-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 72
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
12 changed files
with
436 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
26 changes: 26 additions & 0 deletions
26
...n/java/g3301_3400/s3324_find_the_sequence_of_strings_appeared_on_the_screen/Solution.java
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,26 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3324_find_the_sequence_of_strings_appeared_on_the_screen; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #String #Simulation #2024_10_22_Time_6_ms_(92.04%)_Space_55.7_MB_(44.25%) | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.ArrayList; | ||
| import java.util.List; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public List<String> stringSequence(String t) { | ||
| List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>(); | ||
| int l = t.length(); | ||
| StringBuilder cur = new StringBuilder(); | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) { | ||
| char tCh = t.charAt(i); | ||
| cur.append('a'); | ||
| ans.add(cur.toString()); | ||
| while (cur.charAt(i) != tCh) { | ||
| char lastCh = cur.charAt(i); | ||
| char nextCh = (char) (lastCh == 'z' ? 'a' : lastCh + 1); | ||
| cur.setCharAt(i, nextCh); | ||
| ans.add(cur.toString()); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return ans; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
42 changes: 42 additions & 0 deletions
42
.../g3301_3400/s3324_find_the_sequence_of_strings_appeared_on_the_screen/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,42 @@ | ||
| 3324\. Find the Sequence of Strings Appeared on the Screen | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given a string `target`. | ||
|
|
||
| Alice is going to type `target` on her computer using a special keyboard that has **only two** keys: | ||
|
|
||
| * Key 1 appends the character `"a"` to the string on the screen. | ||
| * Key 2 changes the **last** character of the string on the screen to its **next** character in the English alphabet. For example, `"c"` changes to `"d"` and `"z"` changes to `"a"`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note** that initially there is an _empty_ string `""` on the screen, so she can **only** press key 1. | ||
|
|
||
| Return a list of _all_ strings that appear on the screen as Alice types `target`, in the order they appear, using the **minimum** key presses. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** target = "abc" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** ["a","aa","ab","aba","abb","abc"] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The sequence of key presses done by Alice are: | ||
|
|
||
| * Press key 1, and the string on the screen becomes `"a"`. | ||
| * Press key 1, and the string on the screen becomes `"aa"`. | ||
| * Press key 2, and the string on the screen becomes `"ab"`. | ||
| * Press key 1, and the string on the screen becomes `"aba"`. | ||
| * Press key 2, and the string on the screen becomes `"abb"`. | ||
| * Press key 2, and the string on the screen becomes `"abc"`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** target = "he" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** ["a","b","c","d","e","f","g","h","ha","hb","hc","hd","he"] | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `1 <= target.length <= 400` | ||
| * `target` consists only of lowercase English letters. |
23 changes: 23 additions & 0 deletions
23
src/main/java/g3301_3400/s3325_count_substrings_with_k_frequency_characters_i/Solution.java
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,23 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3325_count_substrings_with_k_frequency_characters_i; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #String #Hash_Table #Sliding_Window #2024_10_22_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_42_MB_(98.69%) | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| public int numberOfSubstrings(String s, int k) { | ||
| int left = 0; | ||
| int result = 0; | ||
| int[] count = new int[26]; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { | ||
| char ch = s.charAt(i); | ||
| count[ch - 'a']++; | ||
|
|
||
| while (count[ch - 'a'] == k) { | ||
| result += s.length() - i; | ||
| char atLeft = s.charAt(left); | ||
| count[atLeft - 'a']--; | ||
| left++; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return result; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
36 changes: 36 additions & 0 deletions
36
.../java/g3301_3400/s3325_count_substrings_with_k_frequency_characters_i/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ | ||
| 3325\. Count Substrings With K-Frequency Characters I | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| Given a string `s` and an integer `k`, return the total number of substrings of `s` where **at least one** character appears **at least** `k` times. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = "abacb", k = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 4 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The valid substrings are: | ||
|
|
||
| * `"aba"` (character `'a'` appears 2 times). | ||
| * `"abac"` (character `'a'` appears 2 times). | ||
