-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 88
TTL Data Diode (breadboard)
The hardware data diode is a device that allows transfer of data from one computer to another, while physically blocking transfer of data to the opposite direction. The data diode blocks all covert return channels of the link in question, even in the case where the serial interfaces (and their connected pins) are compromised, and re-programmed to send and receive data in the opposite direction.
The design of the data diode and this document are based on USB-TTL-USB Data Diode (version 16.10.a) by pseudonym Sancho_P. The design is modified and used under GNU FDL v1.3.
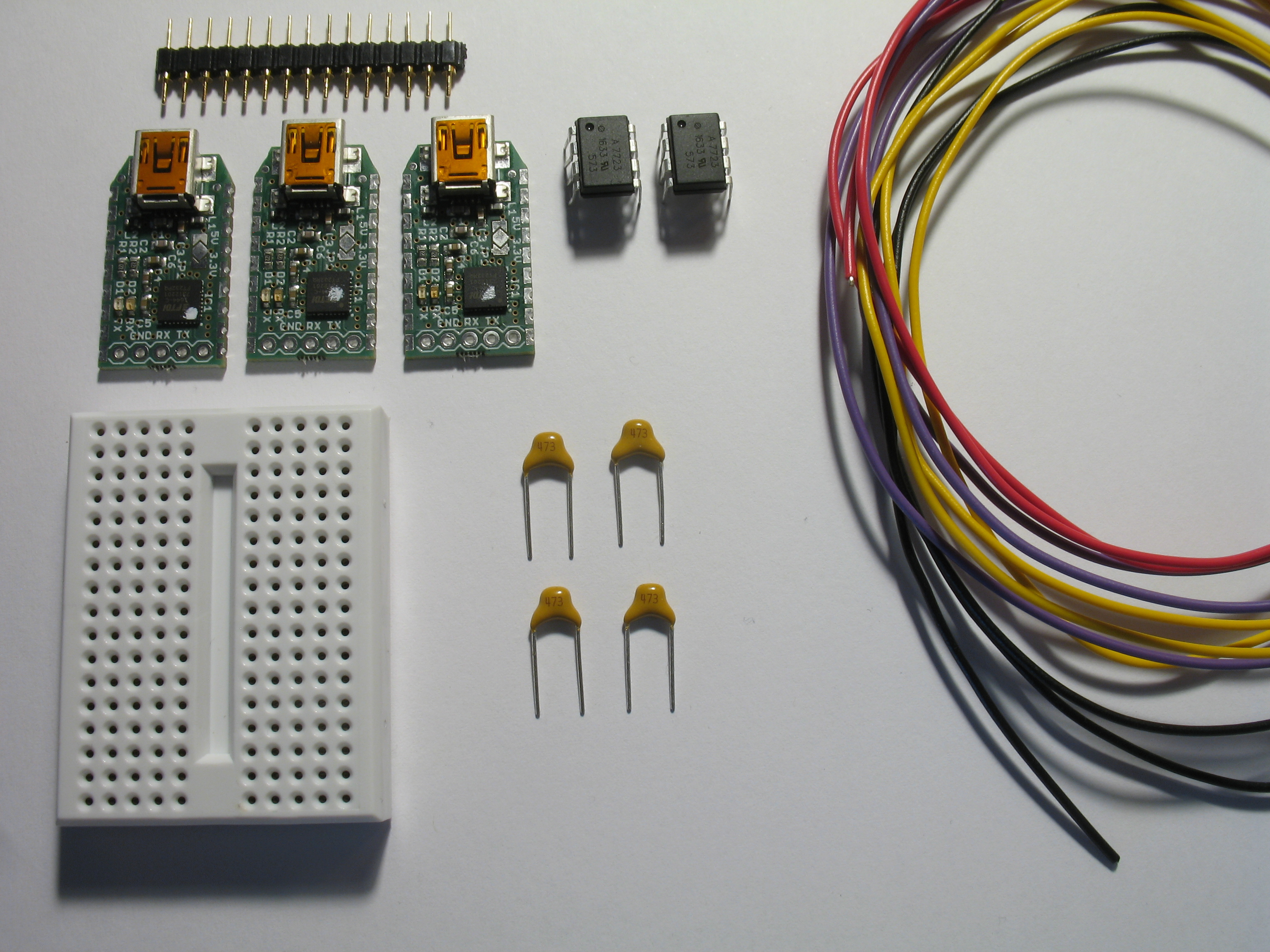
| PCS | Item |
|---|---|
| 1 | Breadboard |
| 3 | 5x1 male header (2.54mm) |
| 2 | HCPL-7723 optocoupler |
| 4 | 0.01-0.1μF capacitor |
| 9 | male-to-male jump wiring |
| 3 | TTL-232R-5V USB-to-TTL adapter |
| 3 | USB 2.0 A - Mini-B cable |
| jump wiring |
As the original TTL-adapter is no longer available, the instructions below are informative only. Please refer to the schematics of the TTL-adapter to see how to connect the male-to-male jump wiring between the data diode and the TTL adapter.
