Node.js version management: no subshells, no profile setup, no convoluted API, just simple.
Want to install Node nightly releases? Try this!
(Unfortunately n is not supported on Windows yet. If you're able to make it work, send in a pull request!)
Since you probably already have node, the easiest way to install n is through npm:
$ npm install -g n
Alternatively, you can clone this repo and
$ make install
to install n to bin/n of the directory specified in the environment variable $PREFIX, which defaults to /usr/local (note that you will likely need to use sudo). To install n in a custom location (such as $CUSTOM_LOCATION/bin/n), run PREFIX=$CUSTOM_LOCATION make install.
Once installed, n installs node versions to subdirectory n/versions of the directory specified in environment variable N_PREFIX, which defaults to /usr/local; the active node/iojs version is installed directly in N_PREFIX.
To change the default to, say, $HOME, prefix later calls to n with N_PREFIX=$HOME or add export N_PREFIX=$HOME to your shell initialization file.
Additionally, consider third-party installer n-install, which allows installation directly from GitHub; for instance,
curl -L https://git.io/n-install | bash
sets both PREFIX and N_PREFIX to $HOME/n, installs n to $HOME/n/bin, modifies the initialization files of supported shells to export N_PREFIX and add $HOME/n/bin to the PATH, and installs the latest stable node version.
As a result, both n itself and all node versions it manages are hosted inside a single, optionally configurable directory, which you can later remove with the included n-uninstall script. n-update updates n itself to the latest version. See the n-install repo for more details.
Simply execute n <version> to install a version of node. If <version> has already been installed (via n), n will activate that version.
A leading v is optional, and a partial version number installs the newest matching version.
$ n 4.9.1
$ n 10
$ n v8.11.3
Execute n on its own to view your currently installed versions. Use the up and down arrow keys to navigate and press enter to select. Use q or ^C (control + C) to exit the selection screen.
If you like vim key bindings during the selection of node versions, you can use j and k to navigate up or down without using arrows.
$ n
node/4.9.1
ο node/8.11.3
node/10.15.0
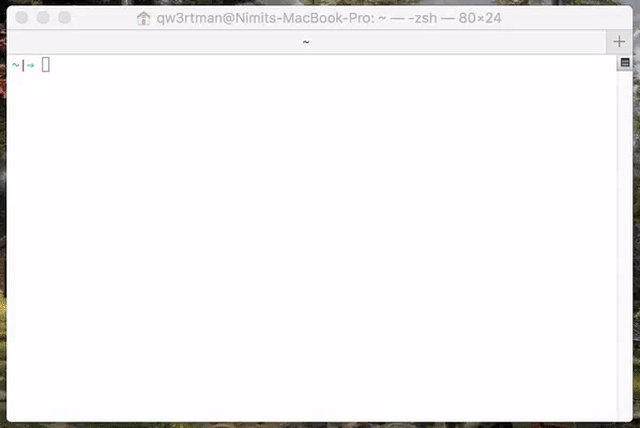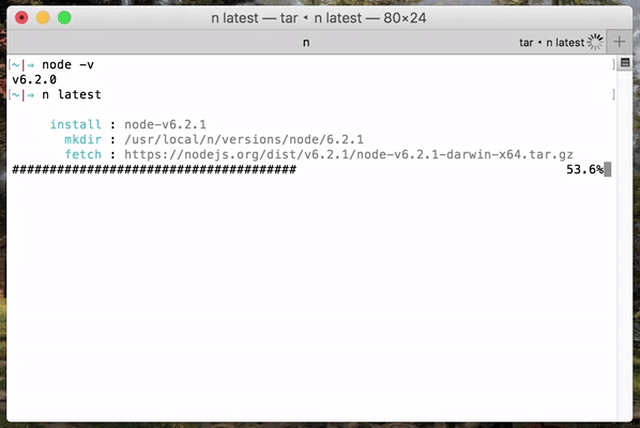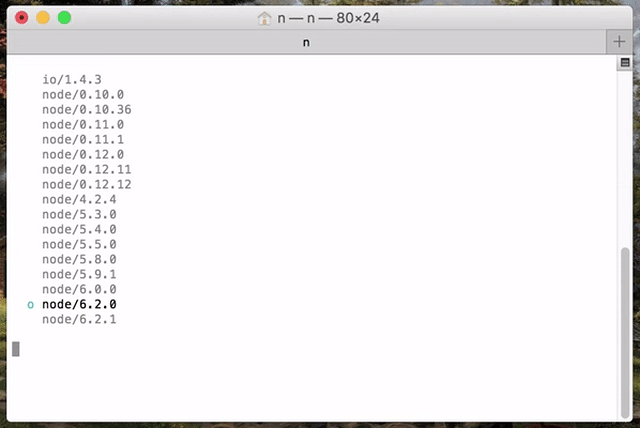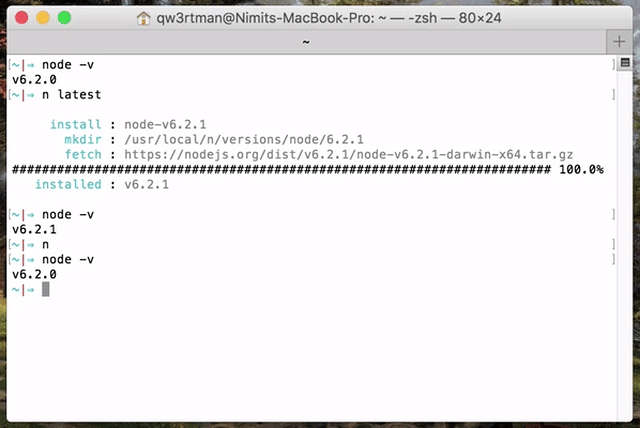
Use or install the latest official release:
$ n latest
Use or install the latest LTS official release:
$ n lts
Remove some versions:
$ n rm 0.9.4 v0.10.0
Alternatively, you can use - in lieu of rm:
$ n - 0.9.4
Removing all versions except the current version:
$ n pruneWhen running multiple versions of node, we can target
them directly by asking n for the binary path:
$ n bin 0.9.4
/usr/local/n/versions/0.9.4/bin/node
Or by using a specific version through n's use sub-command:
$ n use 0.9.4 some.js
Flags also work here:
$ n as 0.9.4 --debug some.js
After switching Node.js versions using n, npm may not work properly. This should fix it (thanks @mikemoser!):
$ curl -0 -L https://npmjs.com/install.sh | sudo shsudo may not be required depending on your system configuration.
