This repository has deployment, installation and clean up instructions on how to deploy and manage Snort3 in AWS with Elastic Container Services and Gateway Load balancer. The solution will deploy Snort3 on Amazon ECS and provides controls to adjust the Snort configuration and rulesets using a GitOps-based workflow.
This Snort3 deployment can then be used as a target for Gateway Load Balancer in a distributed or centralized architecture to use Cisco Snort3 as a scalable, open-source network security IPS/IDS solution.
The quickest way to deploy the full solution that consists of Snort3 running on ECS and the GitOps CI/CD pipeline used for Snort3 configuration is to deploy the solution using the snort_base.yaml cloudformation template. This template will setup the GitOps pipeline and will copy this GitHub Repo into AWS CodeCommit which will be the Git repo you work against to setup Snort3 rules, Snort3 configuration etc.
The snort_base.yaml template will setup a new environment from scratch, including a VPC where Snort3 will be deployed.
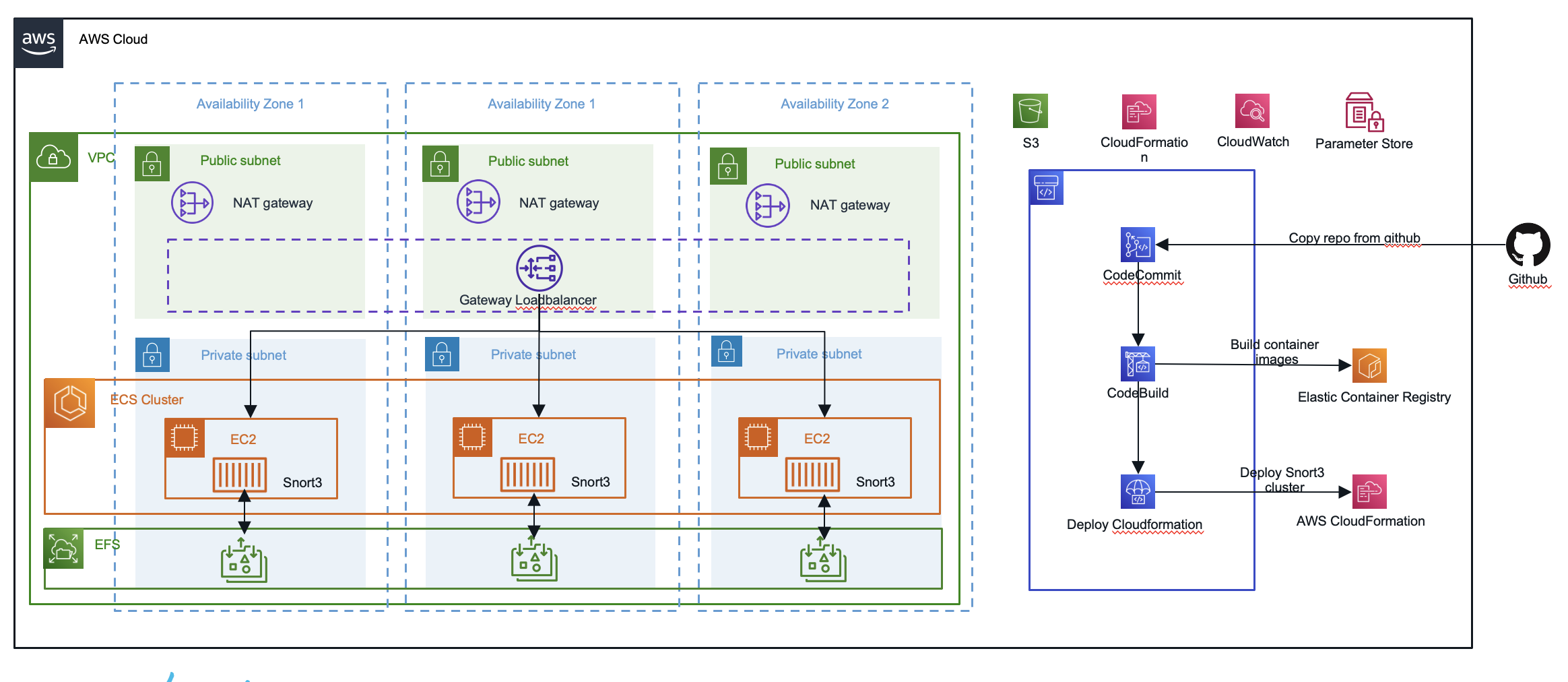 |
|---|
| Fig.1 - Solution Reference Architecture |
After you have deployed the above cloudformation template you simply need to create Gateway Load balancer Endpoints and point your workload route table to those GWLB-endpoints so the Snort3 containers can be used to inspect your networking traffic. In case if you would like to change this behaviour and have IDS (detection only mode) - you need to edit the supervisord.conf and replace the "-Q" parameter to "-v" for passive mode under the [program:snort3] command section.