| * `"abacb"` (character `'a'` appears 2 times). | ||
| * `"bacb"` (character `'b'` appears 2 times). | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** s = "abcde", k = 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 15 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| All substrings are valid because every character appears at least once. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `1 <= s.length <= 3000` | ||
| * `1 <= k <= s.length` | ||
| * `s` consists only of lowercase English letters. |
43 changes: 43 additions & 0 deletions
43
...a/g3301_3400/s3326_minimum_division_operations_to_make_array_non_decreasing/Solution.java
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,43 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3326_minimum_division_operations_to_make_array_non_decreasing; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Array #Math #Greedy #Number_Theory #2024_10_22_Time_20_ms_(97.34%)_Space_73.1_MB_(5.03%) | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| private static final int MAXI = 1000001; | ||
| private static final int[] SIEVE = new int[MAXI]; | ||
| private static boolean precompute = false; | ||
|
|
||
| private static void compute() { | ||
| if (precompute) { | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 2; i < MAXI; i++) { | ||
| if (i * i > MAXI) { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| for (int j = i * i; j < MAXI; j += i) { | ||
| SIEVE[j] = Math.max(SIEVE[j], Math.max(i, j / i)); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| precompute = true; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public int minOperations(int[] nums) { | ||
| compute(); | ||
| int op = 0; | ||
| int n = nums.length; | ||
| for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) { | ||
| while (nums[i] > nums[i + 1]) { | ||
| if (SIEVE[nums[i]] == 0) { | ||
| return -1; | ||
| } | ||
| nums[i] /= SIEVE[nums[i]]; | ||
| op++; | ||
| } | ||
| if (nums[i] > nums[i + 1]) { | ||
| return -1; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return op; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
40 changes: 40 additions & 0 deletions
40
...1_3400/s3326_minimum_division_operations_to_make_array_non_decreasing/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ | ||
| 3326\. Minimum Division Operations to Make Array Non Decreasing | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given an integer array `nums`. | ||
|
|
||
| Any **positive** divisor of a natural number `x` that is **strictly less** than `x` is called a **proper divisor** of `x`. For example, 2 is a _proper divisor_ of 4, while 6 is not a _proper divisor_ of 6. | ||
|
|
||
| You are allowed to perform an **operation** any number of times on `nums`, where in each **operation** you select any _one_ element from `nums` and divide it by its **greatest** **proper divisor**. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the **minimum** number of **operations** required to make the array **non-decreasing**. | ||
|
|
||
| If it is **not** possible to make the array _non-decreasing_ using any number of operations, return `-1`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [25,7] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| Using a single operation, 25 gets divided by 5 and `nums` becomes `[5, 7]`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [7,7,6] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \-1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [1,1,1,1] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 0 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * <code>1 <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>6</sup></code> |
76 changes: 76 additions & 0 deletions
76
src/main/java/g3301_3400/s3327_check_if_dfs_strings_are_palindromes/Solution.java
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,76 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3327_check_if_dfs_strings_are_palindromes; | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #Array #String #Hash_Table #Tree #Hash_Function #Depth_First_Search | ||
| // #2024_10_22_Time_159_ms_(90.40%)_Space_93.9_MB_(80.80%) | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.ArrayList; | ||
| import java.util.List; | ||
|
|
||
| public class Solution { | ||
| private final List<List<Integer>> e = new ArrayList<>(); | ||
| private final StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); | ||
| private String s; | ||
| private int now; | ||
| private int n; | ||
| private int[] l; | ||
| private int[] r; | ||
| private int[] p; | ||
| private char[] c; | ||
|
|
||
| private void dfs(int x) { | ||
| l[x] = now + 1; | ||
| for (int v : e.get(x)) { | ||
| dfs(v); | ||
| } | ||
| stringBuilder.append(s.charAt(x)); | ||
| r[x] = ++now; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private void matcher() { | ||
| c[0] = '~'; | ||
| c[1] = '#'; | ||
| for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { | ||
| c[2 * i + 1] = '#'; | ||
| c[2 * i] = stringBuilder.charAt(i - 1); | ||
| } | ||
| int j = 1; | ||
| int mid = 0; | ||
| int localR = 0; | ||
| while (j <= 2 * n + 1) { | ||
| if (j <= localR) { | ||
| p[j] = Math.min(p[(mid << 1) - j], localR - j + 1); | ||
