-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 740
Description
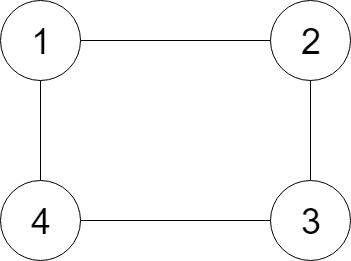
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph, return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
Example:
Input:
{"$id":"1","neighbors":[{"$id":"2","neighbors":[{"$ref":"1"},{"$id":"3","neighbors":[{"$ref":"2"},{"$id":"4","neighbors":[{"$ref":"3"},{"$ref":"1"}],"val":4}],"val":3}],"val":2},{"$ref":"4"}],"val":1}
Explanation:
Node 1's value is 1, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 2's value is 2, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Node 3's value is 3, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 4's value is 4, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Note:
- The number of nodes will be between 1 and 100.
- The undirected graph is a simple graph, which means no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- Since the graph is undirected, if node p has node q as neighbor, then node q must have node p as neighbor too.
- You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
这道无向图的复制问题和之前的 Copy List with Random Pointer 有些类似,那道题的难点是如何处理每个结点的随机指针,这道题目的难点在于如何处理每个结点的 neighbors,由于在深度拷贝每一个结点后,还要将其所有 neighbors 放到一个 vector 中,而如何避免重复拷贝呢?这道题好就好在所有结点值不同,所以我们可以使用 HashMap 来对应原图中的结点和新生成的克隆图中的结点。对于图的遍历的两大基本方法是深度优先搜索 DFS 和广度优先搜索 BFS,这里我们先使用深度优先搜索DFS来解答此题,在递归函数中,首先判空,然后再看当前的结点是否已经被克隆过了,若在 HashMap 中存在,则直接返回其映射结点。否则就克隆当前结点,并在 HashMap 中建立映射,然后遍历当前结点的所有 neihbor 结点,调用递归函数并且加到克隆结点的 neighbors 数组中即可,代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
return helper(node, m);
}
Node* helper(Node* node, unordered_map<Node*, Node*>& m) {
if (!node) return NULL;
if (m.count(node)) return m[node];
Node *clone = new Node(node->val);
m[node] = clone;
for (Node *neighbor : node->neighbors) {
clone->neighbors.push_back(helper(neighbor, m));
}
return clone;
}
};
我们也可以使用 BFS 来遍历图,使用队列 queue 进行辅助,还是需要一个 HashMap 来建立原图结点和克隆结点之间的映射。先克隆当前结点,然后建立映射,并加入 queue 中,进行 while 循环。在循环中,取出队首结点,遍历其所有 neighbor 结点,若不在 HashMap 中,我们根据 neigbor 结点值克隆一个新 neighbor 结点,建立映射,并且排入 queue 中。然后将 neighbor 结点在 HashMap 中的映射结点加入到克隆结点的 neighbors 数组中即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
if (!node) return NULL;
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
queue<Node*> q{{node}};
Node *clone = new Node(node->val);
m[node] = clone;
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *t = q.front(); q.pop();
for (Node *neighbor : t->neighbors) {
if (!m.count(neighbor)) {
m[neighbor] = new Node(neighbor->val);
q.push(neighbor);
}
m[t]->neighbors.push_back(m[neighbor]);
}
}
return clone;
}
};
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/
https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/discuss/42313/C%2B%2B-BFSDFS
https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/discuss/42309/Depth-First-Simple-Java-Solution