This document describes how to query and manipulate ATT&CK data from either this repository or the ATT&CK TAXII server, as well as the formatting of the data itself.
The programmatic uses of ATT&CK demonstrated in this document utilize the stix2 python library. Please refer to the STIX2 Python API Documentation for more information on how to work with STIX programmatically. See also the section on Requirements and imports.
This document describes how ATT&CK implements and extends the STIX format. To find out more about STIX, please see the STIX 2.0 website.
We also recommend reading the ATT&CK Design and Philosophy Paper, which describes high-level overall approach, intention, and usage of ATT&CK.
If you are looking for ATT&CK data represented in STIX 2.1, please see our attack-stix-data GitHub repository. The accompanying USAGE document includes more information on the improved data model of that repository.
- Introduction
The data in this repository is STIX 2.0 and divided into folders, one for each domain of ATT&CK. These domains generally follow the same format with a few departures. Domain differences will be noted in the relevant sections of this document.
ATT&CK uses a mix of predefined and custom STIX objects to implement ATT&CK concepts. The following table is a mapping of ATT&CK concepts to STIX 2.0 objects:
| ATT&CK concept | STIX object type | Custom type? |
|---|---|---|
| Matrix | x-mitre-matrix |
yes |
| Tactic | x-mitre-tactic |
yes |
| Technique | attack-pattern | no |
| Sub-technique | attack-pattern where x_mitre_is_subtechnique = true |
no |
| Procedure | relationship where relationship_type = "uses" and target_ref is an attack-pattern |
no |
| Mitigation | course-of-action | no |
| Group | intrusion-set | no |
| Software | malware or tool | no |
| Data Source | x-mitre-data-source |
yes |
| Campaign | campaign | no |
| Asset | x-mitre-asset |
yes |
Two additional object types are found in the ATT&CK catalog:
| STIX object type | About |
|---|---|
| identity | Referenced in the created_by_ref of all objects to state that the MITRE Corporation created the object |
| marking-definition | Referenced in the object_marking_refs of all objects to express the MITRE Corporation copyright |
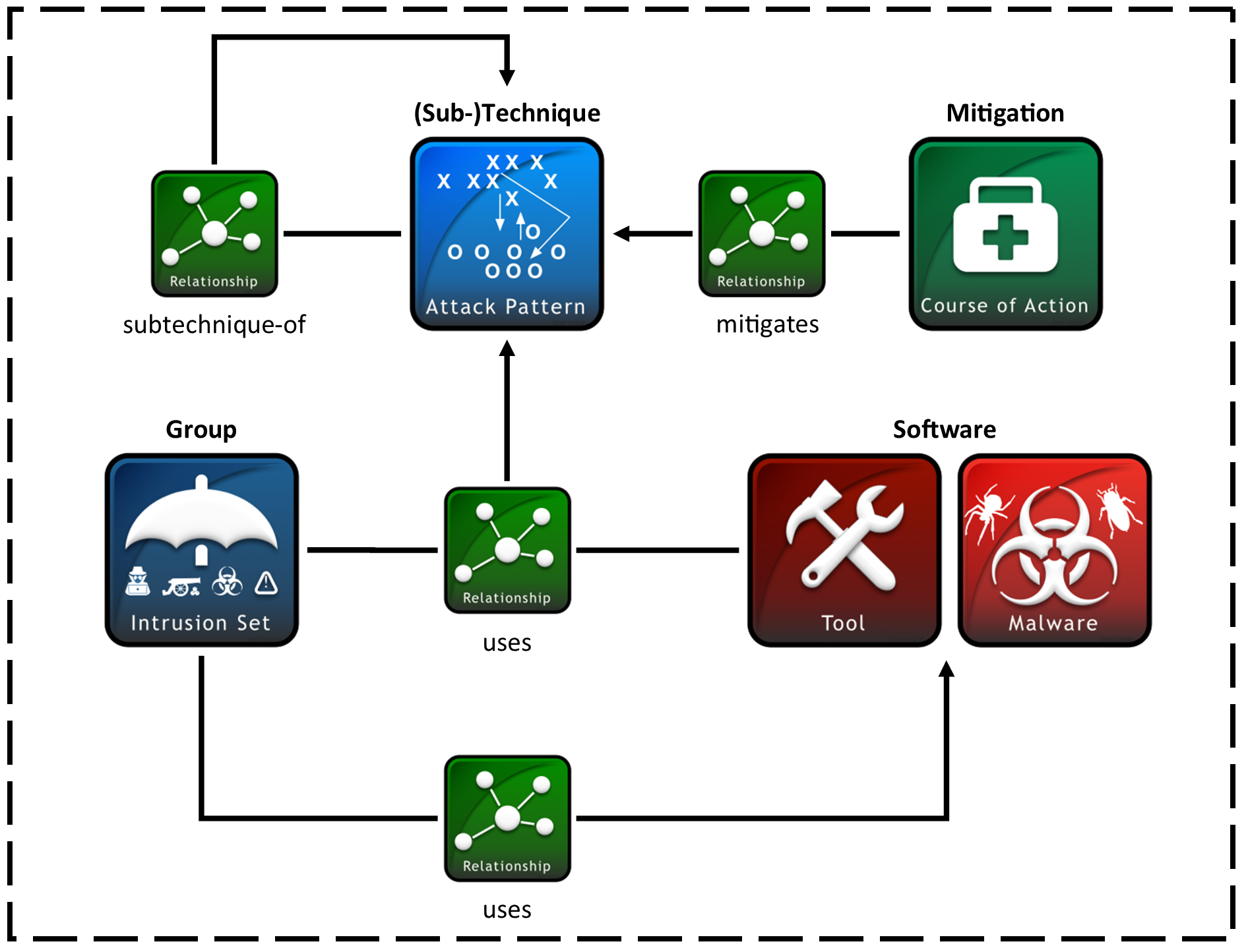
There are three general ways that ATT&CK extends the STIX 2.0 format:
-
Custom object types. Object types prefixed with
x-mitre-, e.gx-mitre-matrix, are custom STIX types extending the STIX 2.0 spec. They follow the general STIX Domain Object pattern but describe concepts not covered by types defined in STIX 2.0. -
Extensions of existing object types. Fields extending the STIX 2.0 spec are prefixed with
x_mitre_, e.gx_mitre_platformsinattack-patterns.All objects except relationships can have the following extended properties applied:
Field Type Description x_mitre_versionstring The version of the object in format major.minorwheremajorandminorare integers. ATT&CK increments this version number when the object content is updated.x_mitre_contributorsstring[] People and organizations who have contributed to the object. x_mitre_deprecatedboolean See Working with deprecated and revoked objects. -
New relationship types. Unlike custom object types and extended fields, custom relationship types are not prefixed with
x_mitre_. You can find a full list of relationship types in the Relationships section, which also mentions whether the type is a default STIX type.