As optocoupler is an integrated circuit the internal functionality of which is hard to audit, to avoid interdiction by nation states, the user should avoid buying the component online.
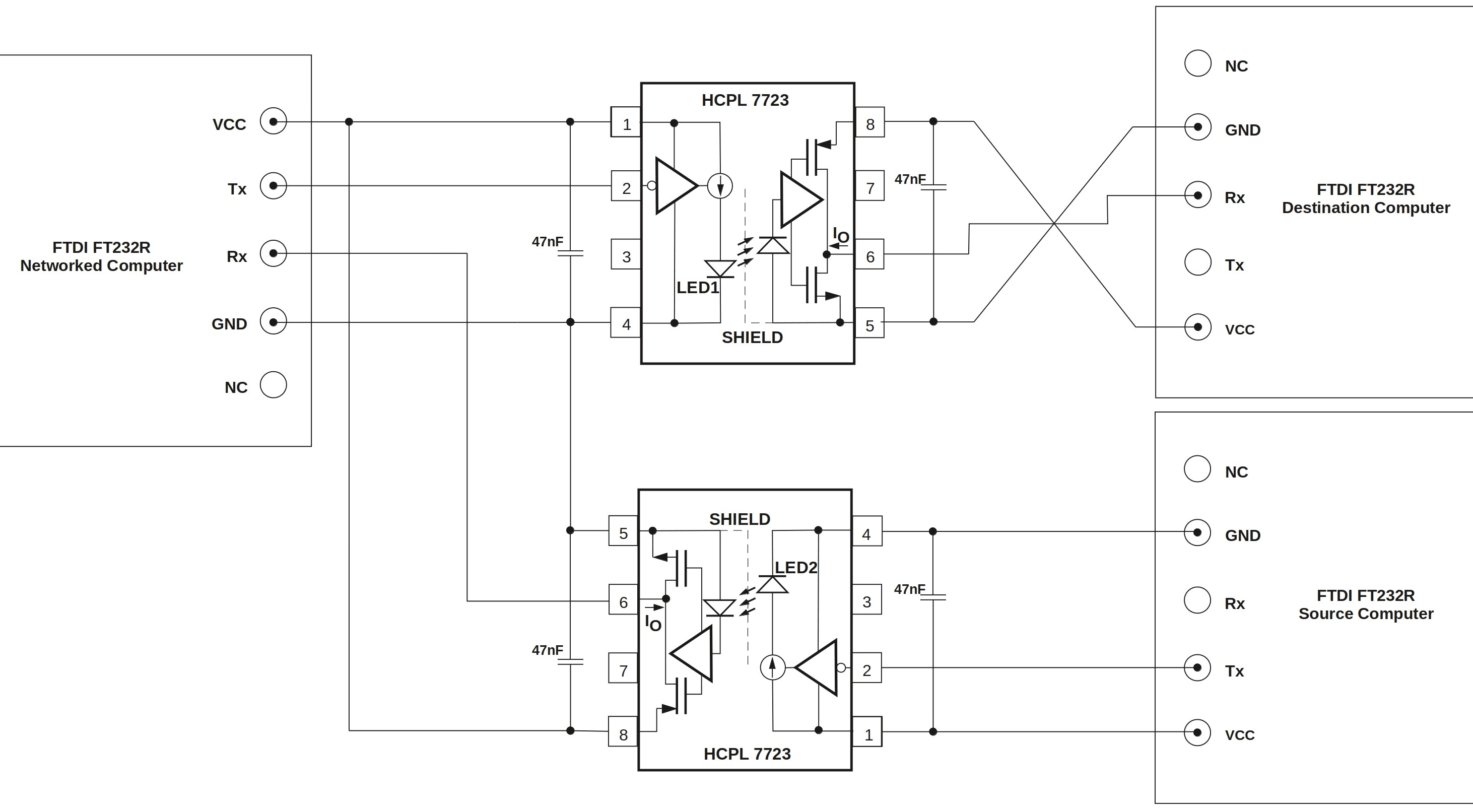
The circuit diagram for the data diode is as follows
Start by cutting the male header strip into three pieces with five contact points each. Solder one male header strip to each USB-to-TTL adapter. You can use the optocouplers and breadboard to support the adapter and pins when soldering.
