-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 321
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Co-authored-by: skyline2006 <skyline2006@163.com> Co-authored-by: Zhikaiiii <1658973216@qq.com>
- Loading branch information
1 parent
18a97f2
commit 4eb809c
Showing
2 changed files
with
187 additions
and
6 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,179 @@ | ||
| # Modelscope-Agent知识库 | ||
|
|
||
| # 背景 | ||
|
|
||
| [modelscope-agent](https://github.com/modelscope/modelscope-agent)是GPTs 开源的实现方案,允许用户通过聊天、直接配置的方式进行llm的定制,可以允许用户使用自定义知识库以及接入多工具的能力。modelscope\_agent当前支持的知识库功能存在:可读文件类型有限、效果不稳定、召回策略固定、对大文件和多文件的支持较弱等问题。 | ||
|
|
||
| 为增强modelscope-agent的知识库能力,我们选择使用llama-index。LlamaIndex 是一个简单、灵活的数据框架,用于将自定义数据源连接到大型语言模型 (LLM)。同时llama-index提供[插件市场](https://llamahub.ai/?tab=tools),支持社区开发者贡献不同类型文件reader、不同召回策略、chunk方法等。结合社区能力,可很好地对modelscope\_agent的知识库能力做补充。 | ||
|
|
||
| # 简介 | ||
|
|
||
| 知识库的处理分为2个阶段:对知识库内容构建索引 -> 根据query召回知识库对应的内容并生成返回。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(urls=['tests/samples/常见QA.pdf']) | ||
| print(memory.run(query='高德天气api怎么申请')) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 基本内部流程如图,其中知识库内容的索引构建沿着浅绿色箭头所示,根据query召回知识库对应内容如深绿色箭头所示。 | ||
|
|
||
| 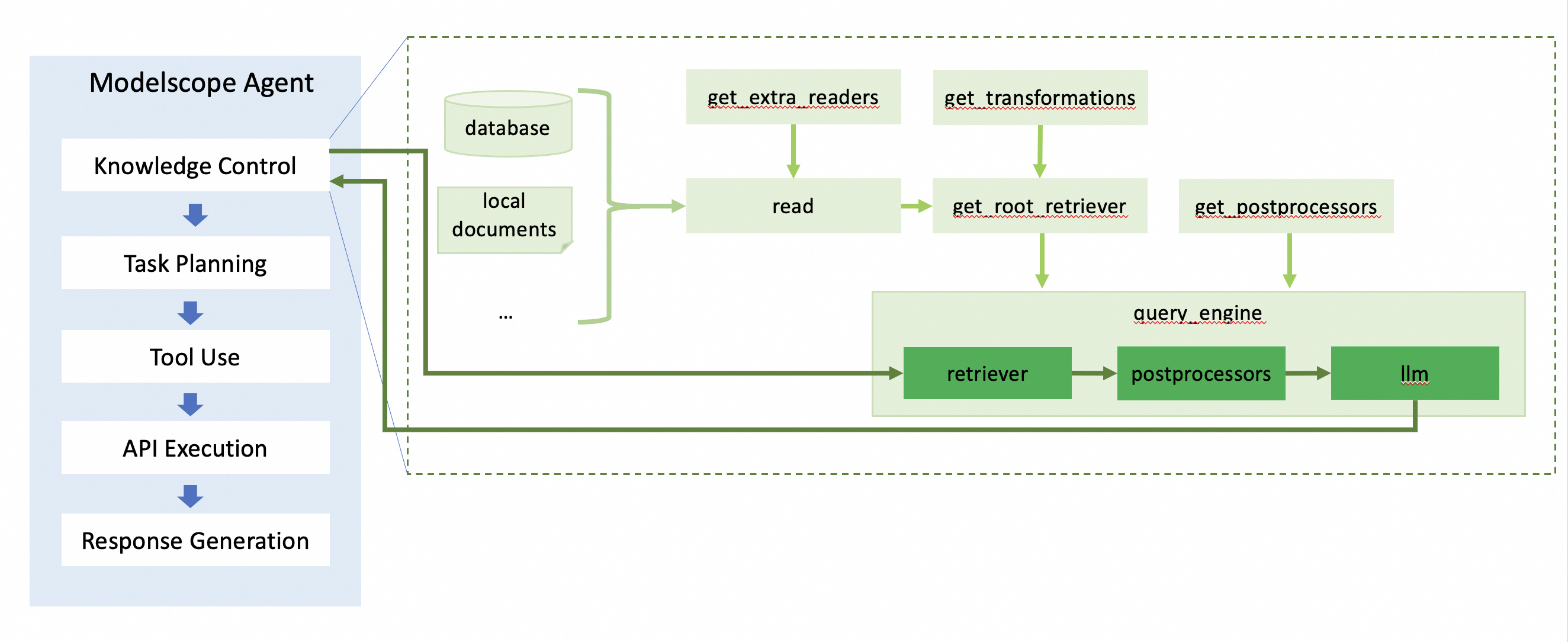 | ||
|
|
||
| 按照流程,内部各模块都支持灵活配置。接下来将依次介绍。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 文件读取 | ||
|
|
||
| 文件读取(read)模块会从不同来源、不同类型文档中读取信息。read中默认提供如下类型文件的读取:\`.hwp\`, \`.pdf\`, \`.docx\`, \`.pptx\`, \`.ppt\`, \`.pptm\`, \`.jpg\`, \`.png\`, \`.jpeg\`, \`.mp3\`, \`.mp4\`, \`.csv\`, \`.epub\`, \`.md\`, \`.mbox\`, \`.ipynb\`, \`txt\`, \`.pd\`, \`.html\`。其他类型的文件未配置默认reader,可在[插件市场](https://llamahub.ai/?tab=readers)选取更多类型文件reader、或自定义reader传入使用。未配置reader的其他类型文件传入时将被忽略。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
| from llama_index.readers.json import JSONReader | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(urls=['/home/test.json'], loaders={'.json': JSONReader}) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 构建索引 | ||
|
|
||
| 构建索引(indexing)包括对文档切片、将每个文档片段向量化(如有)等。由于索引构建方式与召回方式强相关,因此这部分内容与retriever的初始化(get\_root\_retriever)在一个函数内实现。其中,大文档chunk策略默认使用按语义切片(sentence\_spliter)、默认使用向量召回、默认的embedding模型为dashscope提供的text-embedding-v2。 | ||
|
|
||
| 如果您想使用其他chunk方式或emb模型,可以通过transformations和emb参数传入。其中,transformations参数允许接收的类包括:TextSplitter、NodeParser、MetadataExtractor,详情可参考[llama-index相关文档](https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index/blob/main/docs/docs/module_guides/loading/ingestion_pipeline/transformations.md);emb模型可在[插件市场](https://llamahub.ai/?tab=embeddings)选用 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
| from llama_index.core.extractors import TitleExtractor | ||
| from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding | ||
|
|
||
| # transformations参数以TitleExtractor为例 | ||
