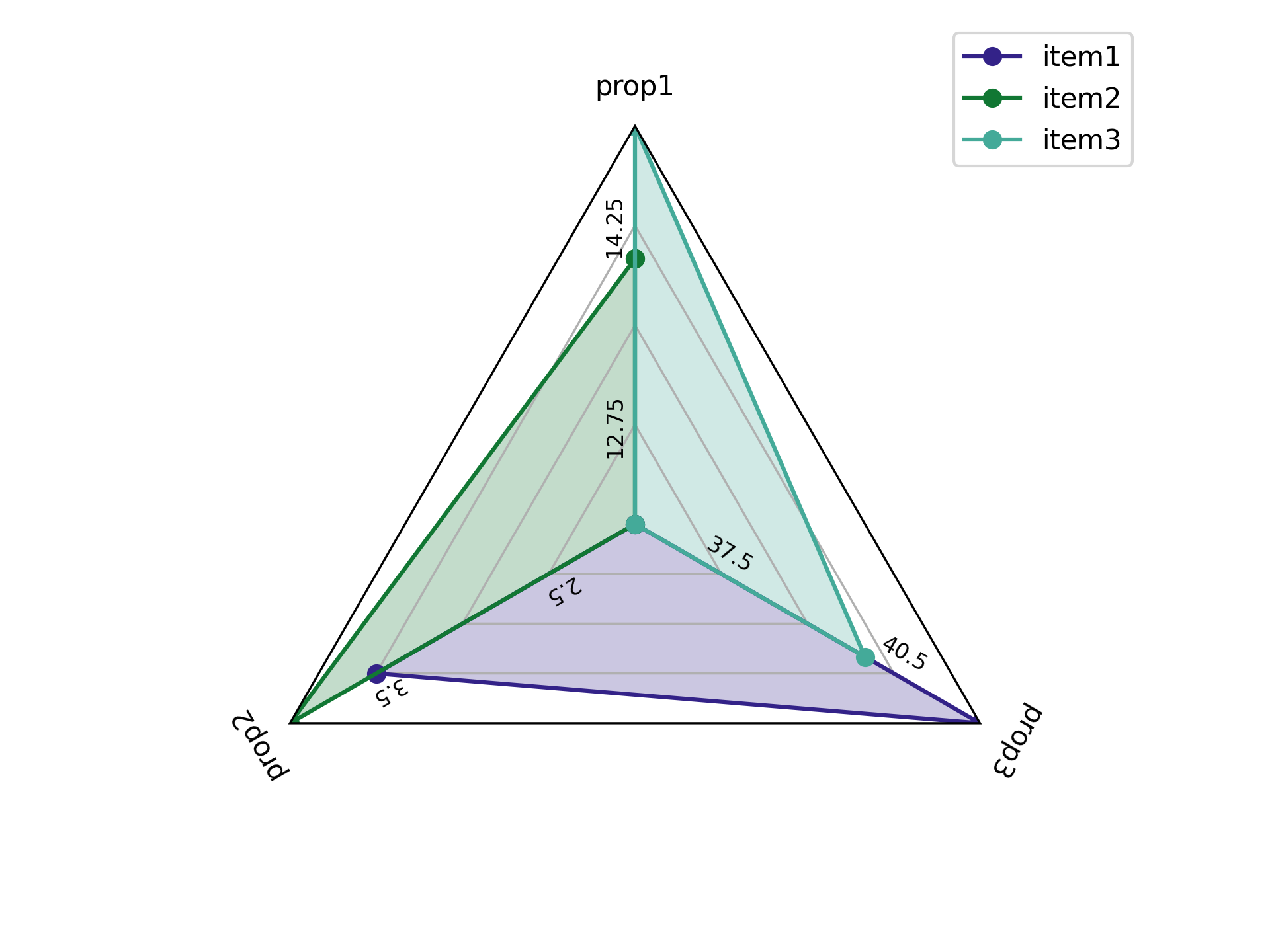
This package creates radar plots. It can generate typical radar plots and plot ranges of values.
