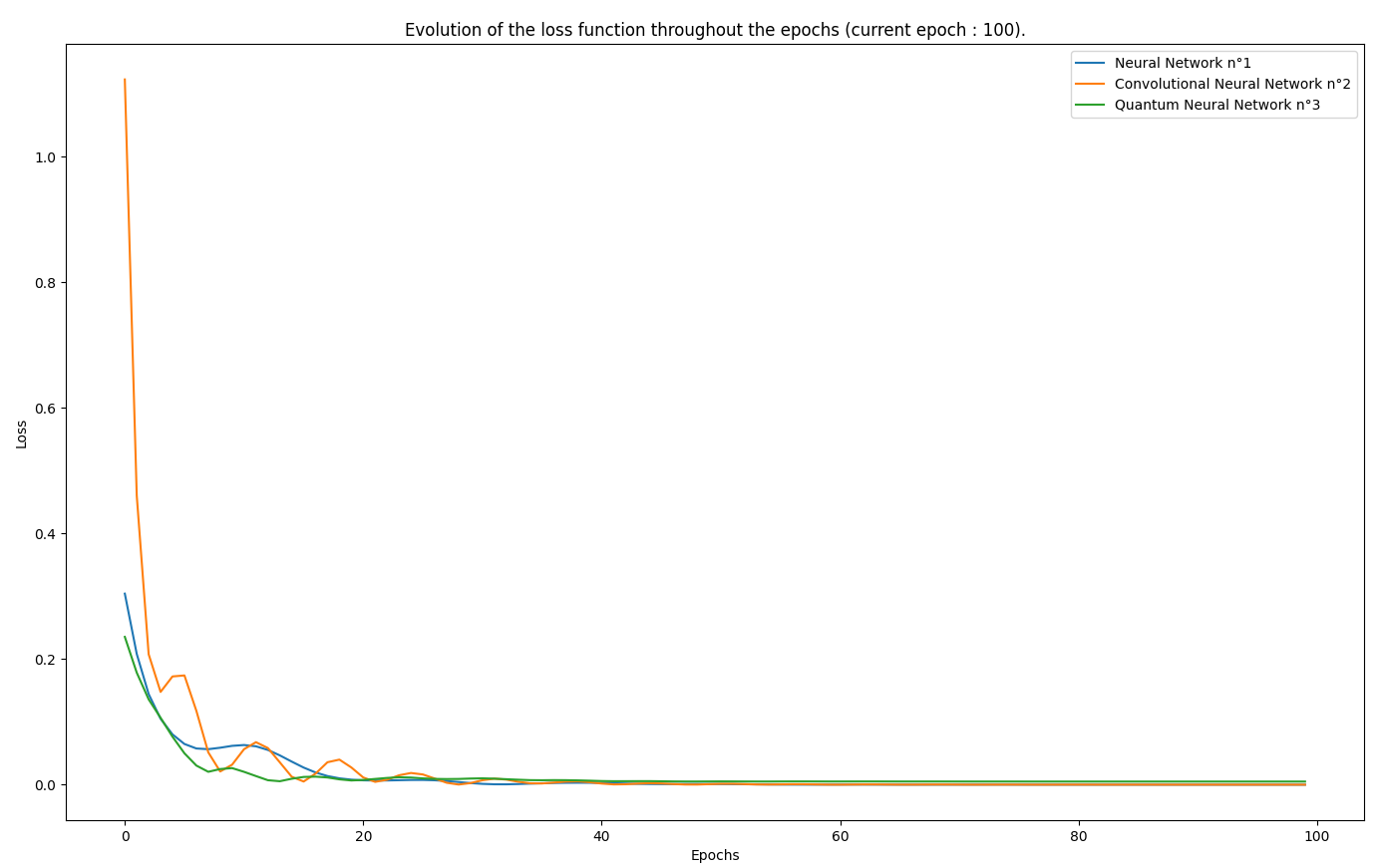
- 2-bits XOR decryption : Encryption was done over 100 epochs with the following key -> [1,0]. The dataset was the 2-bit built-in preset.