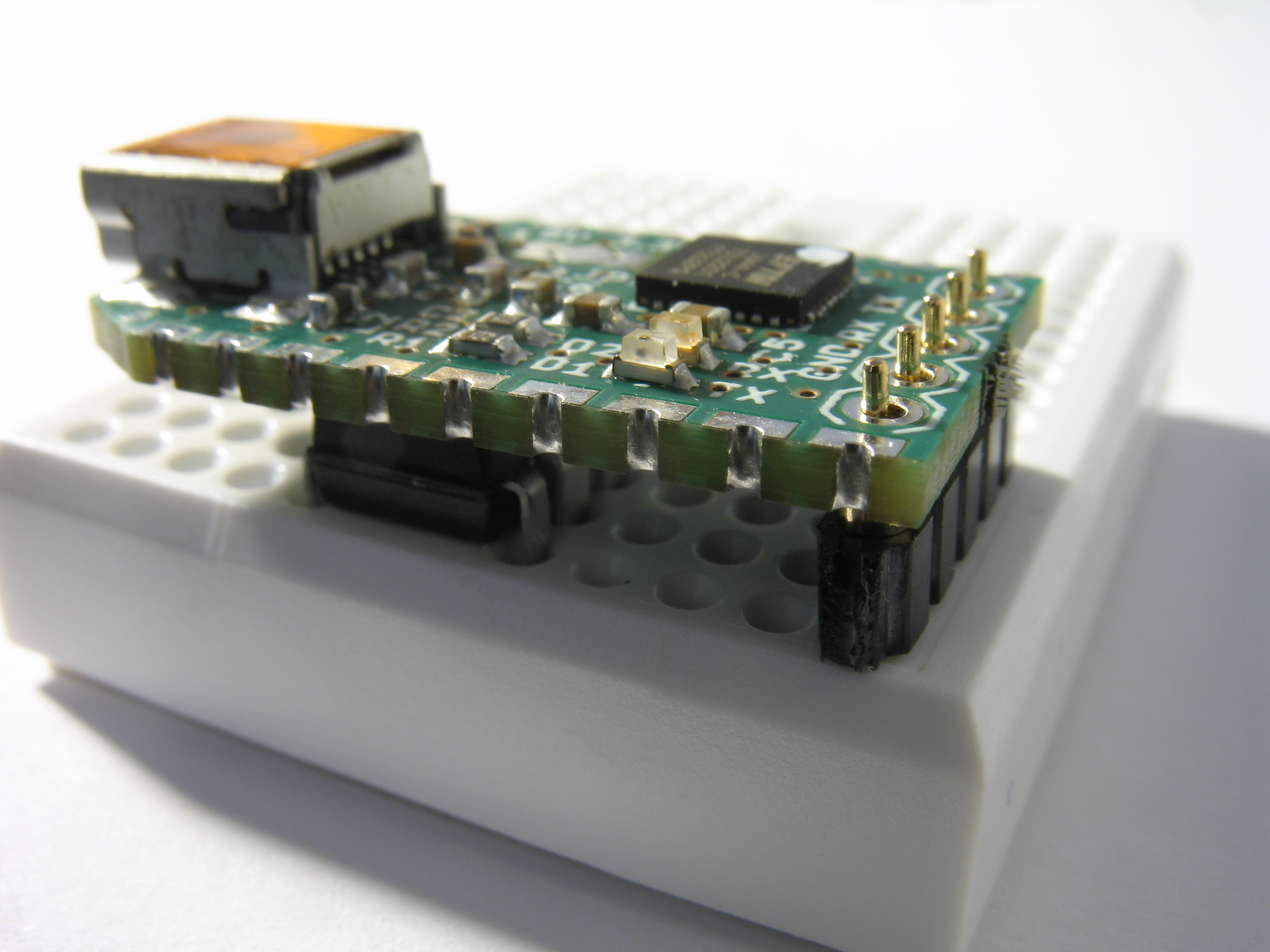
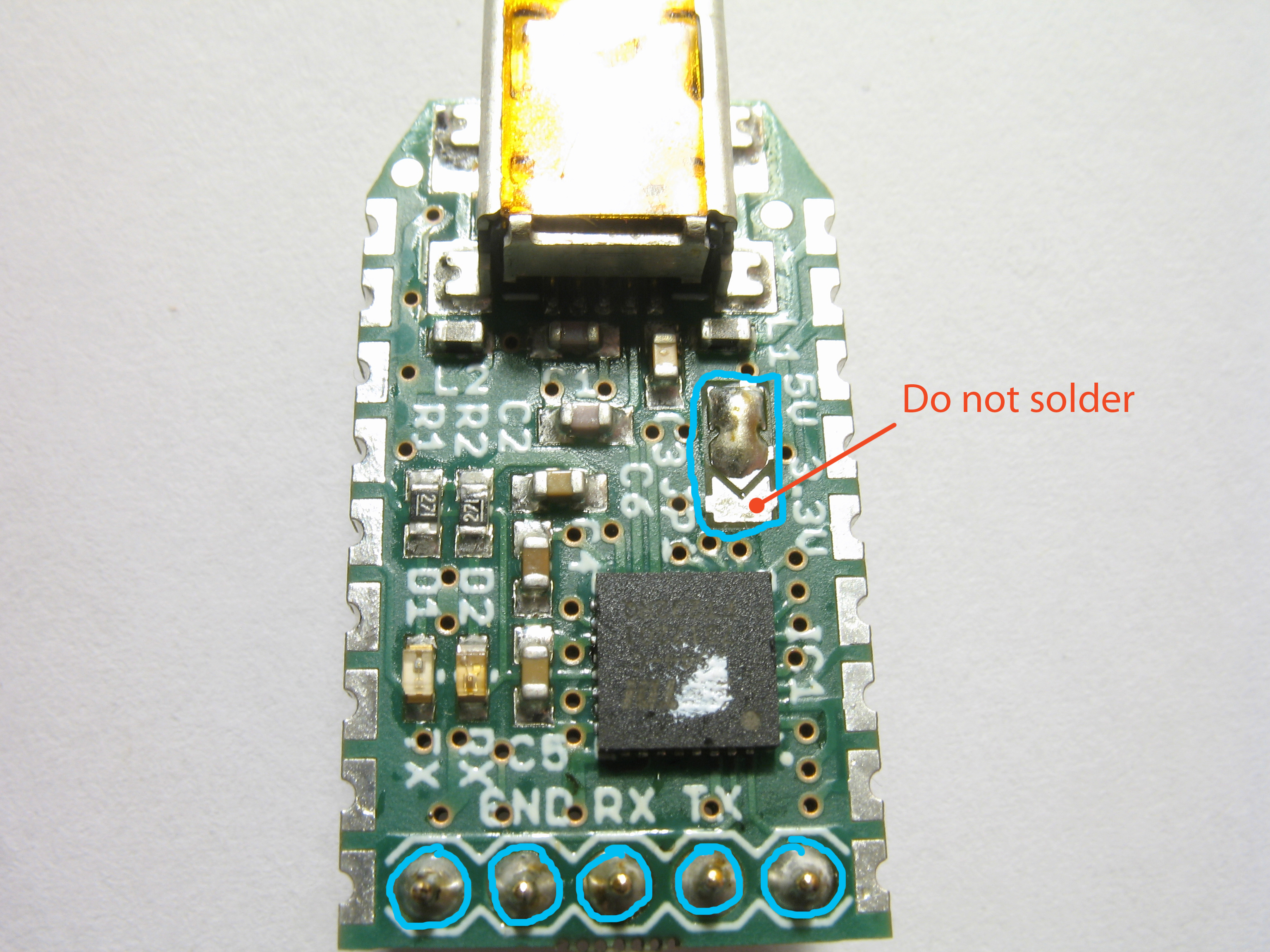
After soldering the headers, solder the voltage selector of each FT232R to the 5V setting. Pay attention to the picture below to see which sections the solder covers. Be careful not to bridge