Data you want to plot must have a tidy format. For instance, if I wanted to plot three properties (let's say prop1, prop2, and prop3 with values 12, 3.5, and 42 respectively) then you should load a csv file into a pandas dataframe that has the following format:
| property | value | item |
|---|---|---|
| prop1 | 12.0 | item1 |
| prop2 | 3.5 | item1 |
| prop3 | 42 | item1 |
If you wanted to plot several items (e.g., item1, item2, and item3) with different values for the properties, then format the data like this:
| property | value | item |
|---|---|---|
| prop1 | 12.0 | item1 |
| prop2 | 3.5 | item1 |
| prop3 | 42 | item1 |
| prop1 | 14.0 | item2 |
| prop2 | 4.0 | item2 |
| prop3 | 36 | item2 |
| prop1 | 15 | item3 |
| prop2 | 2 | item3 |
| prop3 | 40 | item3 |
Following that formatting scheme, you can plot the data as follows
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import radarplt
# see tables above
df = pd.read_csv('example_data.csv')
fig, ax = radarplt.plot(
df,
label_column="property",
value_column="value",
hue_column="item",
)
legend = ax.legend(loc=(0.9, 0.95))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Resulting in the following image
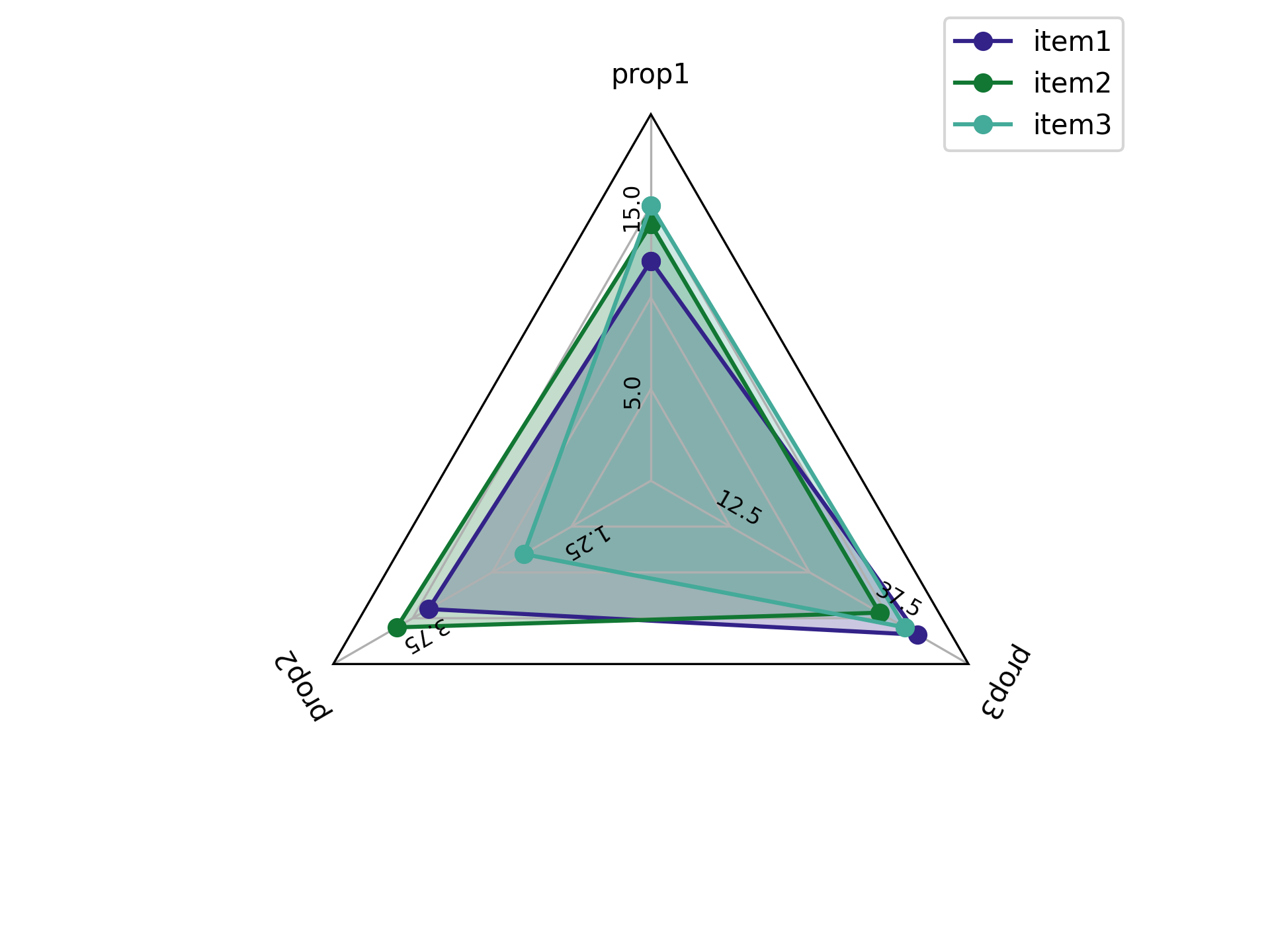
Additional lines are plotted at the .25, .50, and .75 marks on the image. The value at the .25 and .75 line for each property is labeled and values increase/decrease linearly between these points. For instance, the 0.5 mark for property 2 would be 4, the 1 mark would be 6 and the 0 mark would be 2.
