-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Using Contexts
Since MagicalRecord 2.3 the logic around the NSManagedObjectContext did change quite a bit.
When working with Core Data, you will need to deal with NSManagedObjectContext.
Nicely, MagicalRecord initializes, provides and uses a default NSManagedObjectContext object throughout your app.
This default context operates on the main thread, and is great for simple, single-threaded apps.
All this means that if you want to retrieve an entity on the main thread you can directly call the MagicalRecord functions. The default context will be used:
Plane.MR_findFirst()
This will be the same as:
Plane.MR_findFirstInContext(NSManagedObjectContext.MR_defaultContext())
Read the dedicated page to fetch entities between contexts.
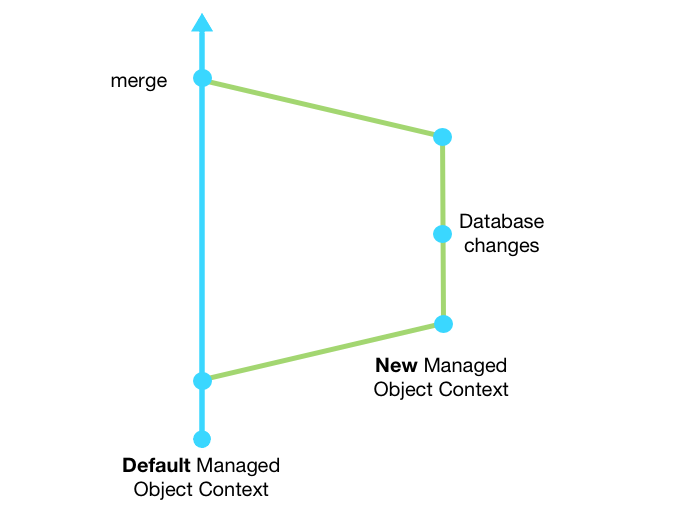
All saving functions provided are executed on a background thread. This way, your database management will not impact the UI performance of your app.
Those functions provide a new NSManagedObjectContext. This context must be used to create, update or delete an entity.
In the end this context will be saved ( or 'merge' ) into the default one.
To learn more about saving in context, read the dedicated page: Save And Update Entities.
In case you would like to create or manually deal with NSManagedObjectContext for non-main threads usage, please refer to the official documentation.
Technically you could create, save or delete entities on the main thread using the default context.
But this is highly not recommended as it might slow down your application, and that your changes will never be saved to the persistent store.