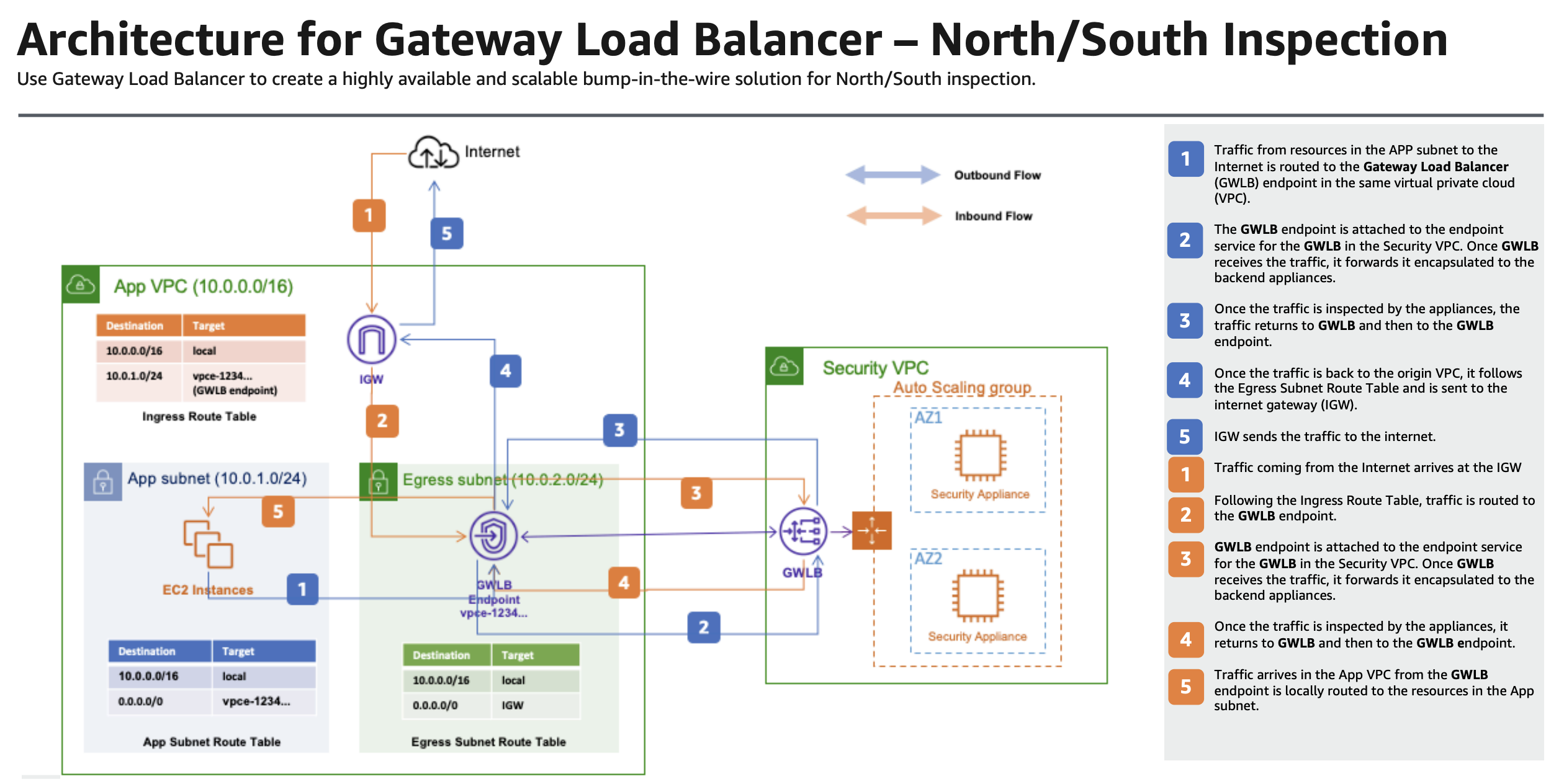 |
|---|
| Fig.2 - North South Inspection Architecture |
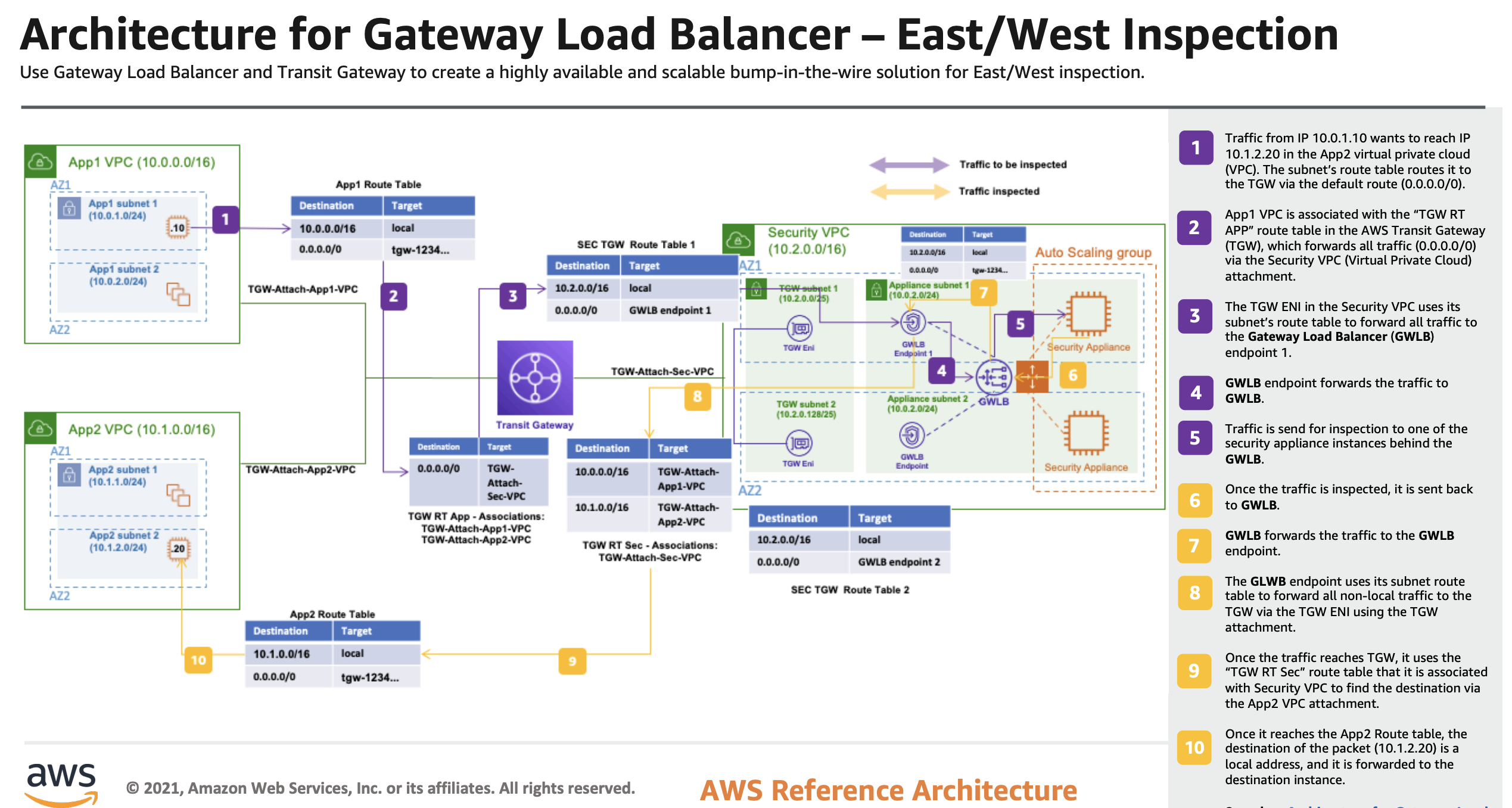 |
|---|
| Fig.3 - East West Inspection Architecture |
How can I add my own rules?
- Connect your development environment such as VSCode to your CodeCommit repository
- Open the local.rules
- Add a new custom rule in a new line based on snort3 rule format as per Rule Writers Guide to Snort3
- Once you've created your new rule - save and commit to the CodeCommit repository - which will kick-off a codepipeline process - and the new rule file will be deployed in couple of minutes to your environment.
How can I make changes to the Snort3 config?
The key configuration files for Snort3 are located under "Dockerfiles/snort":
You don't really need to edit these files for basic functionality. If you are an advanced Snort user - and you have a know-how of the following documents:
What logs are automatically ingested to CloudWatch Logs / S3?
In the default Snort3 configuration provided in this repo, Snort3 will use the following logging modules: alert-csv, file-log, data-log and appid. These logs are tailed and rotated automatically.
All the log files are stored under "/var/log/snort/" folder in the container and ingested by CloudWatch.
alert_csv.txtis your main logging file about IPS and Preprocessor eventsappid-output.log- AppId inspector provides an application level view about the detected applications on the network.file.log- Provides details about the transferred