Fraktal is a software library for procedural function-based representations (FRep) aimed at facilitating computer vision and machine learning research. It is designed to aid research in using the FRep in such applications as:
- 3D reconstruction
- Inverse rendering / procedural modeling / program synthesis
- Learning generative models
- Generating ground-truth synthetic datasets
The core library is a GPU-accelerated FRep evaluator bundled with several utilities:
- Procedures for common primitives, transformations and CSG operators
- Procedures for surface normal evaluation and accelerated ray-surface intersection
- Physically-based path tracer for FReps
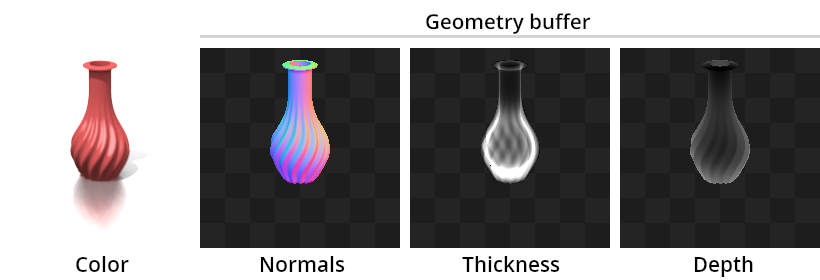
- Multi-target (Depth + Normals + Thickness) rendering
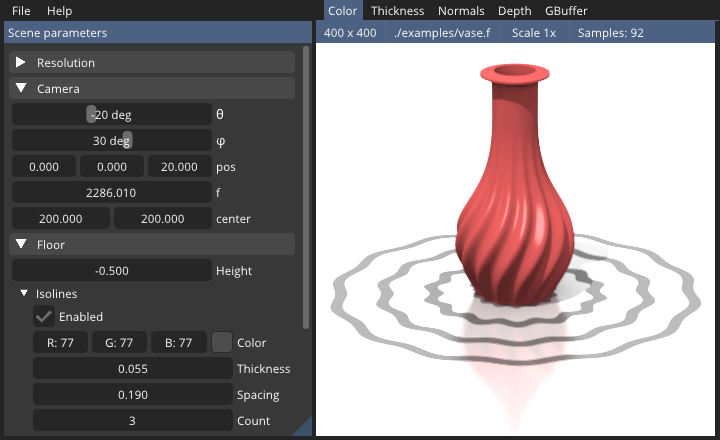
Fraktal also comes with a graphical application, which lets you visualize and live-edit FReps or adjust camera and scene parameters. The bundled renderer uses a novel de-noising algorithm that lets you create publication-quality figures quickly.
The core library provides GPU-acceleration on the major hardware platforms: NVIDIA, AMD and Intel integrated graphics. At minimum, you need a GPU, a driver with OpenGL 3.1 support (most platforms, including MacBook laptops, meet these requirements) and glfw installed.
The interactive FRep viewer:
Note that the core library is not limited to evaluating the function densely over an image, but can also be run on arbitrary input sets, such as point clouds or sparse pixels.
The core library can be compiled from source into a static or dynamic library using the appropriate build script for your platform:
- Windows: build_static_lib.bat or build_dynamic_lib.bat
- Linux/MacOS: make
The GUI application can be compiled from source using the appropriate build script for your platform:
- Windows: build_gui.bat
- Linux/MacOS: make
Python bindings can be found in the python directory. See that directory's readme for installation instructions.
A Function Representation (FRep) is a function that converts a 3D coordinate to a scalar, whose sign determines whether the given point is inside or outside the surface. In C, it would have the following declaration:
float f(float x, float y, float z)
In general f can be an arbitrary computer program, using conditionals, loops, variable declarations and mathematical expression. However, the FRep framework supports a number of high-level modeling operations (which are again defined procedurally), such as
- Geometric primitives
- Boolean combination
- Rigid-body transformation
- Repetition and mirroring
- Bending, twisting and other deformations
These can be combined hierarchically to construct complex shapes or define a library of higher-level primitives that can be reused in other models.
To learn more about FReps, and procedural modeling in general, I recommend the following resources:
- Wikipedia
- HyperFun
- A. Pasko, V. Adzhiev, A. Sourin and V. Savchenko. Function Representation in Geometric Modeling: Concepts, Implementation and Applications. 1995.
- J. Snyder and J. Kajiya. Generative Modeling: A Symbolic System for Geometric Modeling. 1992.