Please see also the STIX documentation on customizing STIX.
Objects in ATT&CK may have several different kinds of IDs.
The most commonly used ID format is what is referred to as the ATT&CK ID or simply ID. Each different type of ATT&CK object has its own variation upon the ATT&CK ID format:
| ATT&CK concept | ID format |
|---|---|
| Matrix | MAxxxx |
| Tactic | TAxxxx |
| Technique | Txxxx |
| Sub-Technique | Txxxx.yyy |
| Mitigation | Mxxxx |
| Group | Gxxxx |
| Software | Sxxxx |
| Data Source | DSxxxx |
| Campaign | Cxxxx |
| Asset | Axxxx |
ATT&CK IDs are typically, but not always, unique. See Collisions with Technique ATT&CK IDs for an edge case involving ID collisions between mitigations and techniques.
ATT&CK IDs can be found in the first external reference of all objects except for relationships (which don't have ATT&CK IDs). The first external reference also includes a url field linking to the page describing that object on the ATT&CK Website.
In addition to ATT&CK IDs, all objects in ATT&CK (including relationships) have STIX IDs in the id field of the object. Unlike ATT&CK IDs, STIX IDs are guaranteed to be unique. STIX IDs are therefore the best way to retrieve and refer to objects programmatically.
Several other IDs can be found in the external references of an object:
- NIST Mobile Threat Catalogue IDs can be found for some techniques in the Mobile domain where the external reference
source_nameis"NIST Mobile Threat Catalogue" - CAPEC IDs can be found for some techniques in the Enterprise domain where the external reference
source_nameis"capec"
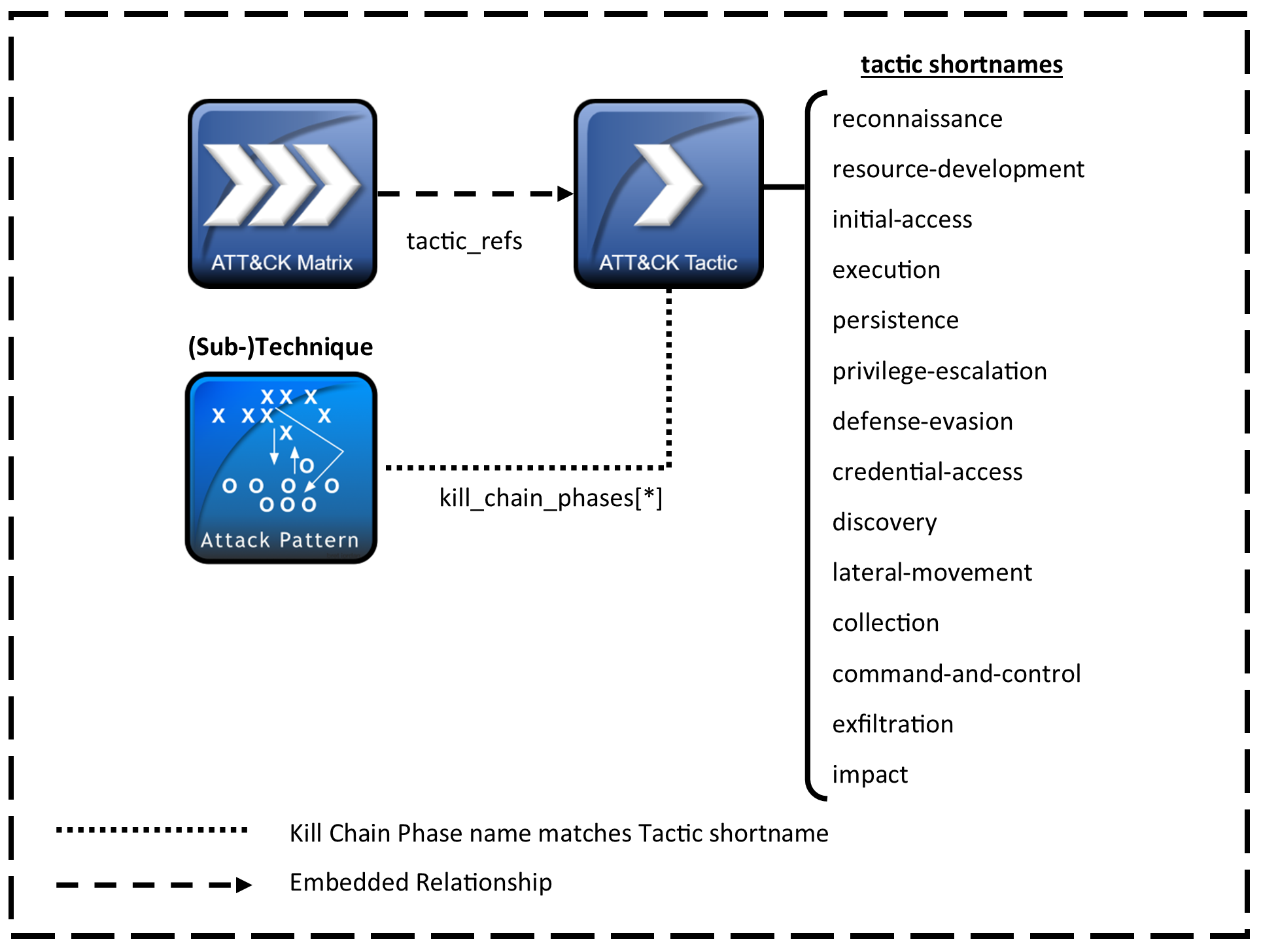
The overall layout of the ATT&CK Matrices is stored in x-mitre-matrix objects. As a custom STIX type they follow only the generic STIX Domain Object pattern.
Matrices extend the generic SDO format with the following field:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
tactic_refs |
string[] | The tactic_refs array of the matrix contains an ordered list of x-mitre-tactic STIX IDs corresponding to the tactics of the matrix. The order of tactic_refs determines the order the tactics should appear within the matrix. |
Techniques map into tactics by use of their kill_chain_phases property. Where the kill_chain_name is mitre-attack, mitre-mobile-attack, or mitre-ics-attack (for enterprise, mobile, and ics domains respectively), the phase_name corresponds to the x_mitre_shortname property of an x-mitre-tactic object. Matrices define their tactics in order using the tactic_refs embedded relationships.
