Mavlink to PyG5 and pyEfis ( MAVlink to Python dictionary for pyEfis and pyG5 by Jerry Fat Dec 21, 2023
#"Diagram of MAVLINK to pyG5 and pyEfis Converter with pyG5 and pyEfis changes"
Block Diagram:

from: https://github.com/jerryfat/FIX-Gateway/blob/master/README-MAVPX4.md
screenshot:
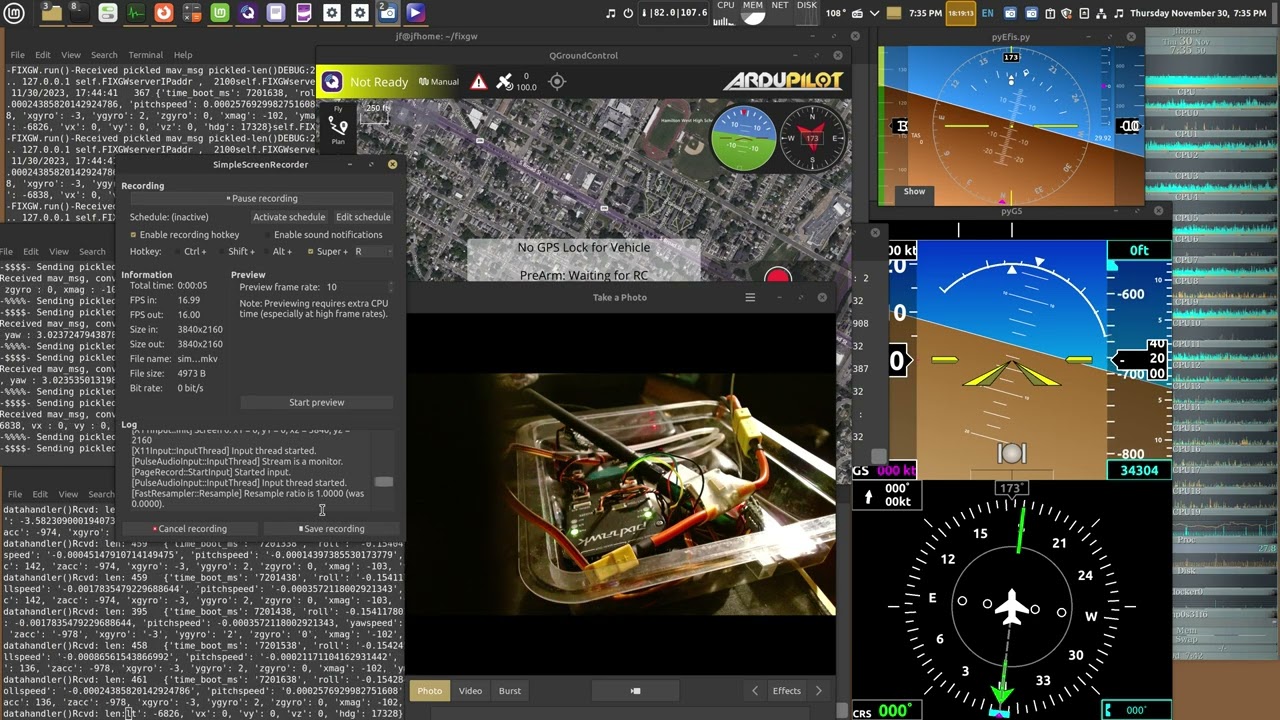
 #"Screenshot Demo pixhawk over 915mhz sik radios, driving my mavlink2PX4G5.py converter and modified pyG5 and added plugin to FIXGW to drive pyEfis"
#"Screenshot Demo pixhawk over 915mhz sik radios, driving my mavlink2PX4G5.py converter and modified pyG5 and added plugin to FIXGW to drive pyEfis"
for MAVLINK converter see: https://github.com/jerryfat/FIX-Gateway/blob/master/README-MAVPX4.md
for MAVLINK converter see this document you are reading:
Ver 3 , Second release Dec 11, 2023 of mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py , added standalone usb joystick support and can fly quad in sitl "
================================================================================================= updated 2024-mar-04
Ver 2 , Second release Dec 11, 2023 of mavlink2PX4G5.py and mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py with added MAVSDK libs
================================================================================================= updated 2023-dec-28
By using these modded (by me) forked repos , a full virtual demo can be run out of the box as above movie mp4 . A complete demo has been tested and working by cloning these repos and running the default.yaml script in FIXGW, This script in FIXGW will startup all the apps (pyG5 FIXGW, pyEfis, PX4 gazebo sitl and my converter code) Tested with PX4 sitl, dronekit sitl, pixhawk over serial, over serial USB, over QGroundcontrol forwarding
These forked repos are modified so they will run a real or demo autopilot using 'mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py' see the FIX-Gateway forked repo dir, new file 'mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py'
The demo runs a PX4 sitl sending mavlink data to pyG5 (modified) and pyEfis via FIXGW server After script tries connecting to a sitl or real autopilot (using mavlink over ip or serial usb ports) the converter code recieves mavlink messages from autopilot and reformats and resends (real or sitl) PX4 or Ardupilot MAVLINK data over IP to forked PyG5 and forked PyEfis (PyEfis via FIXGW server), FIXGW repo modded has new added plugin and config files for FIXGW and also README-MAVPX4G5.md. pyG5 modified by adding a new for now replacement listener code on the same port as xplane. see the README,
in summary the FIXGW fork has changes made to accept and resend MAVLINK msgs. Also added are forked pyEfis and forked pyG5 (whch accepts MAV messages via new listener and datahandler). minor display change to pyEfis app is to use a window after changing 'fullscreen':true in pyEfis/pyefis/main.yaml config file so app runs in a window desktop pc
tested on Ubuntu 22.04 Mint , Python 3.10
$ mkdir newdir create a new dir
$ cd newdir
clone these forked and modified pyEfis and FIXGW and pyG5 repos:
$ git clone https://github.com/jerryfat/FIX-Gateway.git
$ git clone https://github.com/jerryfat/pyEfis.git
$ git clone https://github.com/jerryfat/pyG5.git