| } | ||
| while (c[j - p[j]] == c[j + p[j]]) { | ||
| ++p[j]; | ||
| } | ||
| if (p[j] + j > localR) { | ||
| localR = p[j] + j - 1; | ||
| mid = j; | ||
| } | ||
| ++j; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public boolean[] findAnswer(int[] parent, String s) { | ||
| n = parent.length; | ||
| this.s = s; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { | ||
| e.add(new ArrayList<>()); | ||
| } | ||
| for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { | ||
| e.get(parent[i]).add(i); | ||
| } | ||
| l = new int[n]; | ||
| r = new int[n]; | ||
| dfs(0); | ||
| c = new char[2 * n + 10]; | ||
| p = new int[2 * n + 10]; | ||
| matcher(); | ||
| boolean[] ans = new boolean[n]; | ||
| for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { | ||
| int mid = (2 * r[i] - 2 * l[i] + 1) / 2 + 2 * l[i]; | ||
| ans[i] = p[mid] - 1 >= r[i] - l[i] + 1; | ||
| } | ||
| return ans; | ||
| } | ||
| } |
61 changes: 61 additions & 0 deletions
61
src/main/java/g3301_3400/s3327_check_if_dfs_strings_are_palindromes/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,61 @@ | ||
| 3327\. Check if DFS Strings Are Palindromes | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| You are given a tree rooted at node 0, consisting of `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. The tree is represented by an array `parent` of size `n`, where `parent[i]` is the parent of node `i`. Since node 0 is the root, `parent[0] == -1`. | ||
|
|
||
| You are also given a string `s` of length `n`, where `s[i]` is the character assigned to node `i`. | ||
|
|
||
| Consider an empty string `dfsStr`, and define a recursive function `dfs(int x)` that takes a node `x` as a parameter and performs the following steps in order: | ||
|
|
||
| * Iterate over each child `y` of `x` **in increasing order of their numbers**, and call `dfs(y)`. | ||
| * Add the character `s[x]` to the end of the string `dfsStr`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note** that `dfsStr` is shared across all recursive calls of `dfs`. | ||
|
|
||
| You need to find a boolean array `answer` of size `n`, where for each index `i` from `0` to `n - 1`, you do the following: | ||
|
|
||
| * Empty the string `dfsStr` and call `dfs(i)`. | ||
| * If the resulting string `dfsStr` is a **palindrome**, then set `answer[i]` to `true`. Otherwise, set `answer[i]` to `false`. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the array `answer`. | ||
|
|
||
| A **palindrome** is a string that reads the same forward and backward. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| 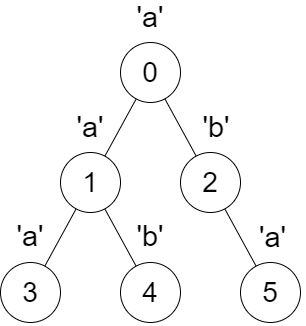 | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,2], s = "aababa" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [true,true,false,true,true,true] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| * Calling `dfs(0)` results in the string `dfsStr = "abaaba"`, which is a palindrome. | ||
| * Calling `dfs(1)` results in the string `dfsStr = "aba"`, which is a palindrome. | ||
| * Calling `dfs(2)` results in the string `dfsStr = "ab"`, which is **not** a palindrome. | ||
| * Calling `dfs(3)` results in the string `dfsStr = "a"`, which is a palindrome. | ||
| * Calling `dfs(4)` results in the string `dfsStr = "b"`, which is a palindrome. | ||
| * Calling `dfs(5)` results in the string `dfsStr = "a"`, which is a palindrome. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| 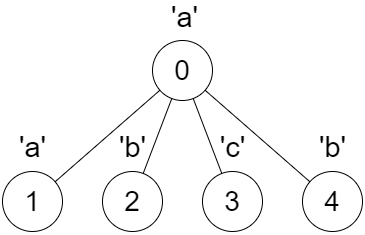 | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** parent = [-1,0,0,0,0], s = "aabcb" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [true,true,true,true,true] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| Every call on `dfs(x)` results in a palindrome string. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `n == parent.length == s.length` | ||
| * <code>1 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `0 <= parent[i] <= n - 1` for all `i >= 1`. | ||
| * `parent[0] == -1` | ||
| * `parent` represents a valid tree. | ||
| * `s` consists only of lowercase English letters. |
26 changes: 26 additions & 0 deletions
26
...va/g3301_3400/s3324_find_the_sequence_of_strings_appeared_on_the_screen/SolutionTest.java
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,26 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3324_find_the_sequence_of_strings_appeared_on_the_screen; | ||
|
|
||
| import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo; | ||
| import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat; | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.List; | ||
| import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; | ||
|
|
||
| class SolutionTest { | ||
| @Test | ||
| void stringSequence() { | ||
| assertThat( | ||
| new Solution().stringSequence("abc"), | ||
| equalTo(List.of("a", "aa", "ab", "aba", "abb", "abc"))); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| @Test | ||
| void stringSequence2() { | ||
| assertThat( | ||
| new Solution().stringSequence("he"), | ||
| equalTo( | ||
| List.of( | ||
| "a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h", "ha", "hb", "hc", "hd", | ||
| "he"))); | ||
| } | ||
| } |
Oops, something went wrong.