the V-shaped gap between the 3.3V source (pointed in red) with the center lead. Doing so will fry at least the TTL adapter once it's powered on.
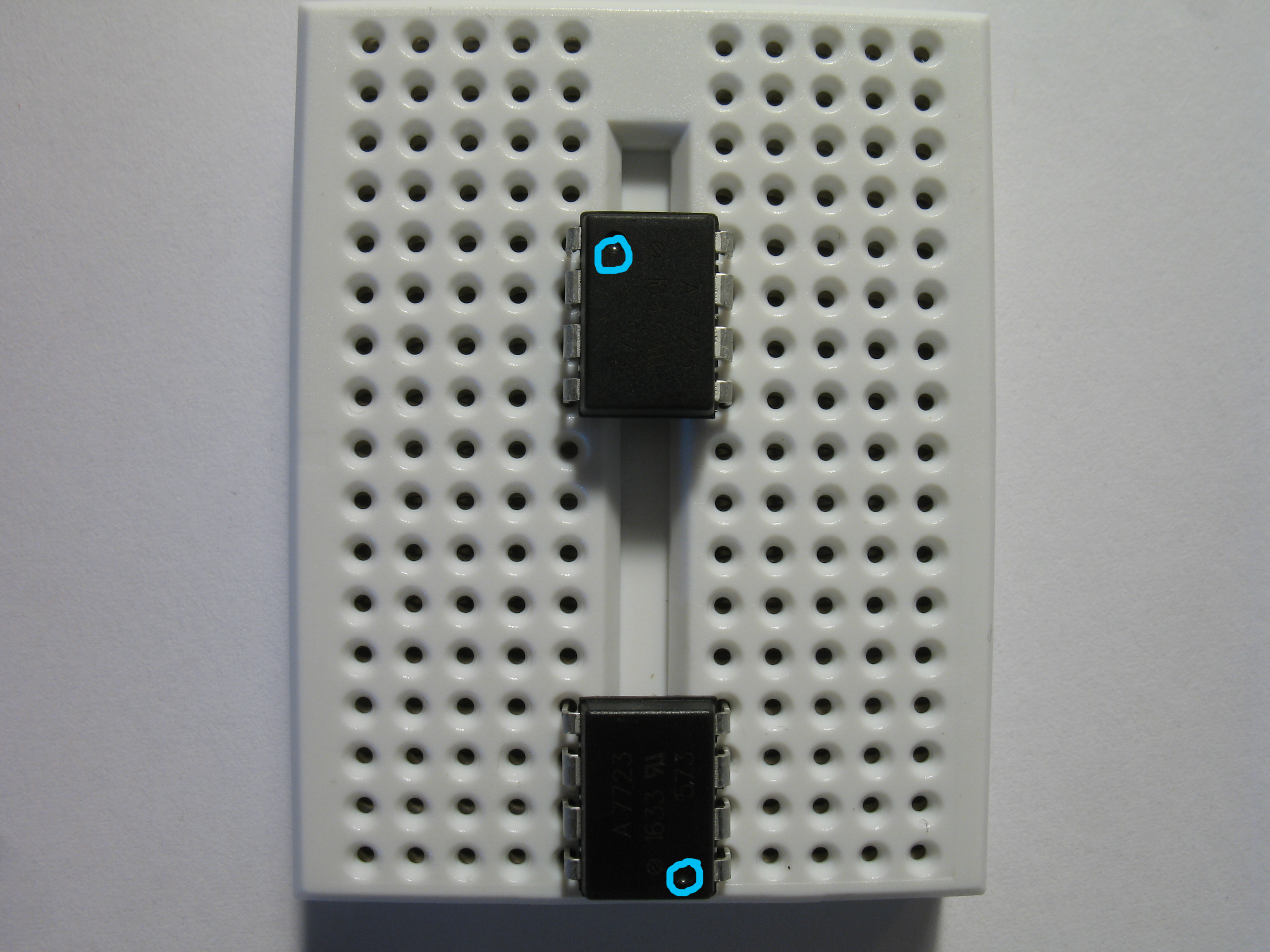
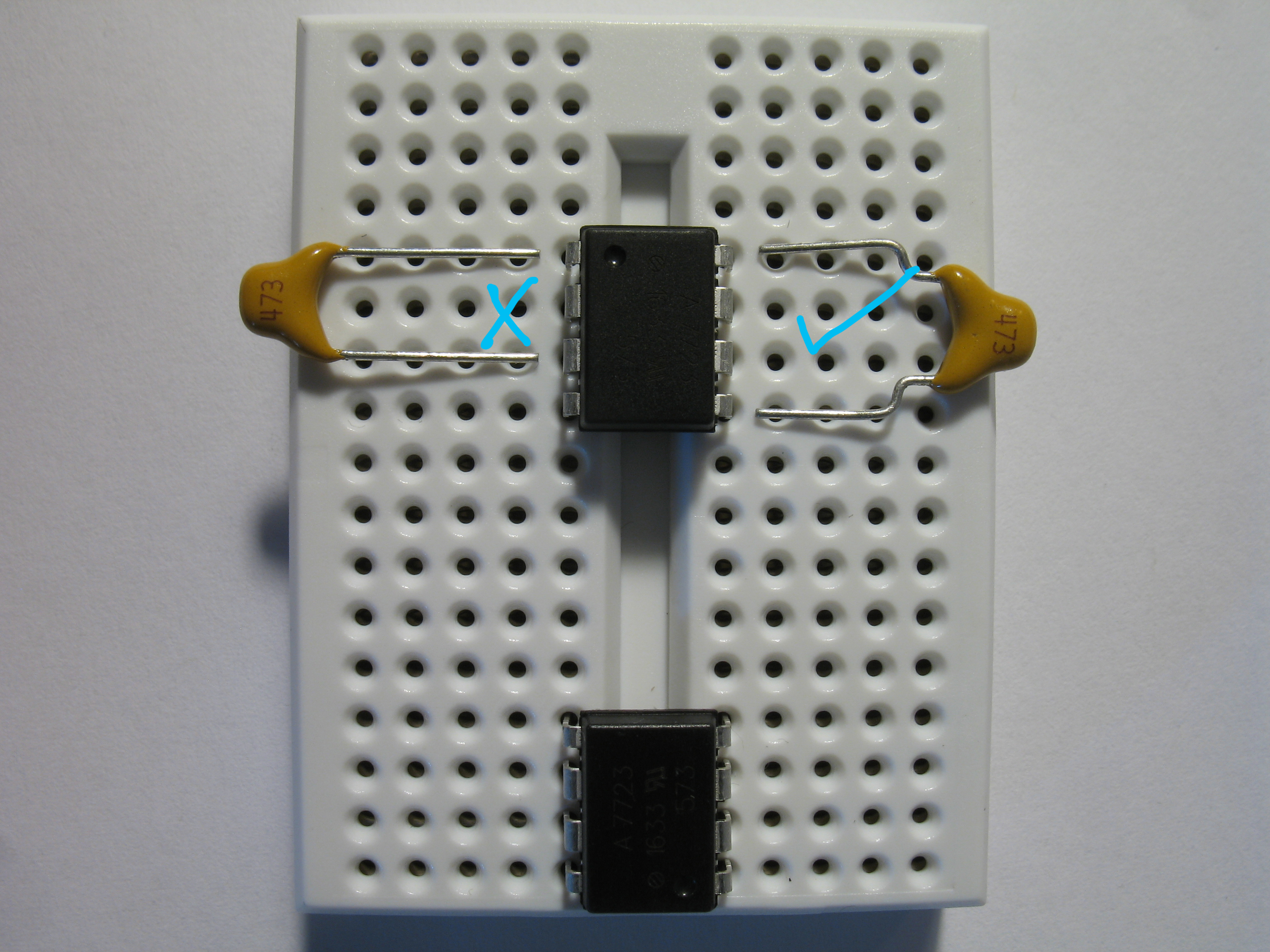
Start the assembly of the data diode by