Let's say you don't like that the prop2 ranges from 1 to 6. To change
these value ranges create a dictionary of the ranges you want for each property and
pass it to the function via the value_ranges parameter.
For instance:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import radarplt
value_ranges = {
"prop1": [0, 20],
"prop2": [0, 5],
"prop3": [0, 50],
}
# see tables above
df = pd.read_csv('example_data.csv')
fig, ax = radarplt.plot(
df,
label_column="property",
value_column="value",
hue_column="item",
value_ranges=value_ranges,
)
legend = ax.legend(loc=(0.9, 0.95))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Resulting in the following image
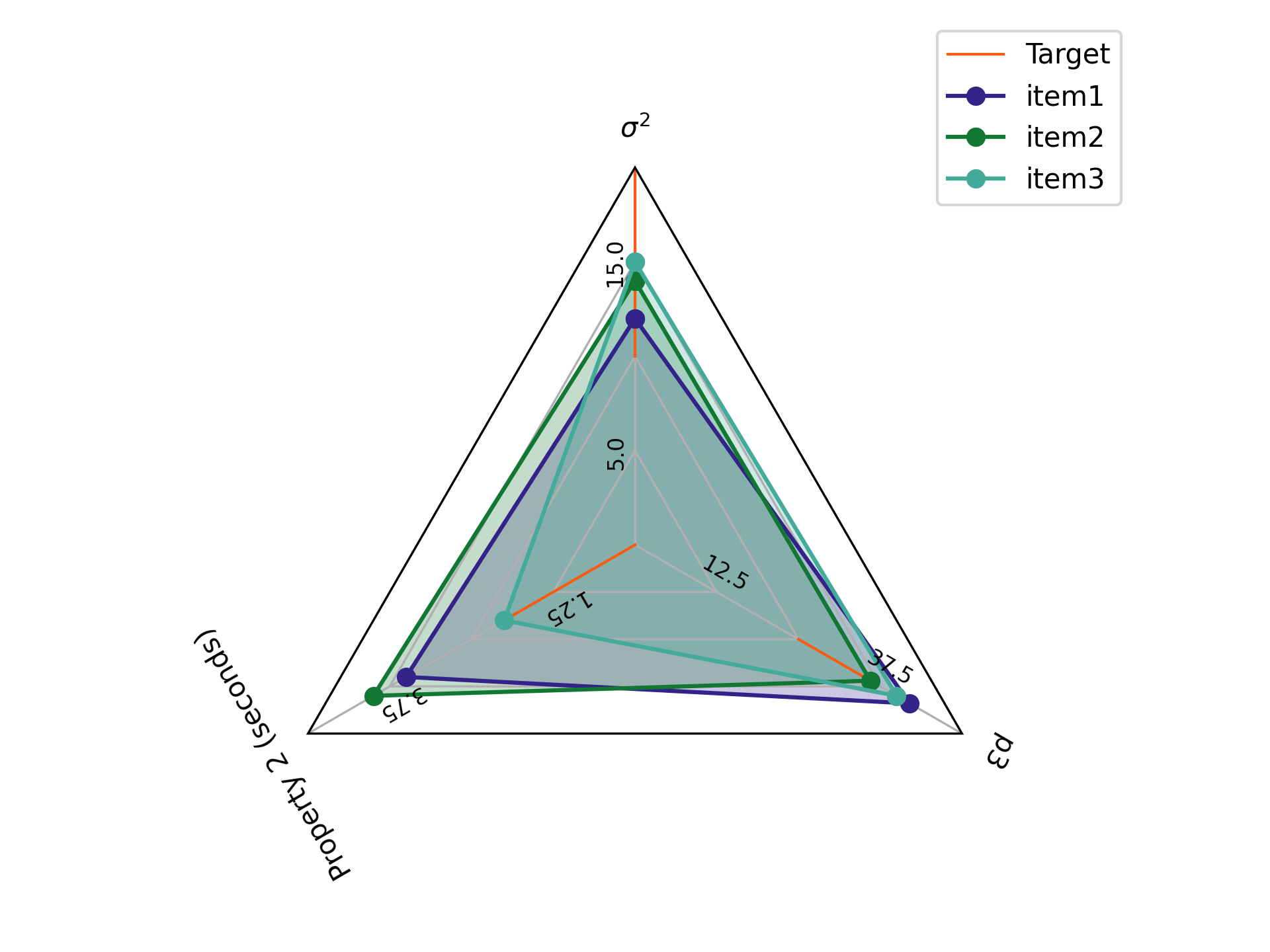
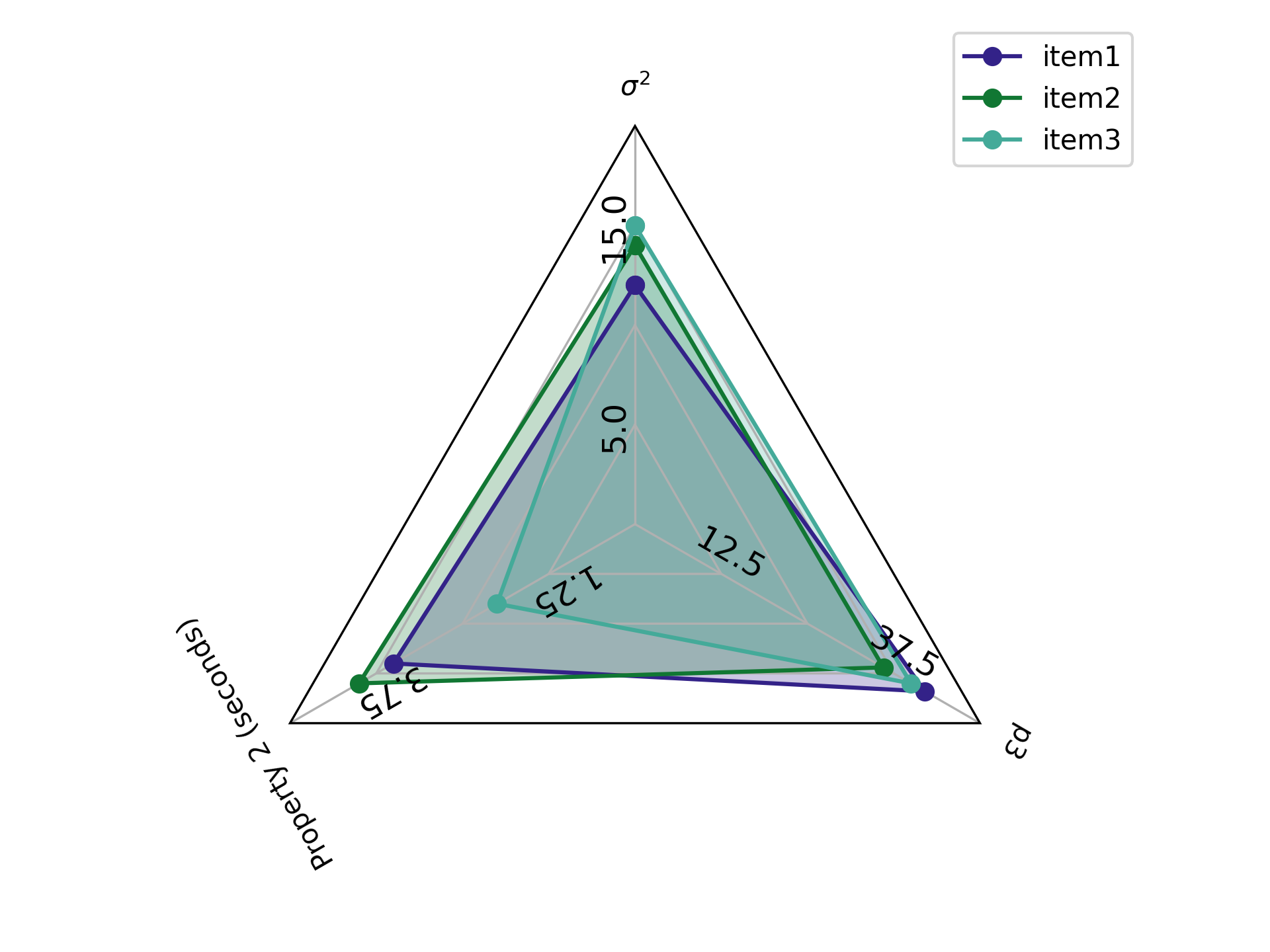
If you don't want the labels for the properties to be the property names,