-
Classic Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.08)
- accuracy : 75%
-
Convolutional Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.08)
- number of filters : 8
- accuracy : 75%
-
Quantum Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.05)
- accuracy : 100%
-
-
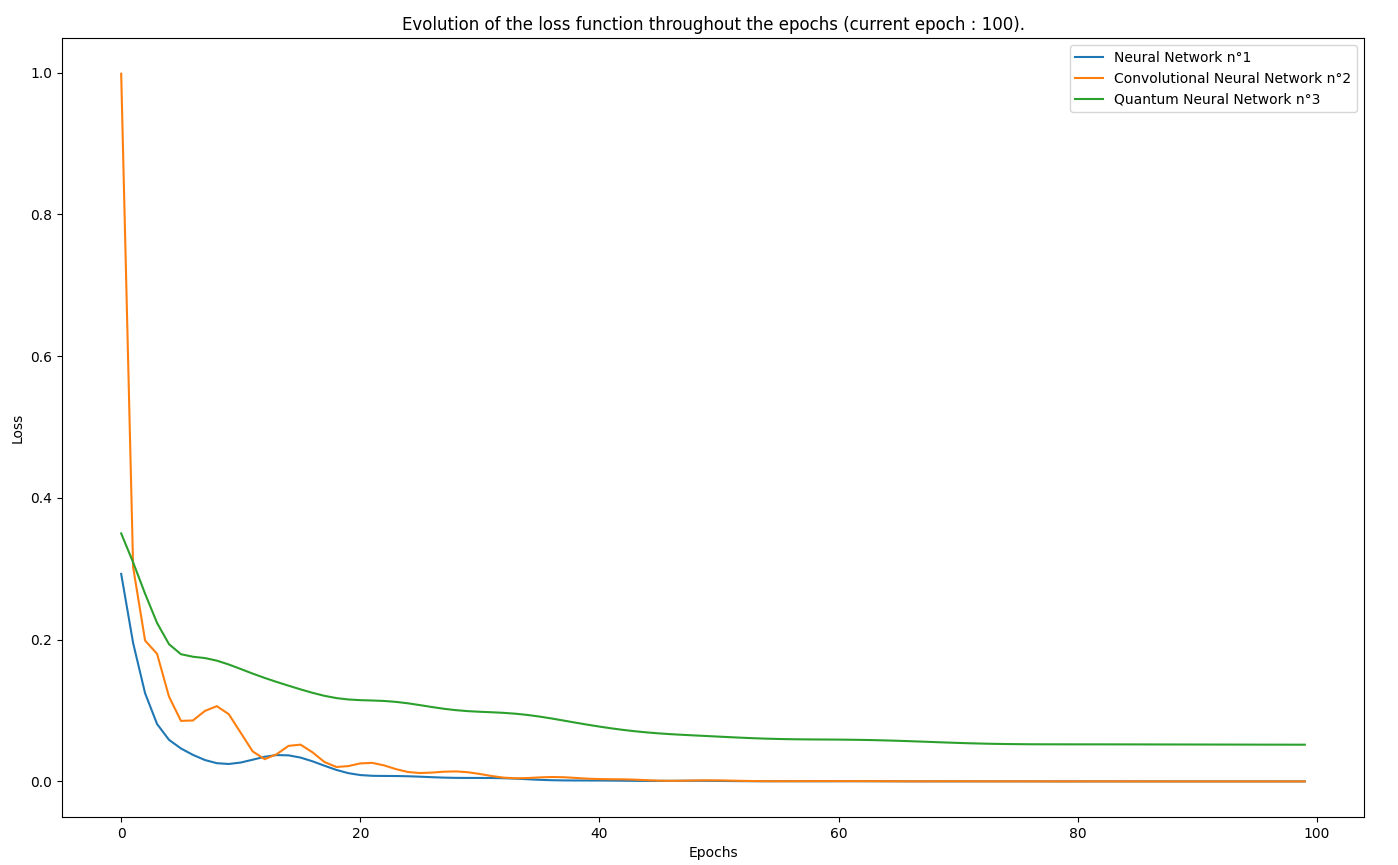
4-bits XOR decryption : Encryption was done over 100 epochs with the following key -> [1, 0, 1, 0]. The dataset was the 4-bit built-in preset.
