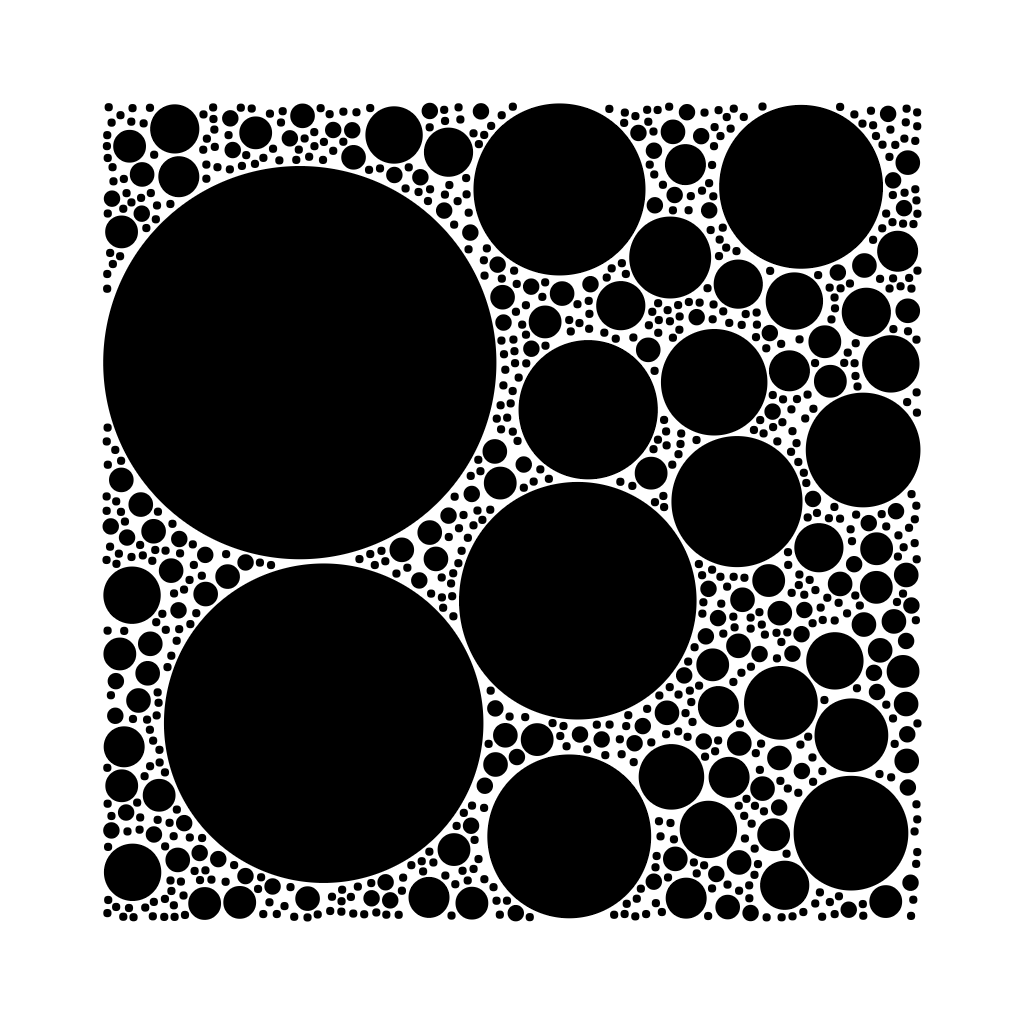
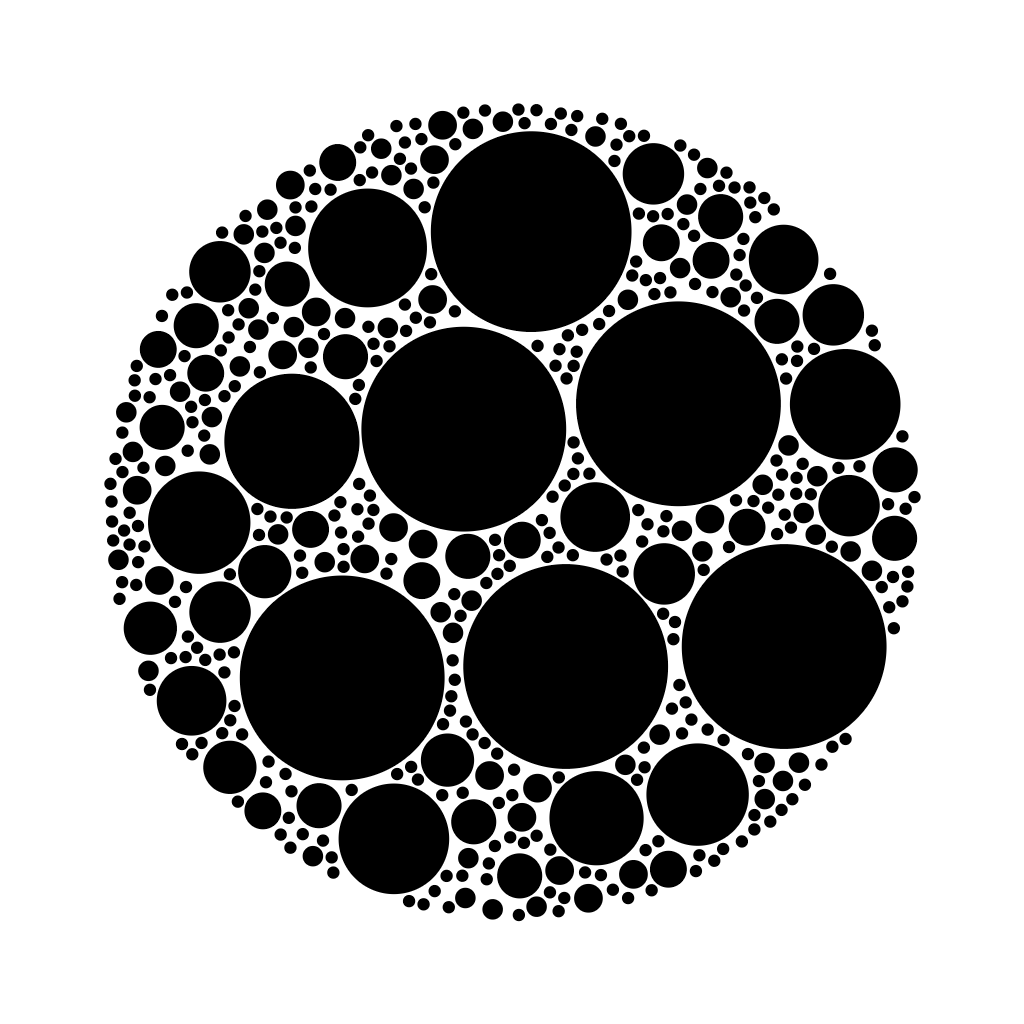
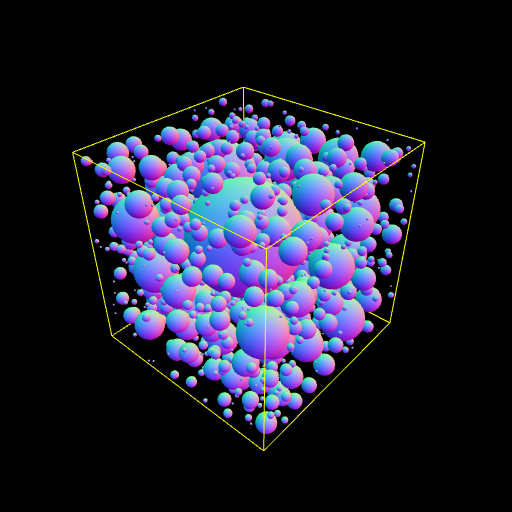
Brute force circle/sphere packing in 2D or 3D.
See ./demos for examples.
const pack = require('pack-spheres');
const circles = pack({
dimensions: 2,
packAttempts: 500,
maxCount: 1000,
minRadius: 0.05,
maxRadius: 0.5,
padding: 0.0025
});
console.log('Got %d circles', circles.length);
console.log(circles[0].position, circles[0].radius);Returns an array of objects with normalized values between -1.0 and 1.0, but the algorithm works on arbitrary units (for example, you could use pixels instead).
[
{
position: [ x, y, z ],
radius: Number
},
...
]If you specify { dimensions: 2 }, the position will only contain [ x, y ].
The algorithm is roughly based on Tim Holman's Circle Packing tutorial, thanks Tim!
Use npm to install.
npm install pack-spheres --savePacks 3D spheres (default) or 2D circles with the given options:
dimensions— Can either be 3 (default) for spheres, or 2 for circlesbounds— The normalized bounding box from-1.0to1.0that spheres are randomly generated within and clip to, default 1.0packAttempts— Number of attempts per sphere to pack within the space, default 500maxCount— The max number of total spheres that will be packed, default 1000 (note: you may not always reach the maxCount if all spheres could not be packed)minRadius— A number or generator function that specifies the min (starting) radius for placed spheres (default 0.01)maxRadius— A number or generator function that specifies the max radius a sphere will grow