Output can also be obtained from n --help.
Usage: n [options/env] [COMMAND] [args]
Environments:
n [COMMAND] [args] Uses default env (node)
Commands:
n Output versions installed
n latest Install or activate the latest node release
n -a x86 latest As above but force 32 bit architecture
n lts Install or activate the latest LTS node release
n <version> Install node <version>
n use <version> [args ...] Execute node <version> with [args ...]
n bin <version> Output bin path for <version>
n rm <version ...> Remove the given version(s)
n prune Remove all versions except the current version
n --latest Output the latest node version available
n --lts Output the latest LTS node version available
n ls Output the versions of node available
Options:
-V, --version Output current version of n
-h, --help Display help information
-q, --quiet Disable curl output (if available)
-d, --download Download only
-a, --arch Override system architecture
Aliases:
which bin
use as
list ls
- rm
stable lts
If you would like to use a project other than the official Node.js project, you can use the special n project [command] which allows you to control the behavior of n using environment variables.
For example, to grab the latest io.js version:
PROJECT_NAME="iojs" PROJECT_URL="https://iojs.org/dist/" n project latest
Required Variables:
PROJECT_NAME: The name the project will be stored underPROJECT_URL: The location to download the project from. Note, this must follow the same format as the Node.js repos
Optional Variables:
HTTP_USER: The username if thePROJECT_URLis protected by basic authenticationHTTP_PASSWORD: The password if thePROJECT_URLis protected by basic authenticationPROJECT_VERSION_CHECK: Many custom projects keep the same version number as the Node.js release they are based on, and maintain their own separate version in process. This allows you to define a JavaScript variable that will be used to check for the version of the process, for example:process.versions.node
By default n picks the binaries matching your system architecture, e.g. n will download 64 bit binaries for a 64 bit system. You can override this by using the -a or --arch option.
Download and use latest 32 bit version of node:
$ n --arch x86 latest
Download and use 64 bit LTS version of node for older Mac Intel Core 2 Duo systems (x86 image is no longer available but x64 runs fine):
$ n --arch x64 lts
n installs versions to /usr/local/n/versions by default. Here, it can see what versions are currently installed and activate previously installed versions accordingly when n <version> is invoked again.
Activated versions are then installed to the prefix /usr/local, which may be altered via the N_PREFIX environment variable.
To alter where n operates, simply export N_PREFIX.
n does not work on Windows at the moment. Pull Requests are appreciated.
If you are searching for the latest version of n below 2.x.x, check out the branch 1.x.x.
- Nimit Kalra – @qw3rtman
- Ted Gaydos – @tedgaydos
- Travis Webb – @tjwebb
Please Read Contributing Docs
(The MIT License)
Copyright (c) 2014 TJ Holowaychuk <tj@vision-media.ca>
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the 'Software'), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED 'AS IS', WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.