$ cd FIX-Gateway/fixgw $ fixgw.py script starts up FIXGW server and pyEfis and pyG5 and converter script and sitl and connects to sitl,qgcs,px4,ardupilot $ python3 ./fixgw.py -v -d -config-file "fixgw/configs/default.yaml" to starrt px4 sitl: sudo docker run --rm -it --env PX4_HOME_LAT=42.397742 --env PX4_HOME_LON=-79.1 --env PX4_HOME_ALT=488.0 jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.14.0 sudo apt install docker
install many python dependencies below dronekit or MAVSDK which doesnt require changing system files in python 3.10 like dronekit dronekit pip install dronekit reprint pip install reprint mavsdk pip install mavsdk pygame pip install // joystick usb support PyQt5 pip install PyQt5 pip install pyavtools pip install geomag pip install PySide6 pip install pyg5 for text to speech: pip install gTTS sudo apt install mpg321
( FIX-Gateway/fixgw/plugins/plugin-mavlink2PX4G5.py )
(..newdir/FIX-Gateway/fixgw/plugins/plugin-mavlink2PX4G5.py)
$ cd FIX-Gateway
$ python3 ./fixgw.py -v -d -config-file "fixgw/configs/default.yaml"
the FIX-Gateway/fixgw/config/default.yaml 'config' file plugin automagically (via xterms) starts up FIX server, pyEfis, pyG5 and 1. sitl if ip addr is 172.17.0.1 or 2. :14550 if qgcs or 3. connects to mavlink source over /dev/serial acmo 4. or usb0
note: from the FIXGW default.yaml config file, the added plugin-mavlink2PX4G5 has config parameters for pyG5 and pyEfis conversion data for mavlink msgs from FIX-Gateway/fixgw/config/default.yaml mavlink2PX4G5: load: yes module: fixgw.plugins.plugin-mavlink2PX4G5 FIXGWserverIPaddr: 127.0.0.1 FIXGWserverIPport: 2100 pyG5SimAddr: 127.0.0.1 pyG5SimPort: 65432 pyefisSimAddr: 127.0.0.1 pyefisSimPort: 2100 pyMAVPX4connect: 127.0.0.1:14445 # /dev/ttyUSB0,57600 usb port sik radio # /dev/ttyACM0,57600 raw usb px connection serial port buffer_size: 1024 timeout: 10.0
$ fixgw $ python3 ./fixgw.py -v -d -config-file "fixgw/configs/default.yaml"
$ python3 ../pyG5/pyG5/pyG5Main.py -m hsi
$ python3 ../pyEfis/pyEfis.py
https://github.com/JonasVautherin/px4-gazebo-headless
$ sudo docker run --rm -it --env PX4_HOME_LAT=42.397742 --env PX4_HOME_LON=-79.1 --env PX4_HOME_ALT=488.0 jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.14.0
$ sudo docker run --rm -it jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.13.2
docker run --rm -it jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.14.0
$ python mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "udp://:14540" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100
$ python3 FIX-Gateway/mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "/dev/ttyUSB0,57600" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100
CLI USEAGE
$ python mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "udp://:14540" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 #works with gazebo px4 headless 1.14 ver $ python mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "serial:///dev/ttyUSB0:57600" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 $ python mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "serial:///dev/ttyUSB0:57600" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 $ python3 FIX-Gateway/mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "/dev/ttyUSB0,57600" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 $ python3 FIX-Gateway/mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "udp://172.17.0.1:14540" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 ?