placing the optocouplers on the breadboard as depicted. Notice the orientation marks of the optocouplers (highlighted with blue circles) point to opposite directions.
Ensure the width of the capacitor leads is four pins. Use needle nose pliers to bend the leads if necessary.
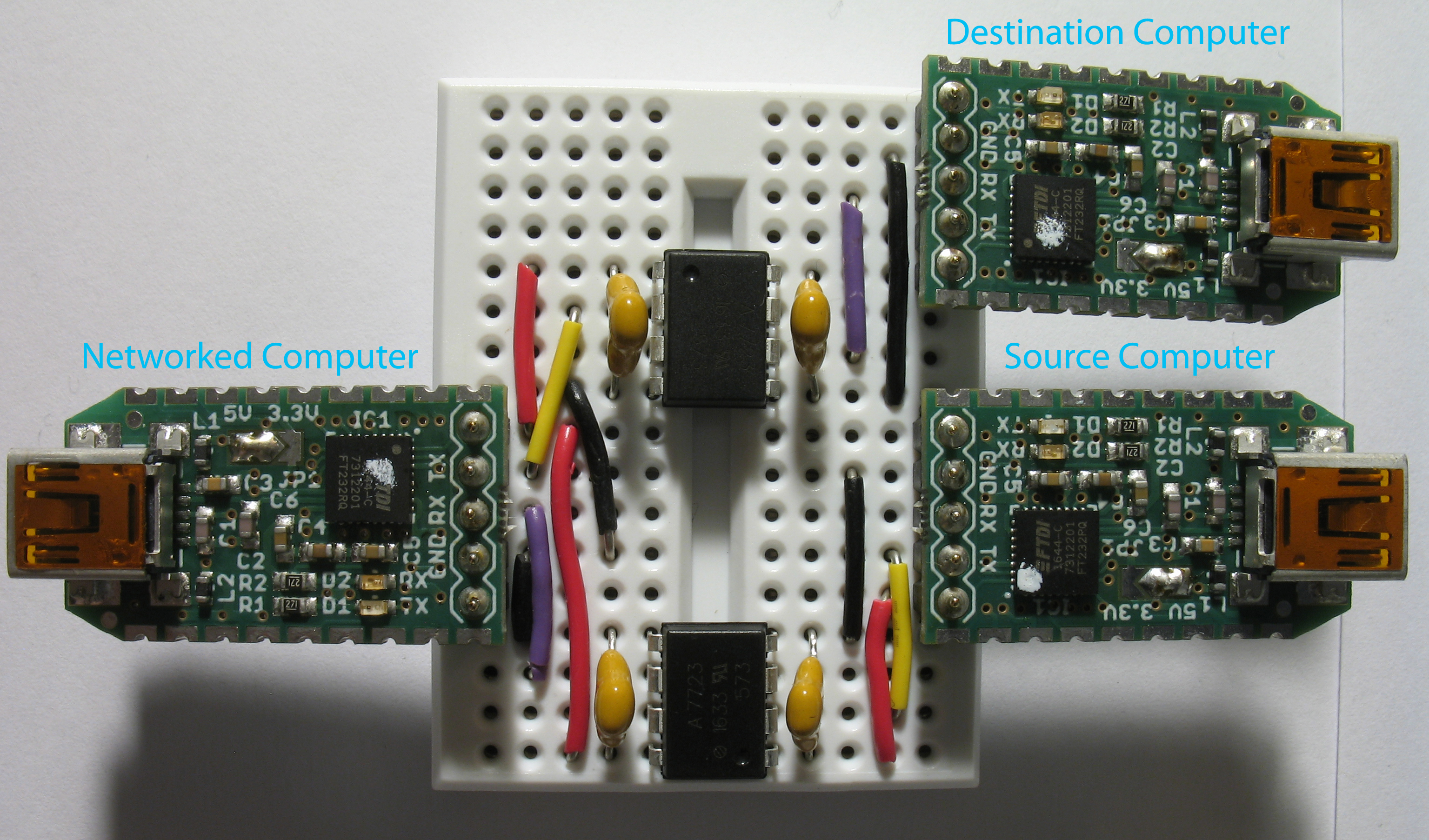
Connect the capacitors and wires to the breadboard as follows. Measuring and cutting the jump wiring takes a surprising amount of time. Use this handy guide if necessary. You can also buy ready-made kits to save a lot of time.