to (default 0.5)maxGrowthSteps— A number or generator function that specifies the max number of steps a sphere will grow before stopping (default Infinity)padding— A number or generator function that specifies the padding around this sphere (default 0)
You can pass in override functions to change the behaviour:
random— A function that returns a 0..1 random value used by the defaultsamplefunction, defaults toMath.random()sample— A function that returns a 2D or 3D vector for where a new sphere should be placedoutside— A function that takes in a sphere's(position, radius, padding)and returnstrueif the sphere is considered to be "outside" of your virtual bounding region. Defaults to a bounding cube/box
// Some utility for randomness
const Random = require('canvas-sketch-util/random');
// Generate circles in a 2D unit circle
const bounds = 1;
const shapes = pack({
bounds,
// Generate a random point inside a 2D circle
sample: () => Random.insideCircle(bounds),
// See if mag(pos - center) >= bounds
outside: (position, radius) => {
const length = Math.sqrt(
position[0] * position[0] + position[1] * position[1]
);
return length + radius >= bounds;
}
});Instead of having all spheres start with, say, a fixed minRadius, you can pass a function that will get used for each new sphere being placed:
// Some utility for randomness
const Random = require('canvas-sketch-util/random');
const spheres = pack({
minRadius: () => Random.range(0, 0.5)
});Thanks to Tim Holman for his Circle Packing tutorial which this code is roughly based on.
MIT, see LICENSE.md for details.