python3 FIX-Gateway/mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m "172.17.0.1:14540" -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100
python mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m 172.17.0.1:14540 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100
python3 ./mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m /dev/ttyUSB0,57600 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 pixhawk usb
python3 ./mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m /dev/ttyACM0,57600 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 sik radio
python3 ./mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m 172.17.0.1:14550 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 sitl
python3 ./mavlinkMAVSDKdronekitCombined.py -m 127.0.0.1:14445 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 qgcs forwarded
$ sudo tcpdump -i lo -n udp port 2100 'port for watching pyEfis data'
$ sudo tcpdump -i lo -n udp port 65432 'port for watching pyG5 data'
$ sudo docker run --rm -it jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.13.2
if(self.pyMAVPX4connect == "172.17.0.1:14550") or (self.pyMAVPX4connect == "udp://:14540")
if using "172.17.0.1:14550" forwarded from qgcs then docker will start up gazebo sim too
seperately
python3 ./mavlink2PX4G5.py -m /dev/ttyUSB0,57600 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 pixhawk usb
python3 ./mavlink2PX4G5.py -m /dev/ttyACM0,57600 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 sik radio
python3 ./mavlink2PX4G5.py -m 172.17.0.1:14550 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 sitl
python3 ./mavlink2PX4G5.py -m 127.0.0.1:14445 -g 127.0.0.1:65432 -e 127.0.0.1:2100 qgcs forwarded
sudo docker run --rm -it jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.13.2
sudo tcpdump -i lo -n udp port 14550 'data from sitl at 172.17.0.1'
sudo tcpdump -i lo -n udp port 14445 'port on jmavsim headless docker 127.0.0.1:14445 default forwarding by qgcs'
sudo tcpdump -i lo -n udp port 2100 'port for pyEfis data'
sudo tcpdump -i lo -n udp port 65432 'port for pyG5 data'
feb17 update: $ xed /home/jf/Documents/pyqt-crom/venv/pyqt-crom-venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dronekit/init.py #import collections try: # for dronekit after python 3.8 # if using Python 3.10+ import collections.abc from collections.abc import MutableMapping except ImportError: # if using Python 3.10- import collections from collections import MutableMapping also change line 2696 to class Parameters(collections.abc.MutableMapping, HasObservers): from class Parameters(collections.MutableMapping, HasObservers):
dronekit python 3.10 error MutableMapping, collections moved to collections.abc ? ""If I have correctly understood the error, and the evolution between Python 3.9 and 3.10, then I propose the following correction (to be confirmed by the owners of the module): Replace "collections.MutableMapping" by "collections.abc.MutableMapping" (in the "dronekit/init.py" file).""