-
Classic Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.07)
- training time : 0.54s
- accuracy : 80~100%
-
Convolutional Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.07)
- training time : 0.567s
- number of filters : 10
- accuracy : 88%
-
Quantum Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.04)
- training time : 64.315s
- number of layers : 6
- accuracy : 72%
-
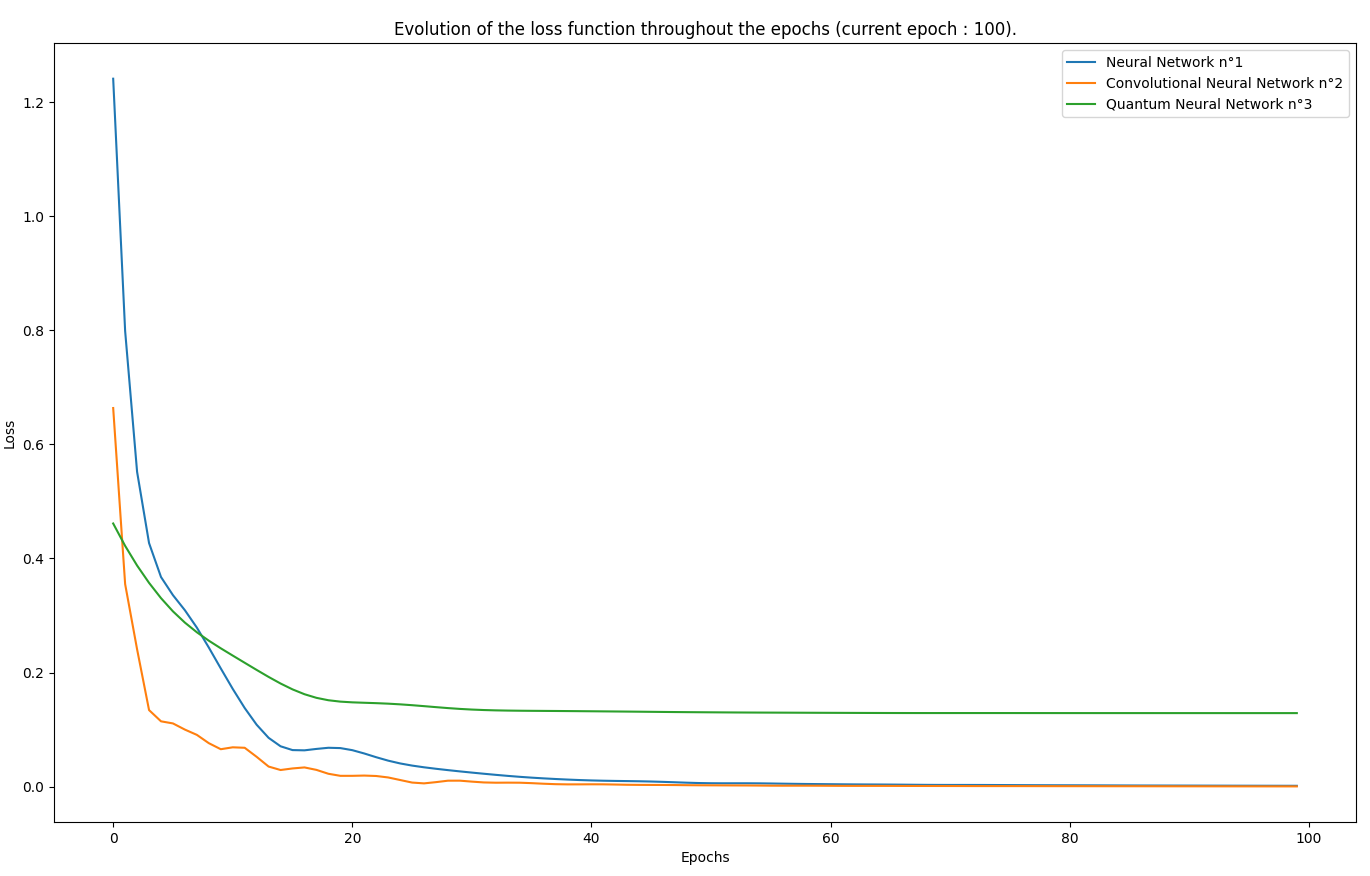
- 8-bits XOR decryption : Encryption was done over 100 to 200 epochs with the following key -> [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]. The dataset was the 8-bit built-in preset.
-
Classic Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.07)
- training time : ~0.6s
- accuracy : 82~88%
-
Convolutional Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.07)
- training time : ~0.5s
- number of filters : 10
- accuracy : 85~91%
-
Quantum Networks specs
- loss function : Mean Squared
- optimizer : Adam (learning rate = 0.06)
- training time : ~300s
- number of layers : 7
- accuracy : 78%
-