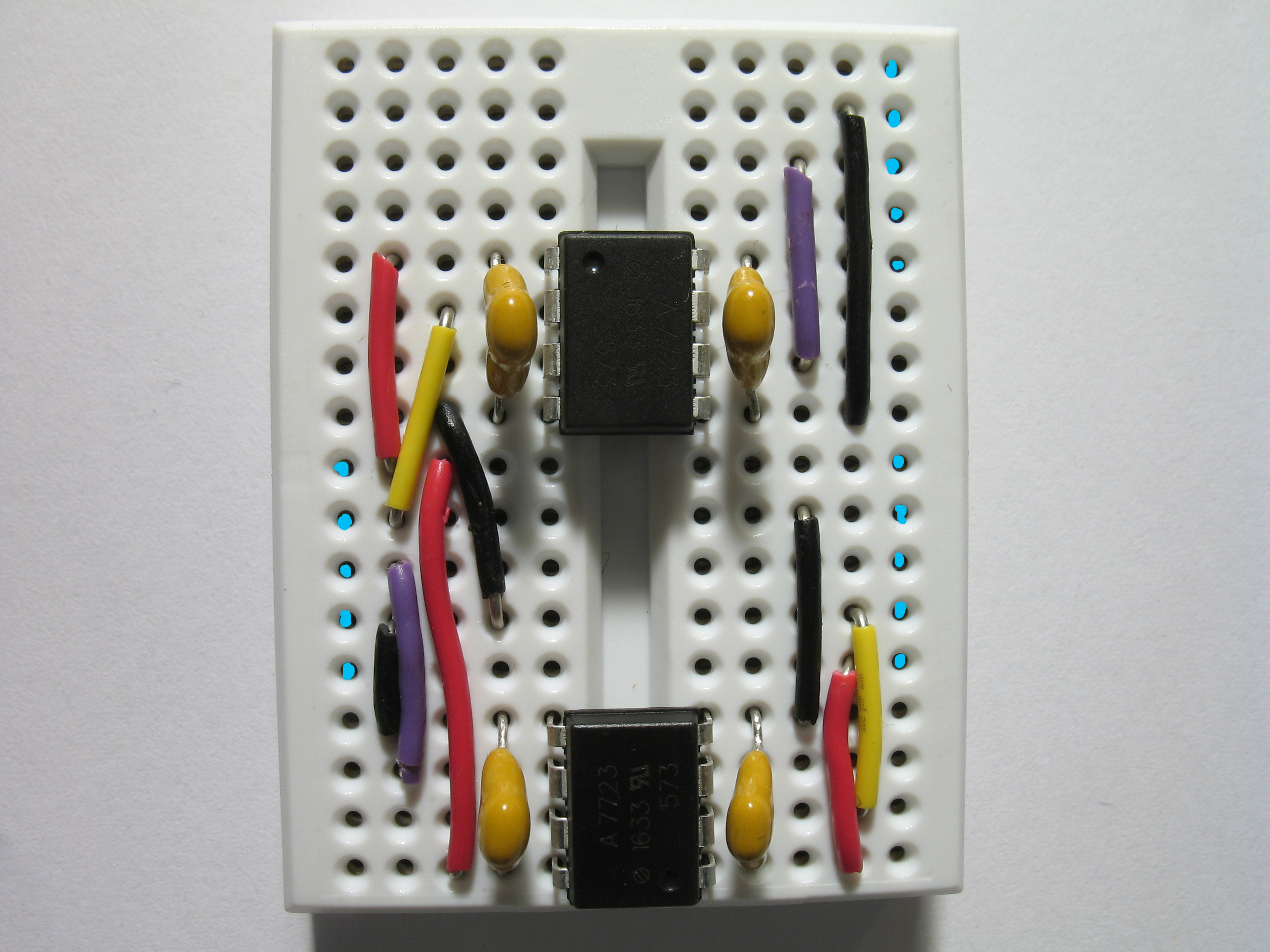
Connect the USB-to-TTL adapters to the breadboard. The rows of blue dots in the previous image represent the holes the adapter leads are connected.