| # emb模型切换以OpenAIEmbedding为例。注意,使用该emb模型时,需要在可访问openai接口的环境中(在环境变量中配置openai的api-key,且需要在能够访问openai的网络环境中) | ||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(transformations=[TitleExtractor],emb=OpenAIEmbedding) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 缓存加载 | ||
|
|
||
| 缓存(storing)将indexing后的信息保存成文件,以便后续再次使用时无需重新indexing,同时也方便将indexing文件移动切换到其他环境使用。默认存储路径在./run下。可以通过storage\_path配置。同时通过use\_knowledge\_cache控制初始化时是否使用cache。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
|
|
||
| # 将2个文件indexing后存储到./tmp/目录 | ||
| MemoryWithRag( | ||
| urls=['tests/samples/modelscope_qa_2.txt', 'tests/samples/常见QA.pdf'], | ||
| storage_path='./tmp/', | ||
| use_knowledge_cache=False, | ||
| ) | ||
| # 从./tmp/目录加载 | ||
| memory = MemoryWithRag( | ||
| storage_path='./tmp/', | ||
| use_knowledge_cache=True, | ||
| ) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 查询 | ||
|
|
||
| 查询(querying):根据query内容从候选的indexed数据中进行召回,用召回的chunks访问llm,得到整合总结后的结果返回给用户。使用上可以在初始化时将文档链接通过urls传入。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(urls=['tests/samples/常见QA.pdf', 'tests/samples/modelscope_qa_2.txt']) | ||
| print(memory.run(query='高德天气api怎么申请')) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 在运行过程中,可以指定本次访问使用的文档范围。如果某个文档在初始化时未被传入,在run的过程中也会先对该文档进行加载、索引、存储。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag() | ||
| print(memory.run(query='模型大文件上传失败怎么办', url=['tests/samples/modelscope_qa_2.txt'])) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| querying的流程主要可分为3步:从候选文档中召回相关片段、对召回内容后处理、传入llm进行总结。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 召回 | ||
|
|
||
| 根据查询的请求内容,在候选知识库中找到相关性最高的一个或多个。前面介绍index时提到,召回方法默认为向量召回。如果您想使用其他召回方法,可以通过配置retriever参数实现。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
| from llama_index.retrievers.bm25 import BM25Retriever | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(retriever=BM25Retriever) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 后处理 | ||
|
|
||
| 在querying的流程中,支持对召回的知识库片段内容进行自定义后处理。比如召回多条内容时,可按照与query的相关性进行重排;您可以在llama-index的[插件市场](https://llamahub.ai/?tab=postprocessor)找到不同的后处理方法。后处理方法可通过post\_processors传入;如果该参数不传入,默认不进行后处理。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
| from llama_index.postprocessor.dashscope_rerank import DashScopeRerank | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(post_processors=[DashScopeRerank]) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### llm调用 | ||
|
|
||
| 召回的文档片段可能内容很多,其中与query查询相关的内容可能仅有一两句,或者需要总结。因此需要llm对召回后的内容进行有效信息抽取总结。您可以配置不同的llm,这个llm可以是modelscope-agent的模型对象或llm\_config配置方法;也可以是[llama-index插件市场](https://llamahub.ai/?tab=llms)中的,初始化完成的llm对象。不配置时,默认使用dashscope提供的qwen-max。 | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
|
|
||