files on the networkdata_log- It is a passive inspector, ie it does nothing until it receives the data it subscribed for (other in the above diagram). By adding the following to your snort.lua configuration, you will get a simple URI logger. data_log = { key = 'http_raw_uri' } - in the basic configuration we've subscribed to the HTTP Request Header events("http_request_header_event")
You can disable these logs or enable other logs by editing the Snort3 config. If you will enable new logging methods you might need to configure the Cloudwatch Agent to pickup the new logs. The Cloudwatch Agent is configured in the cluster.yaml in the "CLOUDWATCH AGENT" section.
In addition, the stdout logs from the Snort3 container are also sent to CloudWatch Logs per default.
Does Snort3 scale automatically?
ECS Autoscaling is enabled for CPU. When the clusters average CPU goes over 80% (configurable) a new ECS task (a Snort3 container) is started. Scale-in is enabled, so if your traffic pattern is changing alot you will see ECS tasks (Snort3 containers) come and go. You can configure the scaling parameters by modifyin the following json config file and committing it to the codecommit repository Gateway Load Balancer will add the new ECS tasks as targets, however existing flows will still go to their old targets so we recommend that you tweak the scaling parameters, configuration and metrics to fit your environment. For example, if you have lots of long-lasting flows, you might want to disable automatic scale-in.