Deliverable 2: Written Analysis of the Results Purpose Since Steve analyzed a limited dataset earlier and is happy with his outcome, he wants to analyze a higher number of stocks. This may increase the amount of time it takes the analysis to produce results. But there is a way to maintain or, even better, improve it! I will now take advantage of improving the workbooks’ efficiency by refactoring the VBA coding. To ensure that I am going in the right direction, I will compare the new execution time with the original workbook. Results: Refactoring the Code To make my code more efficient, I created 3 new arrays: -tickerVolumes(12) to hold volume -tickerStartingPrices(12) to hold starting price -tickerEndingPrices(12) to hold ending price The above 3 arrays store performance data for each stock when a for loop runs analysis on them. The tickers array that I created in the original establishes a ticker symbol that can be called on for each stock. Matching the 3 performance arrays with the ticker array is done by using a variable called the tickerIndex. Now that I have created these arrays, I can use Nested For Loops and variables to loop through the data and complete the analysis. See the Refactored vs Original coding below.
Summary:
Let’s see if the workbook has handled increasing the number of stocks analyzed.
Execution time
With the original code it ran in 0.6601563 seconds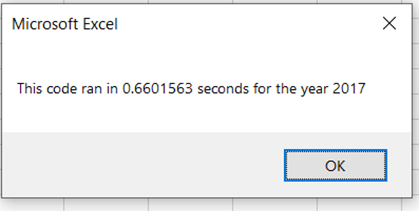
With refactored code, it ran in 0.1328125 secs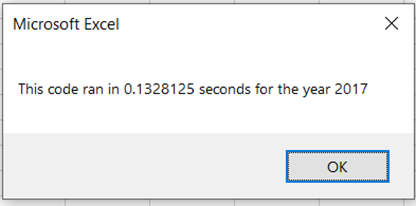
80% efficiency
For 2018:
The original code ran in 0.6445313 secs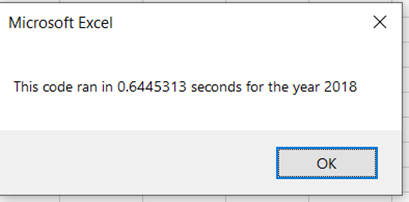
82% efficiency
The refactored code ran in 0.1132813 secs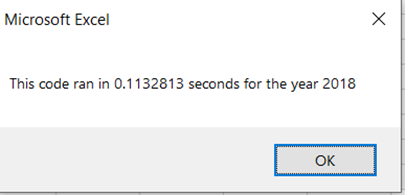
What are the advantages and disadvantages of refactoring the code Deliverable 2 written Analysis.docx
Refactoring code makes it more efficient and saves time. An 80%-82% reduction in execution time can be huge if analyzing thousands of rows of data. A huge risk with refactoring is that the errors may destroy an already working code. It is advisable to run the data first on the limited data set and then expand to a huge data set by saving and debugging the errors.
**How do these pros and cons apply to refactoring the original VBA script **
Refactoring is easier to understand and perhaps easier to maintain since it is easy to put in more functionality as needed. Refactoring, when necessary, preserves a clean and maintainable architecture in evolving code. It also generally reduces bug count. Con, it takes time way from development. It can create cascaded update issues in code that is a client of the refactored code. Sometimes we may underestimate the amount of time for refactoring and end up working on it longer than planned.