print("using python 3.10 /usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py") #from _collections_abc import MutableMapping #(no error if python 3.10+) or from collections import MutableMapping (no error if python 3.10-) #/usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py
#import _collections_abc # orig
from _collections_abc import MutableMapping import _collections_abc
print("using unchanged ~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dronekit/init.py") import collections
''' import _collections_abc # orig I had to repair system dronekit if python3.10+ "/home/jf/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dronekit/init.py" import _collections_abc # replace this line with below J.FAT added code below for import MutableMapping dependency dronekit issue starting with python3.10''' try: # for dronekit after python 3.8 # using Python 3.10+ import _collections_abc from _collections_abc import MutableMapping except ImportError: # using Python 3.10- import _collections from _collections import MutableMapping try: collectionsAbc = _collections_abc except AttributeError: collectionsAbc = _collections
============== another error possible too
/usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py
from collections import MutableMapping
ImportError: cannot import name 'MutableMapping' from 'collections' (/usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py)
error
class 'collections.abc.MutableMapping'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/jf/MAVGCSenv144/JerryGCS144.py", line 53, in
from dronekit import connect, VehicleMode, LocationGlobal, LocationGlobalRelative, Command
File "/home/jf/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dronekit/init.py", line 48, in
from collections import MutableMapping
ImportError: cannot import name 'MutableMapping' from 'collections' (/usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py)
fix line in /usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py import _collections_abc and replace with: try: # for dronekit after python 3.8 using Python 3.10+ import _collections_abc from _collections_abc import MutableMapping except ImportError: using Python 3.10- import _collections from _collections import MutableMapping
class '_collections_abc.MutableMapping' print(MutableMapping)
=================================================================================================
repaired local python 3.10 local installed dronekit mavlink /usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py '''import _collections_abc
try: # for dronekit after python 3.8 using Python 3.10+ import _collections_abc from _collections_abc import MutableMapping except ImportError: using Python 3.10- import _collections from _collections import MutableMapping
class '_collections_abc.MutableMapping' print(MutableMapping)'''
=================================================================================================
$ python Python 3.10.12 (main, Jun 11 2023, 05:26:28) [GCC 11.4.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
import dronekit Traceback (most recent call last): File "", line 1, in File "/home/jf/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dronekit/init.py", line 49, in from collections import MutableMapping ImportError: cannot import name 'MutableMapping' from 'collections' (/usr/lib/python3.10/collections/init.py)
results
from collections.abc import MutableMapping (no error if python 3.10+) or from collections import MutableMapping (no error if python 3.10-)
=================================================================================================
DroneKit-Python can be installed on a Linux, Mac OSX, or Windows computer that has Python 2.7 and can install Python packages from the Internet.
It is installed from pip on all platforms:
pip install dronekit
Installation notes:
Mac and Linux require you prefix the command with sudo.
sudo pip install dronekit
On Linux you may need to first install pip and python-dev:
sudo apt-get install python-pip python-dev
Alternatively, the easy_install tool provides another way to install pip:
sudo easy_install pip
=================================================================================================
https://github.com/blauret/pyG5/blob/main/README.md pyG5 depends on pySide6. Due to failure to install pySide6 from pip on Raspberry Pi OS it is not a dependency of the pyG5. As a result it needs to be installed manually.
> sudo pip3 install pyside6
The install PyG5:
> sudo pip3 install pyG5
Running
> pyG5DualStacked
Running on Raspberry Pi it is recommended to install FreeSans fonts in order to be consistent with the rendering on the current main development platform, ie. macOS. Most liked this is solved with:
> sudo apt-get install libfreetype6
pyEfis works within the MakerPlane Avionics System of Systems and requires the FiX Gateway to pass data to and from the display application. It also has dependencies in order for the application to work correctly. MakerPlane currently does not have a single installer however the following is a step-by-step guide on installation on a linux system (such as the Raspberry Pi or Beaglebone from scratch). This installation guide assumes the user is connected to the internet in order to download the required packages. Step 1: Install PyQT The primary dependency is PyQt. Installation instructions can be found here: https://www.riverbankcomputing.com/static/Docs/PyQt5/installation.html On Debian based distributions apt should work. $ sudo apt-get install python3-pyqt5 Step 2: Install pip3 You will need pip3 to be installed for the rest of these dependencies. See https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/ for information on installing pip and it's associated tools. On Debian based distributions you should be able to simply run: $ sudo apt install python3-pip Step 3: Install geomag Geomag calculates magnetic variation for any latitude/longitude/altitude for any date. It is a requirement for pyEfis and the FiX Gateway. $ sudo pip3 install geomag Step 4: Install FiX Gateway FIX-Gateway is the backend data gathering application. Currently the best way to install FIX- Gateway is to download the current archive from the GitHub repository. $ sudo git clone https://github.com/makerplane/Fix-Gateway.git fixgw This will copy all of the files and create a directory on your machine called ‘fixgw’. Next you'll change into the directory that was created and run the setup utility to install the software. $ cd fixgw $ sudo pip3 install . Now you can run FIX-Gateway with the following command. $ sudo ./fixgwc.py Or $ sudo ./fixgw.py These will run the client and server respectively. It may complain about some missing modules but it should still start up. To verify that it is running correctly you can use the installed client program. At the FIX> prompt type status and it should show information about the state of the FIX- Gateway service. You can use the client to read and write data in the data base to change what pyEfis is displaying. See the FIX-Gateway documentation on the GitHub repository for detailed information on how to use FIX-Gateway. https://github.com/makerplane/FIX-Gateway Step 5: Install pyAvTools Next we need to install pyAvTools. This is a Python package which contains aviation related tools and libraries. The installation is similar to FIX-Gateway and can be done by downloading an $ git clone https://github.com/makerplane/pyAvTools.git pyAvTools Next you'll change into the directory that was created and run the setup utility to install the software. $ cd PyAvTools $ sudo pip3 install . Step 6: Install pyEfis Now we can finally install pyEfis itself. $ sudo git clone https://github.com/makerplane/pyEfis.git pyEfis This will copy all of the files and create a directory on your machine called ‘pyEfis’. Next you'll change into the directory that was created and run the setup utility to install the software. $ cd pyEfis Now you can run pyEfis with the following command. $ sudo ./pyEfis.py If all has worked you should get an EFIS displayed on your desktop. (Make sure you have launched fixgw.py first.) Hints and tips on how to configure pyEFIS and the FiX gateway and launch automatically on startup are in the MakerPlane forum. http://www.makerplane.org/forum/ end pyEfis
=======================
https://github.com/jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless#readme Installation of PX4 SITL using gazebo Installation of gazebo px4 SITL if not using pixhawk autopilot or qgcs forwarded to ip:port gazebo headless PX4 simulator (SITL) https://github.com/jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless The Docker images resulting from this repo are available on Docker Hub.
Note that the following commands are referring to the latest supported release of PX4, which is currently v1.14.0. Run in BROADCAST mode:
In this mode, the simulator will be available from your host (e.g. run the following command, and QGroundControl running on your computer will connect automatically).
docker run --rm -it jonasvautherin/px4-gazebo-headless:1.14.0
In this configuration, the container will send MAVLink to the host on ports 14550 (for QGC) and 14540 (for e.g. MAVSDK).
https://linuxiac.com/how-to-install-docker-on-linux-mint-21/ Step 1: Install Prerequisites
First, run the two commands below to update the package index and install the prerequisite necessary to add and use a new HTTPS repository.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg
Once operations are completed, you can move to the next section, where we’ll add the Docker’s repo GPG key and repo itself to our Linux Mint 21 system. Step 2: Add Docker’s Official GPG Key
Next, import the Docker GPG repository key to your Mint system. This security feature ensures that the software you’re installing is authentic.
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker.gpg ()Add Docker’s repo GPG key.) Notice that the command produces no output.
Step 3: Add Docker Repo to Linux Mint 21
After importing the GPG keys, we’ll add the official Docker repository to our Linux Mint 21 system. This implies that the update package will be made available with the rest of your system’s regular updates if a new version is released.
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu jammy stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Add the official Docker repository to Linux Mint 21. Add the official Docker repository to Linux Mint 21.
As with the previous command, its execution produces no output.
Next, refresh the package list.
sudo apt update
Update the package base. Update the package base.
This command updates the package index on our system. As you can see, the newly added Docker repository is now available and ready to be used. Step 4: Install Docker on Linux Mint 21
Finally, run the below command to install the latest up-to-date Docker release on Linux Mint.
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
Install Docker on Linux Mint 21. Install Docker on Linux Mint 21.
This installs the following Docker components:
docker-ce: The Docker engine itself.
docker-ce-cli: A command line tool that lets you talk to the Docker daemon.
containerd.io: A container runtime that manages the container’s lifecycle.
docker-buildx-plugin: A CLI plugin that extends the Docker build with many new features.
docker-compose-plugin: A configuration management plugin to orchestrate creating and managing Docker containers through compose files.
That’s all! Docker should now be installed; the service started and enabled to start automatically on boot.
In addition, you can check the Docker service status using the following:
sudo systemctl is-active docker
Check the status of the Docker service. Check the status of the Docker service. Step 5: Verify the Docker Installation
Now let’s check if everything with our new Docker installation works properly. For this purpose, we will run a simple application called “hello-world.”
sudo docker run hello-world
Docker successfully installed, up & running on Linux Mint 21. Docker successfully installed, up & running on Linux Mint 21.
Enabling Non-root Users to Run Docker Commands
So far, we have successfully installed Docker on your Linux Mint 21 system.
However, only root and users with sudo privileges can execute Docker commands by default, which can be a security concern. In other words, if you attempt to run the docker command as a regular user without prefixing it with sudo, you’ll get an error message like this: Docker permission denied. Docker permission denied.
==============================================
run Docker commands as a non-root user, you must add your user to the docker group. To do that, type in the following:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
In the above command, ${USER} is an environment variable that holds your username. To apply for the new group membership, reboot your Mint system. You can then execute docker commands without prefixing them with sudo. Run the docker command as a regular user. Run the docker command as a regular user.
This approach can reduce the security risks associated with Docker while enabling non-root users to take advantage of its powerful capabilities. Conclusion
Installing Docker on Linux Mint 21 can initially seem daunting, but with the step-by-step guide provided, it is a relatively straightforward process. Following the steps outlined in the guide, you can successfully install Docker on your Linux Mint 21 machine and start reaping the benefits of containerization.
So, what are you waiting for? Start experimenting with Docker today and see how it can revolutionize how you build and deploy applications.
Let me know if you have any questions or suggestions, and I’ll be happy to follow up with you. Happy dockering!
To learn more about Docker, check out the official Docker documentation. Bobby Borisov Bobby Borisov
Bobby, an editor-in-chief at Linuxiac, is a Linux professional with over 20 years of experience. With a strong focus on Linux and open-source software, he has worked as a Senior Linux System Administrator, Software Developer, and DevOps Engineer for small and large multinational companies.
Think You're an Ubuntu Expert? Let's Find Out!
Put your knowledge to the test in our lightning-fast Ubuntu quiz! Ten questions to challenge yourself to see if you're a Linux legend or just a penguin in the making. POPULAR GNOME's Giant Leap: Open-Source Project Receives €1 Million Boost GNOME’s Giant Leap: Open-Source Project Receives €1 Million Boost Fedora 39 Released, It Is All about GNOME 45 Fedora 39 Released, It Is All about GNOME 45 3 Best Linux Terminal Editors Perfect for Beginners 3 Best Linux Terminal Text Editors Perfect for Beginners How To Protect SSH with Fail2Ban: A Beginner's Guide How To Protect SSH with Fail2Ban: A Beginner’s Guide Ubuntu 23.10 Ubuntu 23.10 “Mantic Minotaur” Released, Here’s What’s New Subscribe to our newsletter!