you can change those as well with the plot_labels parameter.
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import radarplt
value_ranges = {
"prop1": [0, 20],
"prop2": [0, 5],
"prop3": [0, 50],
}
plot_labels = {
"prop1": "$\sigma^{2}$",
"prop2": "Property 2 (seconds)",
"prop3": "p3"
}
# see tables above
df = pd.read_csv('example_data.csv')
fig, ax = radarplt.plot(
df,
label_column="property",
value_column="value",
hue_column="item",
value_ranges=value_ranges,
plot_labels=plot_labels,
# can change fontsize of the numbers in the plot
tick_fontsize=12
)
legend = ax.legend(loc=(0.9, 0.95))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Resulting in the following image
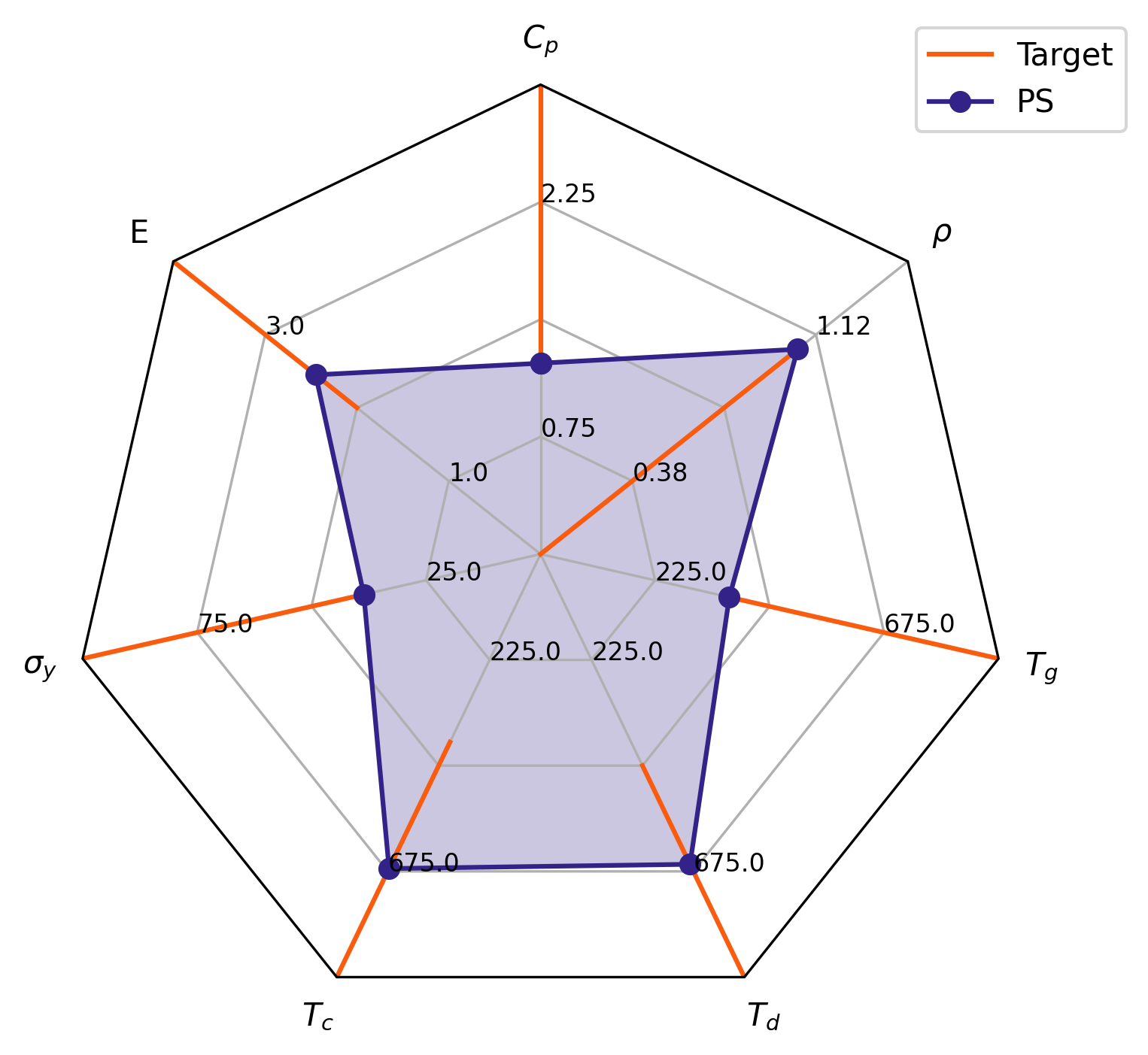
If you want to see if your items' values fall within a certain range, you can add those ranges as well
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import radarplt
target_ranges = {
"prop1": [10, 20],
"prop2": [0, 2],
"prop3": [25, 35]
}
value_ranges = {
"prop1": [0, 20],
"prop2": [0, 5],
"prop3": [0, 50],
}
plot_labels = {
"prop1": "$\sigma^{2}$",
"prop2": "Property 2 (seconds)",
"prop3": "p3"
}
# see tables above
df = pd.read_csv('example_data.csv')
fig, ax = radarplt.plot(
df,
label_column="property",
value_column="value",
hue_column="item",
value_ranges=value_ranges,
plot_labels=plot_labels,
target_ranges=target_ranges
# note, you can also change the radar plot target linewidth
target_linewidth=2
)
legend = ax.legend(loc=(0.9, 0.95))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()