A Tactic in ATT&CK is defined by an x-mitre-tactic object. As a custom STIX type they follow only the generic STIX Domain Object pattern.
Tactics extend the generic SDO format with the following field:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
x_mitre_shortname |
string | The x_mitre_shortname of the tactic is used for mapping techniques into the tactic. It corresponds to kill_chain_phases.phase_name of the techniques in the tactic. See mapping matrices, tactics and techniques for more information. |
A Technique in ATT&CK is defined as an attack-pattern object.
Techniques depart from the attack-pattern format with the following fields. Domain and tactic specific fields are marked in the "applies to" column:
| Field | Type | Applies to | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
x_mitre_detection |
string | All techniques | Strategies for identifying if a technique has been used by an adversary. |
x_mitre_platforms |
string[] | All techniques | List of platforms that apply to the technique. |
x_mitre_data_sources |
string[] | Enterprise* & ICS domains | Sources of information that may be used to identify the action or result of the action being performed. |
x_mitre_is_subtechnique |
boolean | Enterprise domain | If true, this attack-pattern is a sub-technique. See sub-techniques. |
x_mitre_system_requirements |
string[] | Enterprise domain | Additional information on requirements the adversary needs to meet or about the state of the system (software, patch level, etc.) that may be required for the technique to work. |
x_mitre_tactic_type |
string[] | Mobile domain | "Post-Adversary Device Access", "Pre-Adversary Device Access", or "Without Adversary Device Access". |
x_mitre_permissions_required |
string[] | Enterprise domain in the Privilege Escalation tactic | The lowest level of permissions the adversary is required to be operating within to perform the technique on a system. |
x_mitre_effective_permissions |
string[] | Enterprise domain in the Privilege Escalation tactic | The level of permissions the adversary will attain by performing the technique. |
x_mitre_defense_bypassed |
string[] | Enterprise domain in the Defense Evasion tactic | List of defensive tools, methodologies, or processes the technique can bypass. |
x_mitre_remote_support |
boolean | Enterprise domain in the Execution tactic | If true, the technique can be used to execute something on a remote system. |
x_mitre_impact_type |
string[] | Enterprise domain in the Impact tactic | Denotes if the technique can be used for integrity or availability attacks. |
* In the Enterprise domain data sources are represented via x-mitre-data-source and x-mitre-data-component objects, and their relationship with techniques through relationships of type detects. The x_mitre_data_sources field will still be maintained on enterprise techniques for backwards-compatibility purposes but we advise against its use as it does not include the full context of the data model.
See mapping matrices, tactics and techniques for more information about how techniques map into tactics and matrices.
A sub-technique in ATT&CK is represented as an attack-pattern and follows the same format as techniques. They differ in that they have a boolean field (x_mitre_is_subtechnique) marking them as sub-techniques, and a relationship of the type subtechnique-of where the source_ref is the sub-technique and the target_ref is the parent technique. A sub-technique can only have 1 parent technique, but techniques can have multiple sub-techniques.
Additionally:
- Sub-technique ATT&CK IDs are a suffix of their parent IDs. For a given sub-technique ID
Txxxx.yyy,Txxxxis the parent technique ID andyyyis the sub-technique ID. Sub-techniques have unique STIX IDs. - Sub-techniques have the same tactics as their parent technique.
- Sub-techniques have a subset of their parent technique's platforms.
Sub-techniques only exist in the enterprise domain.
ATT&CK does not represent procedures under their own STIX type. Instead, procedures are represented as relationships of type uses where the target_ref is a technique. This means that procedures can stem from usage by both groups (intrusion-sets) and software (malware or tools). The content of the procedure is described in the relationship description.
A Mitigation in ATT&CK is defined as a course-of-action object. ATT&CK Mitigations do not depart from the STIX course-of-action spec.
In ATT&CK versions prior to v5 (released in July of 2019), mitigations had 1:1 relationships with techniques and shared their technique's ID. These old 1:1 mitigations are deprecated in subsequent ATT&CK releases, and can be filtered out in queries — see Removing revoked and deprecated objects.
A Group in ATT&CK is defined as an intrusion-set object. ATT&CK Groups do not depart from the STIX intrusion-set format.
Software in ATT&CK is the union of two distinct STIX types: malware and tool.
Both malware and tool type software depart from the STIX format with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
x_mitre_platforms |
string[] | List of platforms that apply to the software. |
x_mitre_aliases |
string[] | List of aliases for the given software. |
Data Sources and Data Components represent data which can be used to detect techniques. Data components are nested within a data source but have their own STIX object.
- A Data Component can only have one parent Data Source.
- A Data Source can have any number of Data Components.
- Data Components can map to any number of techniques.
The general structure of data sources and data components is as follows:
"detects" x_mitre_data_source_ref
relationship embedded relationship
│ │
┌───────────┐ ▼ ┌────────────────┐ │ ┌───────────┐
│Technique 1│◄────┤ │ │ │ │
└───────────┘ │ │ ▼ │ │
│Data Component 1├────►│ │
┌───────────┐ │ │ │ │
│Technique 2│◄────┤ │ │Data Source│
└───────────┘ └────────────────┘ │ │
│ │
┌───────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ │ │
│Technique 3│◄────┤Data Component 2├────►│ │
└───────────┘ └────────────────┘ └───────────┘Prior to ATT&CK v10 data sources were stored in a x_mitre_data_sources field on techniques. This representation is still available for backwards-compatibility purposes, and does properly reflect the current set of data sources. However, because information is lost in that representation we advise against using it except in legacy applications. The ATT&CK for ICS domain still uses only the x_mitre_data_sources field.
A Data Source in ATT&CK is defined by an x-mitre-data-source object. As a custom STIX type they follow only the generic STIX Domain Object pattern.
Data Sources extend the generic SDO format with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
x_mitre_platforms |
string[] | List of platforms that apply to the data source. |
x_mitre_collection_layers |
string[] | List of places the data can be collected from. |
A Data Component in ATT&CK is represented as an x-mitre-data-component object. As a custom STIX type they follow only the generic STIX Domain Object pattern.
Data Components extend the generic SDO format with the following field:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
x_mitre_data_source_ref |
embedded relationship (string) | STIX ID of the data source this component is a part of. |
A Campaign in ATT&CK is defined as a campaign object.
Campaigns extend the generic SDO format with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
x_mitre_first_seen_citation |
string | One to many citations for when the Campaign was first reported in the form “(Citation: <citation name>)” where <citation name> can be found as one of the source_name of one of the external_references. |
x_mitre_last_seen_citation |
string | One to many citations for when the Campaign was last reported in the form “(Citation: <citation name>)” where <citation name> can be found as one of the source_name of one of the external_references. |
An Asset in ATT&CK is defined by an x-mitre-asset object. As a custom STIX type they follow only the generic STIX Domain Object pattern.
Assets extend the generic SDO format with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
x_mitre_sectors |
string[] | List of industry sector(s) an asset may be commonly observed in. |
x_mitre_related_assets |
related_asset[] | Related assets describe sector specific device names or aliases that may be commonly associated with the primary asset page name or functional description. Related assets include a description of how the related asset is associated with the page definition. |
The related_asset subtype is an object with the properties:
| Field | Type |
|---|---|
name |
string |
related_asset_sectors |
string[] |
description |
string |
Objects in ATT&CK are related to each other via STIX relationship objects. These relationships convey concepts like groups using techniques (also called "procedure examples" on the technique pages), the hierarchy of techniques and sub-techniques, and so on.
Unlike other objects in the dataset, relationships cannot be revoked or deprecated. Relationships are considered deprecated/revoked if one of the objects it is attached to is revoked or deprecated. See Working with deprecated and revoked objects for more information on revoked objects.
Relationships oftentimes have descriptions which contextualize the relationship between the objects.
| Source Type | Relationship Type | Target Type | Custom Type? | About |
|---|---|---|---|---|
intrusion-set |
uses |
malware or tool |
No | Group using a software. |
intrusion-set |
uses |
attack-pattern |
No | Group using a technique, which is also considered a procedure example. |
malware or tool |
uses |
attack-pattern |
No | Software using a technique, which is also considered a procedure example. |
campaign |
uses |
malware or tool |
No | Campaign using a software. |
campaign |
uses |
attack-pattern |
No | Campaign using a technique, which is also considered a procedure example. |
campaign |
attributed-to |
intrusion-set |
No | Campaign attributed to a group. |
course-of-action |
mitigates |
attack-pattern |
No | Mitigation mitigating a technique. |
attack-pattern |
subtechnique-of |
attack-pattern |
Yes | Sub-technique of a technique, where the source_ref is the sub-technique and the target_ref is the parent technique. |
x-mitre-data-component |
detects |
attack-pattern |
Yes | Data component detecting a technique. |
attack-pattern |
targets |
x-mitre-asset |
Yes | Technique targets an asset. |
| any type | revoked-by |
any type | Yes | The target object is a replacement for the source object. Only occurs where the objects are of the same type, and the source object will have the property revoked = true. See Working with deprecated and revoked objects for more information on revoked objects. |
Note that because groups use software and software uses techniques, groups can be considered indirect users of techniques used by their software. See Getting techniques used by a group's software.
There are several ways to acquire the ATT&CK data in Python. All of them will provide an object implementing the DataStore API and can be used interchangeably with the recipes provided in the Python recipes section.
This section utilizes the stix2 python library. Please refer to the STIX2 Python API Documentation for more information on how to work with STIX programmatically.
Before installing requirements, we recommend setting up a virtual environment:
- Create virtual environment:
- macOS and Linux:
python3 -m venv env - Windows:
py -m venv env
- macOS and Linux:
- Activate the virtual environment:
- macOS and Linux:
source env/bin/activate - Windows:
env/Scripts/activate.bat
- macOS and Linux:
stix2 can be installed by following the instructions on their repository. Imports for the recipes in this repository can be done from the base package, for example:
from stix2 import FilterHowever, if you are aiming to extend the ATT&CK dataset with new objects or implement complex workflows, you may need to use the v20 specifier for some imports. This ensures that the objects use the STIX 2.0 API instead of the STIX 2.1 API. For example:
from stix2.v20 import AttackPatternYou can see a full list of the classes which have versioned imports here.
taxii2-client can be installed by following the instructions on their repository. The ATT&CK TAXII server implements the 2.0 version of the TAXII specification, but the default import of taxii2client (version 2.0.0 and above) uses the 2.1 version of the TAXII specification, which can lead to 406 responses when connecting to our TAXII server if not accounted for.
If the TAXII Client is getting a 406 Response, make sure you are running the latest version (pip install --upgrade stix2 or pip install --upgrade taxii2-client). In addition, make sure you are running the 2.0 version of the client (using the v20 import) as shown below in order to communicate with the ATT&CK TAXII 2.0 Server.
from taxii2client.v20 import CollectionMany users may opt to access the ATT&CK content via a local copy of the STIX data on this repo. This can be advantageous for several reasons:
- Doesn't require internet access after the initial download
- User can modify the ATT&CK content if desired
- Downloaded copy is static, so updates to the ATT&CK catalog won't cause bugs in automated workflows. User can still manually update by cloning a fresh version of the data
Each domain in this repo is formatted according to the STIX2 FileSystem spec.
Therefore you can use a FileSystemSource to load a domain, for example to load the enterprise-attack domain:
from stix2 import FileSystemSource
src = FileSystemSource('./cti/enterprise-attack')If you instead prefer to download just the domain bundle, e.g enterprise-attack.json, you can still load this using a MemoryStore:
from stix2 import MemoryStore
src = MemoryStore()
src.load_from_file("enterprise-attack.json")Some users may instead prefer to access "live" ATT&CK content over the internet. This is advantageous for several reasons:
- Always stays up to date with the evolving ATT&CK catalog
- Doesn't require an initial download of the ATT&CK content, generally requires less setup
Users can access the ATT&CK data from the official ATT&CK TAXII server. In TAXII, the ATT&CK domains are represented as collections with static IDs:
| domain | collection ID |
|---|---|
enterprise-attack |
95ecc380-afe9-11e4-9b6c-751b66dd541e |
mobile-attack |
2f669986-b40b-4423-b720-4396ca6a462b |
ics-attack |
02c3ef24-9cd4-48f3-a99f-b74ce24f1d34 |
You can also get a list of available collection from the server directly:
from taxii2client.v20 import Server # only specify v20 if your installed version is >= 2.0.0
server = Server("https://cti-taxii.mitre.org/taxii/")
api_root = server.api_roots[0]
# Print name and ID of all ATT&CK domains available as collections
for collection in api_root.collections:
print(collection.title.ljust(20) + collection.id)The following recipe demonstrates how to access the enterprise-attack data from the TAXII server.
from stix2 import TAXIICollectionSource
from taxii2client.v20 import Collection # only specify v20 if your installed version is >= 2.0.0
collections = {
"enterprise_attack": "95ecc380-afe9-11e4-9b6c-751b66dd541e",
"mobile_attack": "2f669986-b40b-4423-b720-4396ca6a462b",
"ics-attack": "02c3ef24-9cd4-48f3-a99f-b74ce24f1d34"
}
collection = Collection(f"https://cti-taxii.mitre.org/stix/collections/{collections['enterprise_attack']}/")
src = TAXIICollectionSource(collection)For more about TAXII, please see oasis-open's Introduction to TAXII.
Users can alternatively access the data from MITRE/CTI using HTTP requests, and load the resulting content into a MemoryStore. While typically the TAXII method is more desirable for "live" access, this method can be useful if you want to access data on a branch of the MITRE/CTI repo (the TAXII server only holds the master branch) or in the case of a TAXII server outage.
import requests
from stix2 import MemoryStore
def get_data_from_branch(domain, branch="master"):
"""get the ATT&CK STIX data from MITRE/CTI. Domain should be 'enterprise-attack', 'mobile-attack' or 'ics-attack'. Branch should typically be master."""
stix_json = requests.get(f"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mitre/cti/{branch}/{domain}/{domain}.json").json()
return MemoryStore(stix_data=stix_json["objects"])
src = get_data_from_branch("enterprise-attack")ATT&CK versions are tracked on the MITRE/CTI repo using tags. Tags prefixed with ATT&CK-v correspond to ATT&CK versions and tags prefixed with CAPEC-v correspond to CAPEC versions. You can find more information about ATT&CK versions on the versions of ATT&CK page on the ATT&CK website.
In addition to checking out the repo under the tag for a given version or downloading the STIX from github using your browser, you can also use a variation on the requests method to access a particular version of ATT&CK:
import requests
from stix2 import MemoryStore
def get_data_from_version(domain, version):
"""get the ATT&CK STIX data for the given version from MITRE/CTI. Domain should be 'enterprise-attack', 'mobile-attack' or 'ics-attack'."""
stix_json = requests.get(f"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mitre/cti/ATT%26CK-v{version}/{domain}/{domain}.json").json()
return MemoryStore(stix_data=stix_json["objects"])
src = get_data_from_version("enterprise-attack", "5.2")You can get a list of ATT&CK versions programmatically using the github API:
import requests
import re
refToTag = re.compile(r"ATT&CK-v(.*)")
tags = requests.get("https://api.github.com/repos/mitre/cti/git/refs/tags").json()
versions = list(map(lambda tag: refToTag.search(tag["ref"]).groups()[0] , filter(lambda tag: "ATT&CK-v" in tag["ref"], tags)))
# versions = ["1.0", "2.0", ...]Because ATT&CK is stored in multiple domains (as of this writing, enterprise-attack, mobile-attack and ics-attack), the above methodologies will only allow you to work with a single domain at a time. While oftentimes the hard separation of domains is advantageous, occasionally it is useful to combine domains into a single DataStore. Use any of the methods above to acquire the individual datastores, and then use the following approach to combine them into a single CompositeDataSource:
from stix2 import CompositeDataSource
src = CompositeDataSource()
src.add_data_sources([enterprise_attack_src, mobile_attack_src, ics_attack_src])You can then use this CompositeDataSource just as you would the DataSource for an individual domain.
Below are example python recipes which can be used to work with ATT&CK data. They assume the existence of an object implementing the DataStore API. Any of the methods outlined in the Accessing ATT&CK data in python section should provide an object implementing this API.
This section utilizes the stix2 python library. Please refer to the STIX2 Python API Documentation for more information on how to work with STIX programmatically. See also the section on Requirements and imports.
The recipes in this section address how to query the dataset for a single object.
The following recipe can be used to retrieve an object according to its STIX ID. This is typically the preferred way to retrieve objects when working with ATT&CK data because STIX IDs are guaranteed to be unique.
g0075 = src.get("intrusion-set--f40eb8ce-2a74-4e56-89a1-227021410142")The following recipe can be used to retrieve an object according to its ATT&CK ID:
from stix2 import Filter
g0075 = src.query([ Filter("external_references.external_id", "=", "G0075") ])[0]Note: in prior versions of ATT&CK, mitigations had 1:1 relationships with techniques and shared their technique's ID. Therefore the above method does not work properly for techniques because technique ATT&CK IDs are not truly unique. By specifying the STIX type you're looking for as attack-pattern you can avoid this issue.
from stix2 import Filter
t1134 = src.query([
Filter("external_references.external_id", "=", "T1134"),
Filter("type", "=", "attack-pattern")
])[0]The old 1:1 mitigations causing this issue are deprecated, so you can also filter them out that way — see Removing revoked and deprecated objects.
The following recipe retrieves an object according to its name:
from stix2 import Filter
def get_technique_by_name(thesrc, name):
filt = [
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern'),
Filter('name', '=', name)
]
return thesrc.query(filt)
# get the technique titled "System Information Discovery"
get_technique_by_name(src, 'System Information Discovery')The following methodology can be used to find the group corresponding to a given alias:
from stix2 import Filter
def get_group_by_alias(thesrc, alias):
return thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'intrusion-set'),
Filter('aliases', '=', alias)
])[0]
get_group_by_alias(src, 'Cozy Bear')The recipes in this section address how to query the dataset for multiple objects.
⚠ When working with queries to return objects based on a set of characteristics, it is likely that you'll end up with a few objects which are no longer maintained by ATT&CK. These are objects marked as deprecated or revoked. We keep these outdated objects around so that workflows depending on them don't break, but we recommend you avoid using them when possible. Please see the section Working with deprecated and revoked objects for more information.
See The ATT&CK data model for mappings of ATT&CK type to STIX type.
from stix2 import Filter
# use the appropriate STIX type in the query according to the desired ATT&CK type
groups = src.query([ Filter("type", "=", "intrusion-set") ])ATT&CK Techniques and sub-techniques are both represented as attack-pattern objects. Therefore further parsing is necessary to get specifically techniques or sub-techniques.
from stix2 import Filter
def get_techniques_or_subtechniques(thesrc, include="both"):
"""Filter Techniques or Sub-Techniques from ATT&CK Enterprise Domain.
include argument has three options: "techniques", "subtechniques", or "both"
depending on the intended behavior."""
if include == "techniques":
query_results = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern'),
Filter('x_mitre_is_subtechnique', '=', False)
])
elif include == "subtechniques":
query_results = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern'),
Filter('x_mitre_is_subtechnique', '=', True)
])
elif include == "both":
query_results = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern')
])
else:
raise RuntimeError("Unknown option %s!" % include)
return query_results
subtechniques = get_techniques_or_subtechniques(src, "subtechniques")
subtechniques = remove_revoked_deprecated(subtechniques) # see https://github.com/mitre/cti/blob/master/USAGE.md#removing-revoked-and-deprecated-objectsBecause software are the union of two STIX types (tool and malware), the process for accessing software is slightly more complicated.
from itertools import chain
from stix2 import Filter
def get_software(thesrc):
return list(chain.from_iterable(
thesrc.query(f) for f in [
Filter("type", "=", "tool"),
Filter("type", "=", "malware")
]
))
get_software(src)Sometimes it may be useful to query objects by the content of their description:
from stix2 import Filter
def get_techniques_by_content(thesrc, content):
techniques = src.query([ Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern') ])
return list(filter(lambda t: content.lower() in t.description.lower(), techniques))
# Get all techniques where the string LSASS appears in the description
get_techniques_by_content(src, 'LSASS')Techniques are associated with one or more platforms. You can query the techniques under a specific platform with the following code:
from stix2 import Filter
def get_techniques_by_platform(thesrc, platform):
return thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern'),
Filter('x_mitre_platforms', '=', platform)
])
# get techniques in the windows platform
get_techniques_by_platform(src, 'Windows')Techniques are related to tactics by their kill_chain_phases property.
The phase_name of each kill chain phase corresponds to the x_mitre_shortname of a tactic.
from stix2 import Filter
def get_tactic_techniques(thesrc, tactic):
# double checking the kill chain is MITRE ATT&CK
# note: kill_chain_name is different for other domains:
# - enterprise: "mitre-attack"
# - mobile: "mitre-mobile-attack"
# - ics: "mitre-ics-attack"
return thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern'),
Filter('kill_chain_phases.phase_name', '=', tactic),
Filter('kill_chain_phases.kill_chain_name', '=', 'mitre-attack'),
])
# use the x_mitre_shortname as argument
get_tactic_techniques(src, 'defense-evasion')The tactics are individual objects (x-mitre-tactic), and their order in a matrix (x-mitre-matrix) is
found within the tactic_refs property in a matrix. The order of the tactics in that list matches
the ordering of the tactics in that matrix. The following recipe returns a structured list of tactics within each matrix of the input DataStore.
from stix2 import Filter
def getTacticsByMatrix(thesrc):
tactics = {}
matrix = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'x-mitre-matrix'),
])
for i in range(len(matrix)):
tactics[matrix[i]['name']] = []
for tactic_id in matrix[i]['tactic_refs']:
tactics[matrix[i]['name']].append(thesrc.get(tactic_id))
return tactics
# get tactic layout
getTacticsByMatrix(src)Sometimes you may want to get a list of objects which have been created or modified after a certain time.
from stix2 import Filter
def get_created_after(thesrc, timestamp):
filt = [
Filter('created', '>', timestamp)
]
return thesrc.query(filt)
get_created_after(src, "2018-10-01T00:14:20.652Z")
def get_modified_after(thesrc, timestamp):
filt = [
Filter('modified', '>', timestamp)
]
return thesrc.query(filt)
get_modified_after(src, "2018-10-01T00:14:20.652Z")We don't recommend you use this method to detect a change to the contents of the knowledge base. For detecting an update to the overall knowledge base we recommend using requests to check the list of released versions of ATT&CK.
A large part of working with ATT&CK revolves around parsing relationships between objects. It is useful to track not only the related object but the relationship itself because a description is often present to contextualize the nature of the relationship. The following recipes demonstrate some common uses of relationships.
NOTE: The following code is intended to be used with the ATT&CK v12 release which includes Campaign Objects. The examples are backwards-compatible for previous versions af ATT&CK that omit those objects.
This microlibrary can be used to build a lookup table of stixID to related objects and relationships. The argument to each accessor function is a STIX2 MemoryStore to build the relationship mappings from.
from pprint import pprint
from stix2 import MemoryStore, Filter
# See section below on "Removing revoked and deprecated objects"
def remove_revoked_deprecated(stix_objects):
"""Remove any revoked or deprecated objects from queries made to the data source"""
# Note we use .get() because the property may not be present in the JSON data. The default is False
# if the property is not set.
return list(
filter(
lambda x: x.get("x_mitre_deprecated", False) is False and x.get("revoked", False) is False,
stix_objects
)
)
def get_related(thesrc, src_type, rel_type, target_type, reverse=False):
"""build relationship mappings
params:
thesrc: MemoryStore to build relationship lookups for
src_type: source type for the relationships, e.g "attack-pattern"
rel_type: relationship type for the relationships, e.g "uses"
target_type: target type for the relationship, e.g "intrusion-set"
reverse: build reverse mapping of target to source
"""
relationships = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'relationship'),
Filter('relationship_type', '=', rel_type),
Filter('revoked', '=', False),
])
# See section below on "Removing revoked and deprecated objects"
relationships = remove_revoked_deprecated(relationships)
# stix_id => [ { relationship, related_object_id } for each related object ]
id_to_related = {}
# build the dict
for relationship in relationships:
if src_type in relationship.source_ref and target_type in relationship.target_ref:
if (relationship.source_ref in id_to_related and not reverse) or (relationship.target_ref in id_to_related and reverse):
# append to existing entry
if not reverse:
id_to_related[relationship.source_ref].append({
"relationship": relationship,
"id": relationship.target_ref
})
else:
id_to_related[relationship.target_ref].append({
"relationship": relationship,
"id": relationship.source_ref
})
else:
# create a new entry
if not reverse:
id_to_related[relationship.source_ref] = [{
"relationship": relationship,
"id": relationship.target_ref
}]
else:
id_to_related[relationship.target_ref] = [{
"relationship": relationship,
"id": relationship.source_ref
}]
# all objects of relevant type
if not reverse:
targets = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', target_type),
Filter('revoked', '=', False)
])
else:
targets = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', src_type),
Filter('revoked', '=', False)
])
# build lookup of stixID to stix object
id_to_target = {}
for target in targets:
id_to_target[target.id] = target
# build final output mappings
output = {}
for stix_id in id_to_related:
value = []
for related in id_to_related[stix_id]:
if not related["id"] in id_to_target:
continue # targeting a revoked object
value.append({
"object": id_to_target[related["id"]],
"relationship": related["relationship"]
})
output[stix_id] = value
return output
# software:group
def software_used_by_groups(thesrc):
"""returns group_id => {software, relationship} for each software used by the group and each software used by campaigns attributed to the group."""
# get all software used by groups
tools_used_by_group = get_related(thesrc, "intrusion-set", "uses", "tool")
malware_used_by_group = get_related(thesrc, "intrusion-set", "uses", "malware")
software_used_by_group = {**tools_used_by_group, **malware_used_by_group} # group_id -> [{software, relationship}]
# get groups attributing to campaigns and all software used by campaigns
software_used_by_campaign = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "tool")
malware_used_by_campaign = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "malware")
for id in malware_used_by_campaign:
if id in software_used_by_campaign:
software_used_by_campaign[id].extend(malware_used_by_campaign[id])
else:
software_used_by_campaign[id] = malware_used_by_campaign[id]
campaigns_attributed_to_group = {
"campaigns": get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "attributed-to", "intrusion-set", reverse=True), # group_id => {campaign, relationship}
"software": software_used_by_campaign # campaign_id => {software, relationship}
}
for group_id in campaigns_attributed_to_group["campaigns"]:
software_used_by_campaigns = []
# check if attributed campaign is using software
for campaign in campaigns_attributed_to_group["campaigns"][group_id]:
campaign_id = campaign["object"]["id"]
if campaign_id in campaigns_attributed_to_group["software"]:
software_used_by_campaigns.extend(campaigns_attributed_to_group["software"][campaign_id])
# update software used by group to include software used by a groups attributed campaign
if group_id in software_used_by_group:
software_used_by_group[group_id].extend(software_used_by_campaigns)
else:
software_used_by_group[group_id] = software_used_by_campaigns
return software_used_by_group
def groups_using_software(thesrc):
"""returns software_id => {group, relationship} for each group using the software and each software used by attributed campaigns."""
# get all groups using software
groups_using_tool = get_related(thesrc, "intrusion-set", "uses", "tool", reverse=True)
groups_using_malware = get_related(thesrc, "intrusion-set", "uses", "malware", reverse=True)
groups_using_software = {**groups_using_tool, **groups_using_malware} # software_id => {group, relationship}
# get campaigns attributed to groups and all campaigns using software
campaigns_using_software = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "tool", reverse=True)
campaigns_using_malware = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "malware", reverse=True)
for id in campaigns_using_malware:
if id in campaigns_using_software:
campaigns_using_software[id].extend(campaigns_using_malware[id])
else:
campaigns_using_software[id] = campaigns_using_malware[id]
groups_attributing_to_campaigns = {
"campaigns": campaigns_using_software,# software_id => {campaign, relationship}
"groups": get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "attributed-to", "intrusion-set") # campaign_id => {group, relationship}
}
for software_id in groups_attributing_to_campaigns["campaigns"]:
groups_attributed_to_campaigns = []
# check if campaign is attributed to group
for campaign in groups_attributing_to_campaigns["campaigns"][software_id]:
campaign_id = campaign["object"]["id"]
if campaign_id in groups_attributing_to_campaigns["groups"]:
groups_attributed_to_campaigns.extend(groups_attributing_to_campaigns["groups"][campaign_id])
# update groups using software to include software used by a groups attributed campaign
if software_id in groups_using_software:
groups_using_software[software_id].extend(groups_attributed_to_campaigns)
else:
groups_using_software[software_id] = groups_attributed_to_campaigns
return groups_using_software
# software:campaign
def software_used_by_campaigns(thesrc):
"""returns campaign_id => {software, relationship} for each software used by the campaign."""
tools_used_by_campaign = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "tool")
malware_used_by_campaign = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "malware")
return {**tools_used_by_campaign, **malware_used_by_campaign}
def campaigns_using_software(thesrc):
"""returns software_id => {campaign, relationship} for each campaign using the software."""
campaigns_using_tool = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "tool", reverse=True)
campaigns_using_malware = get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "malware", reverse=True)
return {**campaigns_using_tool, **campaigns_using_malware}
# campaign:group
def groups_attributing_to_campaign(thesrc):
"""returns campaign_id => {group, relationship} for each group attributing to the campaign."""
return get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "attributed-to", "intrusion-set")
def campaigns_attributed_to_group(thesrc):
"""returns group_id => {campaign, relationship} for each campaign attributed to the group."""
return get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "attributed-to", "intrusion-set", reverse=True)
# technique:group
def techniques_used_by_groups(thesrc):
"""returns group_id => {technique, relationship} for each technique used by the group and each
technique used by campaigns attributed to the group."""
# get all techniques used by groups
techniques_used_by_groups = get_related(thesrc, "intrusion-set", "uses", "attack-pattern") # group_id => {technique, relationship}
# get groups attributing to campaigns and all techniques used by campaigns
campaigns_attributed_to_group = {
"campaigns": get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "attributed-to", "intrusion-set", reverse=True), # group_id => {campaign, relationship}
"techniques": get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "attack-pattern") # campaign_id => {technique, relationship}
}
for group_id in campaigns_attributed_to_group["campaigns"]:
techniques_used_by_campaigns = []
# check if attributed campaign is using technique
for campaign in campaigns_attributed_to_group["campaigns"][group_id]:
campaign_id = campaign["object"]["id"]
if campaign_id in campaigns_attributed_to_group["techniques"]:
techniques_used_by_campaigns.extend(campaigns_attributed_to_group["techniques"][campaign_id])
# update techniques used by groups to include techniques used by a groups attributed campaign
if group_id in techniques_used_by_groups:
techniques_used_by_groups[group_id].extend(techniques_used_by_campaigns)
else:
techniques_used_by_groups[group_id] = techniques_used_by_campaigns
return techniques_used_by_groups
def groups_using_technique(thesrc):
"""returns technique_id => {group, relationship} for each group using the technique and each campaign attributed to groups using the technique."""
