EasyLoader provides a set of ready-to-use PyTorch DataSet and DataLoader classes that efficiently load data from a variety of sources.
By introducing various efficiencies and additional functionality, EasyLoader can make data access faster by up to an order of magnitude, removing hidden data bottlenecks from model training!
You can install EasyLoader using pip: pip install easyloader.
Three flavours of EasyLoader and EasyDataset class are provided.
ArrayDataset and ArrayDataLoader are for loading from NumPy arrays. The inputted arrays can either be a single array or a list of arrays of equal length. Like this:
from easyloader.dataset import ArrayDataset
from easyloader.loader import ArrayDataLoader
ds = DFDataset(df, arrays=[array_1, array_2])
X = ds[:10]
dl = DFDataLoader(df, arrays=array_1)
for batch in dl:
print(batch)
DFDataset and DFDataLoader are for loading from Pandas DataFrames. The inputted columns can be used to specify which columns to extract. Like this:
from easyloader.dataset import DFDataset
from easyloader.loader import DFDataLoader
ds = DFDataset(df, columns=[['column_1', 'column_2'], 'column_3'])
X, y = ds[:10]
dl = DFDataLoader(df, columns=['column_1', 'column_2'], batch_size=10)
for batch in dl:
print(batch)
If columns is left blank, all columns are used.
H5Dataset andH5DataLoader for loading from an H5 File. The keys attribute can be used to specify one or more keys to load, like this:
from easyloader.dataset import H5Dataset
from easyloader.loader import H5DataLoader
ds = H5Dataset(h5_file, keys=['key_1', 'key_2'])
values = ds[:10]
dl = H5DataLoader(h5_file, keys='key_1', batch_size=10)
for batch in dl:
print(batch)
Each EasyDataset can be shuffled and sampled directly, modifying the index of the underlying dataset. Separate seeds can be specified for each action, by specifying sample_seed and shuffle_seed.
Datasets can be sampled using ds.sample(sample_fraction=sample_fraction), or sampled on creation using the same argument. This can be useful when restricting to a small subset of the data for protyping.
Datasets can be shuffled using ds.shuffle(). In DataLoaders, if shuffle=True is set, then the data will be shuffled at the beginning of every loop of the data.
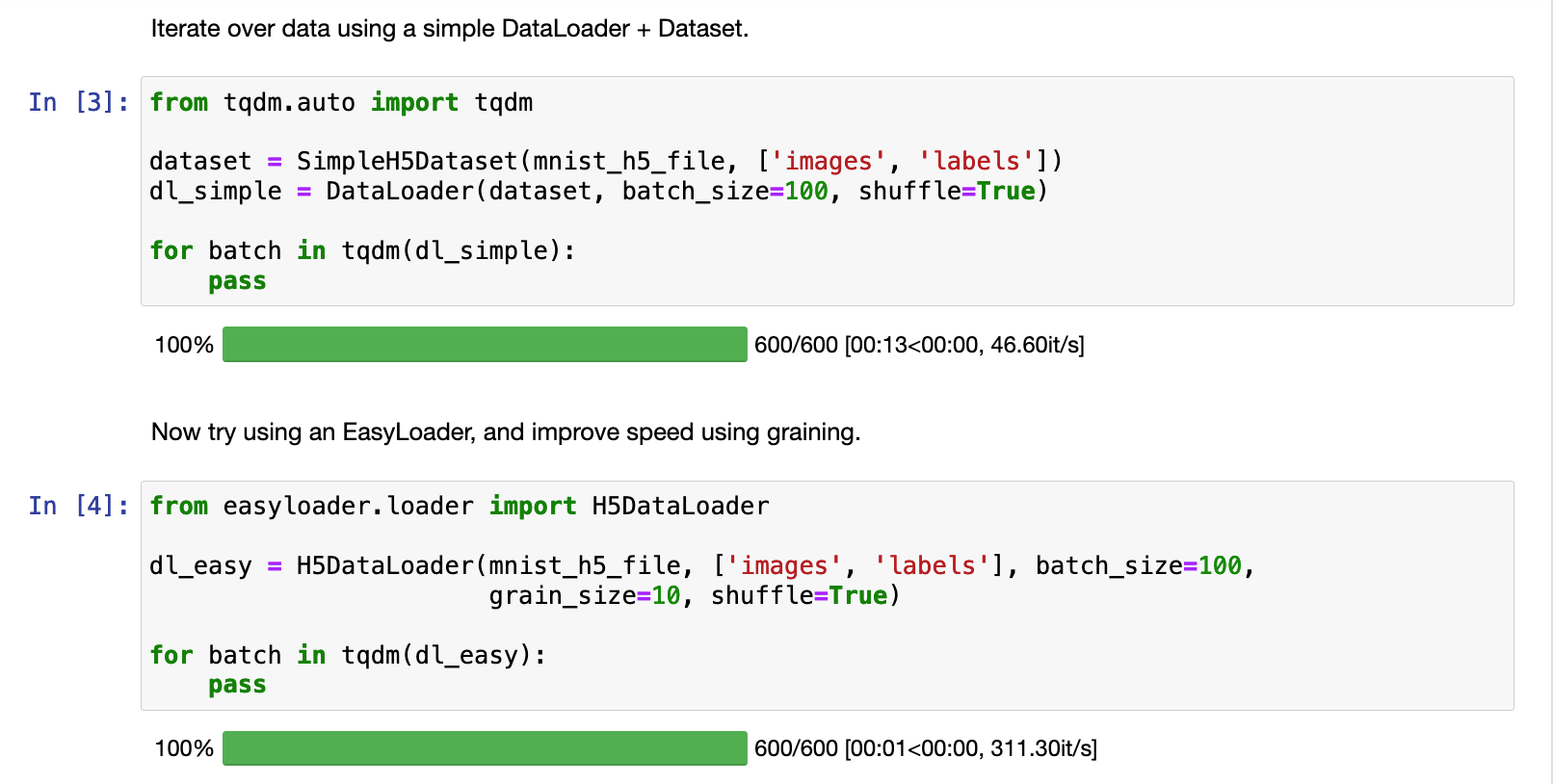
For H5 files, data is most efficiently loaded when it is contiguous on the disk. When data is shuffled, the chances that any two samples that are adjacent in the batch are also adjacent on the disk is low. To solve this, we use graining. Rather then shuffling or sampling fully, we break the data into grains and shuffle/sample those grains (see this blog post for more info).
It massively increases the speed of H5 access, generally without affecting model performance. To use graining with any data set, just set the grain_size parameter to anything higher than 1.
For example, graining with grain_size=10 improved the access speed for this H5 data set 13x:
It's often useful to keep track of the which sequences were used in each training or testing run.
For this purpose, both EasyDataset and EasyDataLoader classes have an ids attribute:
- For
ArrayDataset/ArrayDataLoader, this is inputted as a list of IDs - For
DFDataset/DFDataLoader, this also be specified as a column in the H5 file. - For
H5Dataset/H5DataLoader, this can be specified as a key in the H5 file.
In all cases, the numeric index will be used if this argument is left blank.
The IDs are accessed using ds.ids and will update whenever the data is shuffled or sampled. Wow!