If you want you can optionally create an inspectable tamper barrier for your data diode at this point.
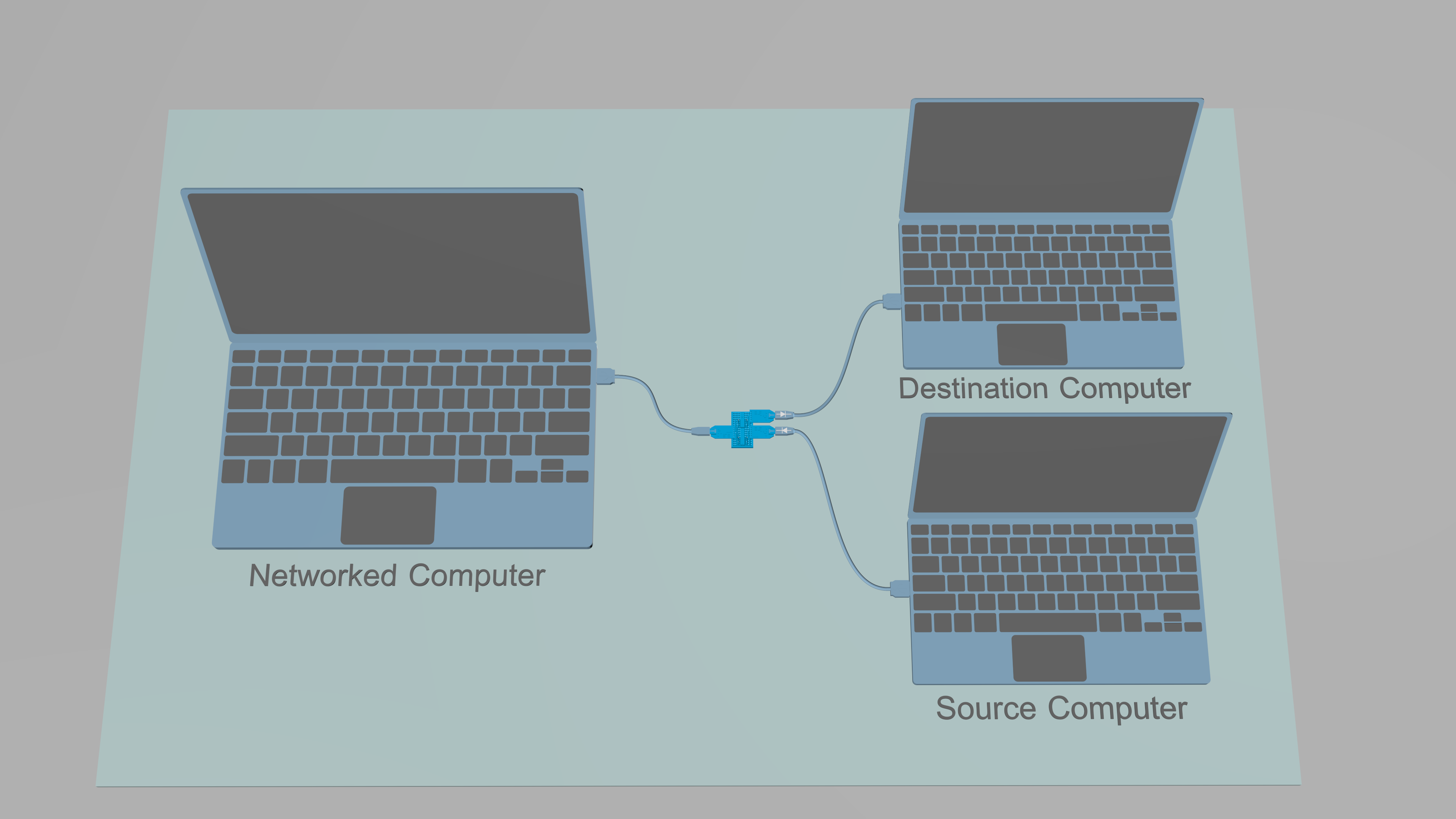
The data diode is now complete. Connect the data diode between Source, Destination, and Networked Computer.