# get all groups using techniques
groups_using_techniques = get_related(thesrc, "intrusion-set", "uses", "attack-pattern", reverse=True) # technique_id => {group, relationship}
# get campaigns attributed to groups and all campaigns using techniques
groups_attributing_to_campaigns = {
"campaigns": get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "attack-pattern", reverse=True), # technique_id => {campaign, relationship}
"groups": get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "attributed-to", "intrusion-set") # campaign_id => {group, relationship}
}
for technique_id in groups_attributing_to_campaigns["campaigns"]:
campaigns_attributed_to_group = []
# check if campaign is attributed to group
for campaign in groups_attributing_to_campaigns["campaigns"][technique_id]:
campaign_id = campaign["object"]["id"]
if campaign_id in groups_attributing_to_campaigns["groups"]:
campaigns_attributed_to_group.extend(groups_attributing_to_campaigns["groups"][campaign_id])
# update groups using techniques to include techniques used by a groups attributed campaign
if technique_id in groups_using_techniques:
groups_using_techniques[technique_id].extend(campaigns_attributed_to_group)
else:
groups_using_techniques[technique_id] = campaigns_attributed_to_group
return groups_using_techniques
# technique:campaign
def techniques_used_by_campaigns(thesrc):
"""returns campaign_id => {technique, relationship} for each technique used by the campaign."""
return get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "attack-pattern")
def campaigns_using_technique(thesrc):
"""returns technique_id => {campaign, relationship} for each campaign using the technique."""
return get_related(thesrc, "campaign", "uses", "attack-pattern", reverse=True)
# technique:software
def techniques_used_by_software(thesrc):
"""return software_id => {technique, relationship} for each technique used by the software."""
techniques_by_tool = get_related(thesrc, "tool", "uses", "attack-pattern")
techniques_by_malware = get_related(thesrc, "malware", "uses", "attack-pattern")
return {**techniques_by_tool, **techniques_by_malware}
def software_using_technique(thesrc):
"""return technique_id => {software, relationship} for each software using the technique."""
tools_by_technique_id = get_related(thesrc, "tool", "uses", "attack-pattern", reverse=True)
malware_by_technique_id = get_related(thesrc, "malware", "uses", "attack-pattern", reverse=True)
return {**tools_by_technique_id, **malware_by_technique_id}
# technique:mitigation
def mitigation_mitigates_techniques(thesrc):
"""return mitigation_id => {technique, relationship} for each technique mitigated by the mitigation."""
return get_related(thesrc, "course-of-action", "mitigates", "attack-pattern", reverse=False)
def technique_mitigated_by_mitigations(thesrc):
"""return technique_id => {mitigation, relationship} for each mitigation of the technique."""
return get_related(thesrc, "course-of-action", "mitigates", "attack-pattern", reverse=True)
# technique:sub-technique
def subtechniques_of(thesrc):
"""return technique_id => {subtechnique, relationship} for each subtechnique of the technique."""
return get_related(thesrc, "attack-pattern", "subtechnique-of", "attack-pattern", reverse=True)
def parent_technique_of(thesrc):
"""return subtechnique_id => {technique, relationship} describing the parent technique of the subtechnique"""
return get_related(thesrc, "attack-pattern", "subtechnique-of", "attack-pattern")[0]
# technique:data-component
def datacomponent_detects_techniques(thesrc):
"""return datacomponent_id => {technique, relationship} describing the detections of each data component"""
return get_related(thesrc, "x-mitre-data-component", "detects", "attack-pattern")
def technique_detected_by_datacomponents(thesrc):
"""return technique_id => {datacomponent, relationship} describing the data components that can detect the technique"""
return get_related(thesrc, "x-mitre-data-component", "detects", "attack-pattern", reverse=True)
# Example usage:
src = MemoryStore()
src.load_from_file("path/to/enterprise-attack.json")
group_id_to_software = software_used_by_groups(src)
pprint(group_id_to_software["intrusion-set--2a158b0a-7ef8-43cb-9985-bf34d1e12050"]) # G0019
# [
# {
# "object": Malware, # S0061
# "relationship": Relationship # relationship between G0019 and S0061
# },
# {
# ...
# }
# ]Because a group uses software, and software uses techniques, groups can be considered indirect users of techniques used by their software. These techniques are oftentimes distinct from the techniques used directly by a group, although there are occasionally intersections in these two sets of techniques.
The following recipe can be used to retrieve the techniques used by a group's software:
from stix2.utils import get_type_from_id
from stix2 import Filter
def get_techniques_by_group_software(thesrc, group_stix_id):
# get the malware, tools that the group uses
group_uses = [
r for r in thesrc.relationships(group_stix_id, 'uses', source_only=True)
if get_type_from_id(r.target_ref) in ['malware', 'tool']
]
# get the technique stix ids that the malware, tools use
software_uses = thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'relationship'),
Filter('relationship_type', '=', 'uses'),
Filter('source_ref', 'in', [r.source_ref for r in group_uses])
])
#get the techniques themselves
return thesrc.query([
Filter('type', '=', 'attack-pattern'),
Filter('id', 'in', [r.target_ref for r in software_uses])
])
get_techniques_by_group_software(src, "intrusion-set--f047ee18-7985-4946-8bfb-4ed754d3a0dd")Objects that are deemed no longer beneficial to track as part of the knowledge base are marked as deprecated, and objects which are replaced by a different object are revoked. In both cases, the old object is marked with a field (either x_mitre_deprecated or revoked) noting their status. In the case of revoked objects, a relationship of type revoked-by is also created targeting the replacing object.
Unlike other objects in the dataset, relationships cannot be revoked or deprecated. Relationships are considered deprecated/revoked if one of the objects it is attached to is revoked or deprecated.
Revoked and deprecated objects are kept in the knowledge base so that workflows relying on those objects are not broken. We recommend you filter out revoked and deprecated objects from your views whenever possible since they are no longer maintained by ATT&CK.
We recommend not using built-in STIX filters for removing revoked objects (e.g Filter('revoked', '=', False)). This is because the behavior of this specific filter is inconsistent depending on the method of access (using local data or accessing via the TAXII server). We recommend using the following code example to filter revoked objects instead. See issue #127 for more details.
from stix2 import Filter
def remove_revoked_deprecated(stix_objects):
"""Remove any revoked or deprecated objects from queries made to the data source"""
# Note we use .get() because the property may not be present in the JSON data. The default is False
# if the property is not set.
return list(
filter(
lambda x: x.get("x_mitre_deprecated", False) is False and x.get("revoked", False) is False,
stix_objects
)
)
mitigations = src.query([ Filter("type", "=", "course-of-action") ])
mitigations = remove_revoked_deprecated(mitigations)When an object is replaced by another object, it is marked with the field revoked and a relationship of type revoked-by is created where the source_ref is the revoked object and the target_ref is the revoking object. This relationship can be followed to find the replacing object:
from stix2 import Filter
def getRevokedBy(stix_id, thesrc):
relations = thesrc.relationships(stix_id, 'revoked-by', source_only=True)
revoked_by = thesrc.query([
Filter('id', 'in', [r.target_ref for r in relations]),
Filter('revoked', '=', False)
])
if revoked_by is not None:
revoked_by = revoked_by[0]
return revoked_by
getRevokedBy("attack-pattern--c16e5409-ee53-4d79-afdc-4099dc9292df", src)