| llm_config = {'model': 'qwen-max', 'model_server': 'dashscope'} | ||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(llm=llm_config) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| # 深度使用 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 多策略 | ||
|
|
||
| 如果单一的召回策略无法满足使用需求,需要定制复杂多策略。可以自定义实现多种召回器混用的召回策略。以下示例实现了一个混用向量召回和最佳匹配的召回器: | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from typing import List | ||
| from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex | ||
| from llama_index.retrievers.bm25 import BM25Retriever | ||
| from llama_index.core.base.base_retriever import BaseRetriever | ||
| from llama_index.core.schema import NodeWithScore | ||
| from llama_index.core.schema import QueryBundle | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
|
|
||
| class MyRetriever(BaseRetriever): | ||
| def __init__(self, index: VectorStoreIndex, **kwargs) -> None: | ||
| self._vector_retriever = index.as_retriever() | ||
| self._best_match_retriever = BM25Retriever.from_defaults(index) | ||
| super().__init__(**kwargs) | ||
|
|
||
| def _retrieve(self, query_bundle: QueryBundle) -> List[NodeWithScore]: | ||
| vector_nodes = self._vector_retriever.retrieve(query_bundle) | ||
| bs_nodes = self._best_match_retriever.retrieve(query_bundle) | ||
|
|
||
| vector_ids = {n.node.node_id for n in vector_nodes} | ||
| bs_ids = {n.node.node_id for n in bs_nodes} | ||
|
|
||
| combined_dict = {n.node.node_id: n for n in vector_nodes} | ||
| combined_dict.update({n.node.node_id: n for n in bs_nodes}) | ||
|
|
||
| retrieve_ids = vector_ids.intersection(bs_ids) | ||
|
|
||
| retrieve_nodes = [combined_dict[rid] for rid in retrieve_ids] | ||
| return retrieve_nodes | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(retriever=MyRetriever, urls=['tests/samples/modelscope_qa_2.txt']) | ||
| print(memory.run(query='模型大文件上传失败怎么办')) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 多模态 | ||
|
|
||
| 前面介绍文件读取时有提到,默认支持的除文本文件外,还支持 `.jpg`, `.png`, `.jpeg`, `.mp3`, `.mp4`等图片、音频、视频模态文件。以图片模态为例,图片对应的阅读器是[ImageReader](https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index/blob/main/llama-index-integrations/readers/llama-index-readers-file/llama_index/readers/file/image/base.py),其参数\`parse\_text\`为True时,会自动从hf下载调用识图模型`naver-clova-ix/donut-base-finetuned-cord-v2`,对图像内容进行理解,作为图像信息供后续的召回参考。由于从hf下载模型需要在特定的网络环境下,所以我们默认不使用读图功能,因此在默认配置中,图像模态给到召回器可参考的信息只有:这是个图像+图片路径与文件名。 | ||
|
|
||
| 后续我们会对此进行优化,增加图像理解模型的可选范围。如果当前您想使用图像理解功能,在能够使用 [naver-clova-ix/donut-base-finetuned-cord-v2](https://huggingface.co/naver-clova-ix/donut-base-finetuned-cord-v2) 的环境下可以这样操作: | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from modelscope_agent.memory import MemoryWithRag | ||
| from llama_index.readers.file import ImageReader | ||
|
|
||
| memory = MemoryWithRag(urls=['tests/samples/rag.png'], loaders={'.png': ImageReader(parse_text=True)}) | ||
| ``` |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters