A project completed for a class during my undergraduate studies to implement two different types of navigation algorithms with visualisation. The goal was to use the visualisation to be able to explain given algorithms to first year students during lectures while demonstrating them in real time.
Both algorithms are implemented in MATLAB. Simply add the directory to MATLAB's path or set it as the current directory and run the following:
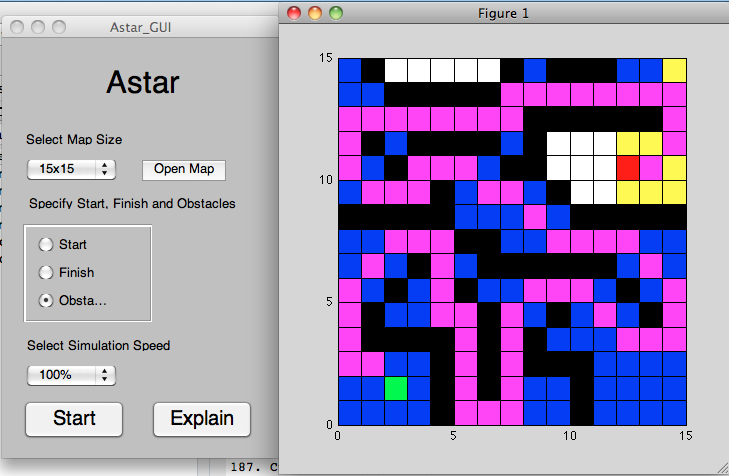
- A-star: Astar_GUI
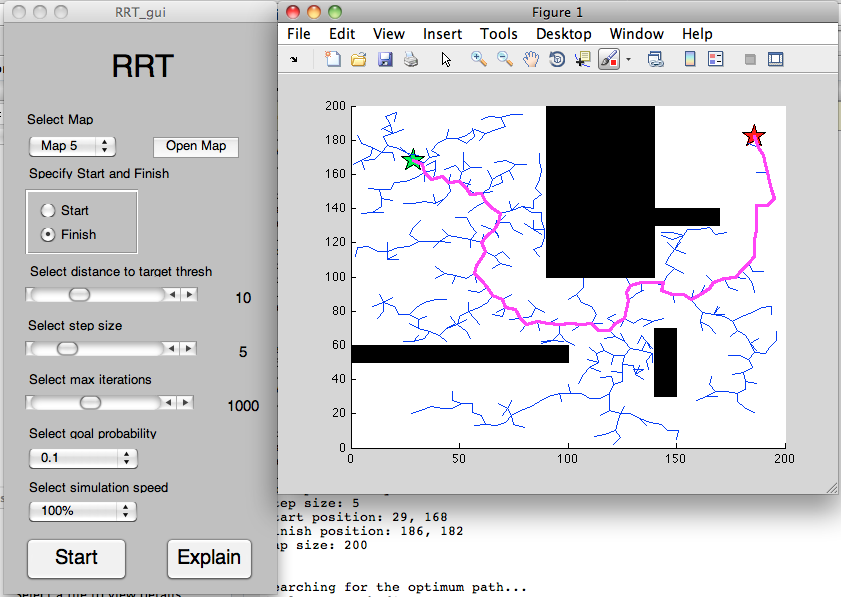
- RRT: RRT_gui
More detailed instructions can be found under "Explain" button on the GUI of each algorithm.
One of the main algorithms falling into the Best-first Graph Search category. It is a relatively simple algorithm, which knows the exact location of the robot and target coordinates that it is trying to reach. At each step, surrounding area is analysed to see if it is suitable for driving - no obstacle is present there. If so, a score for each possible step is calculated, which consists of distance from the current position to the new one and distance from new position to the goal. Calculation does not take into consideration any obstructions on the way, it analyses straight line distance. Next step is made by going to the position, which has the lowest score, thus is closest to the goal.
Using this type of search the first time in the environment might be a bit inefficient as the robot can wonder around until the correct path is found, but once the goal is reached it always knows the fastest route as long as obstacles do not change. In addition, for real world environment, costs can be adjusted according to surface. For example, driving on bumpy grass will be slower than on smooth tarmac, so grass spot would have higher cost, because in some cases it is quicker to take a bit longer route, but on better surface. Also, some robots might want to avoid sand if there is any alternative path, because it can dig in wheels getting it stuck.
RRT is a probabilistic based search algorithm. In some cases, using random choices can be very efficient. This idea was incorporated in probabilistic based search algorithms like Real-Time Randomised Path Planning (RRT) method. It is also using heuristics to move towards the goal, but that happens only every 10th of a step or so. Other times it just simply goes random direction, building up tree-like structure. This type of algorithms are based on the idea, that often there are many obstacles between starting point and the goal and much time can be wasted by trying to go straight towards the target and hitting dead ends. Instead, larger area around is being searched, thus alternative path can be quickly found. Main advantages of RRT are: uniformly distributed search - it covers all area, always moves towards the goal (not necessarily every step) and the simplicity of it provides high execution speed.