-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 40
Autonomy
This chapter describes a simple high-level autonomy solution provided with OceanWATERS, and provides basic usage instructions.
- Approach
- Autonomy Repository
ow_plexilpackage and launch file- PLEXIL
- Fault Support
- System Health Monitor
- Architecture
As an autonomy testbed, it is not in the scope of the OceanWATERS project to develop a comprehensive autonomy solution for ocean world surface missions. In consequence, this release offers only basic autonomy capabilities that exercise the testbed and provide baseline functionality. The approach is a basic one: autonomy is provided by an onboard executive that executes onboard automation plans. PLEXIL is an open-source plan specification language and executive, chosen for this purpose because of the development team’s expertise (some were among PLEXIL’s early developers), its success in prior NASA autonomy efforts, and its suitability for basic Ocean Worlds lander autonomy as demonstrated in early prototypes.
The concept of operations envisioned for this approach has the entirety of high-level autonomy needed for a given ocean world mission encoded in PLEXIL plans resident on the lander and activated after the lander becomes operational on the surface of the world. A single top-level plan would be loaded and executed when the PLEXIL executive starts.
OceanWATERS’ autonomy components are contained entirely in the ow_autonomy repository. At present there is just one package in this repository, containing the PLEXIL plan executive and plans.
The ow_plexil package contains the PLEXIL executive and sample PLEXIL plans
for OceanWATERS. This package is built by default when building OceanWATERS. It
can also be individually built with the following command.
catkin build ow_plexil
The central autonomy component is a ROS node named ow_exec_node and is
henceforth referred to simply as the “executive node”. The PLEXIL executive is
embedded in the executive node, and accessed through the node’s interface and not
directly. The executive node interacts with different ROS nodes comprising the
testbed, found in different packages. It sends commands to, and reads telemetry
from, the simulated lander.
The executive node is normally started as part of the ow_exec.launch file:
roslaunch ow_plexil ow_exec.launch
The following sections provide essential instructions for use of the
ow_plexil package and executive node. Additional details are found
in the README files in this package.
PLEXIL (PLan EXecution Interchange Language) is an open-source software package available on GitHub. It should be built from source code in a particular way described in the installation instructions for OceanWATERS.
PLEXIL user documentation is found on a different GitHub page. Here there is a reference manual covering the language, the PLEXIL executive, the interfacing framework, and many other components of PLEXIL. If you are new to PLEXIL, we suggest that you start here, and then proceed to examine the PLEXIL plans provided with OceanWATERS, referring to the PLEXIL documentation as needed.
PLEXIL plans for OceanWATERS are found in
ow_plexil/src/plans.
This directory directly contains plans specific to OceanWATERS. Plans
shared by OceanWATERS and a sibling (proprietery) testbed at JPL
called OWLAT - Ocean Worlds Lander Autonomy
Testbed
are found in the common subdirectory, and those specific to OWLAT
are found in owlat. New PLEXIL plans must be added to the
appropriate subdirectory and, when compiled, will then be loadable by
the executive node and appear in its GUI for plan selection, described
below.
OceanWATERS plans are encoded as .plp files. This variant of PLEXIL
plan files allows the definition and use of C language macros, and in
particular the #include and #define macros are useful, as PLEXIL
does not support file inclusion or named constants directly. Compiled
PLEXIL plans have the extension .plx 1 and are generated
(as symbolic links to a deeper location) in following directory:
<ow_workspace>/devel/etc/plexil
All PLEXIL plans, except for brand new plans2, that need
compilation are automatically compiled when the ow_plexil package is
built. Plans (including new ones) can be individually compiled with
ow_plexil/scripts/ow-compile-plan, and this is much faster than
catkin build for compiling one or a few plans.
Plans interact with the lander by reading and reacting to telemetry, and commanding lander operations. Telemetry is read through PLEXIL Lookups, and lander operations are invoked through PLEXIL Commands.
The
ow-interface.h
and
ow-commands.h
files declare all of the Commands and Lookups available in
OceanWATERS. Please see these files for further information.
The ow_autonomy/ow_plexil/src/plans directory contains a variety of
PLEXIL plans. Some are described in its
README.md
file. They include test and demonstration plans, Europa reference
mission plans that simplify Sol 0 activities as described in JPL's
Europa Lander
study,
fault handling examples, and library plans for the operations of both
OceanWATERS and JPL's OWLAT simulator.
There are three ways PLEXIL plans can be selected for execution: specify a plan when starting the executive node, type in a plan name when prompted, or use the Plan Selection GUI in rqt.
- Specify a plan at start. The optional
plan:=parameter can be passed to the launch file to immediately begin running a given plan, e.g.
roslaunch ow_plexil ow_exec.launch plan:="ReferenceMission1.plx"
- Type a plan name when prompted. Once running, the executive node
terminal will prompt for a valid
.plxplan name whenever a plan is not already running. When entered, the plan will be executed, and then (if this plan terminates) the prompt will reappear.
[ INFO]: Starting PLEXIL executive node...
[ INFO]: Executive node started, ready for PLEXIL plans.
Enter a plan to execute (or use the rqt GUI):
A PLEXIL plan specified via the plan argument, or entered at the
terminal prompt, must correspond to a file with the same base name but
a .plp extension in the ow_plexil/src/plans directory.
- The Plan Selection GUI provides a bit more control and information
over what plans have been run, and displays their current status. It
is brought up in the
rqtviewer as a plugin when the simulator side launch file is started (e.g.europa_terminator_workspace.launch) but will not be able to function until theow_exec.launch filehas begun.

The Plan List column contains all plans applicable to the running testbed. A plan is staged for execution by selecting it and clicking "Add". A staged plan may be removed by selecting it and clicking "Remove". Staged Plans are sent for execution in the order listed; this order may be changed by selecting plans and clicking "Move Up" or "Move Down". The status of each plan is shown in the Active Plans column, and this list may be cleared with the "Clear" button.3
NOTE: Any plans that require input arguments (have interface variables) cannot be run at the top level by any of these means. They will return as "FAILED" in the Plan Selection GUI.
Commands and Lookups are handled by the Adapters listed in
plans/ow-config.xml. Each adapter registers itself to handle specific Commands
and Lookups, and the adapters are tried in the order listed. The final adapter
"ow_adapter", which is implemented by plexil-adapter/OwAdapter.cpp is the
default handler for anything that passes through, i.e. the domain-specific
Lookups and Commands.
Faults are referenced at two levels of granularity in the PLEXIL plan interface. A general fault refers to the presence of any fault in a subsystem. A specific fault corresponds to a specific fault flag published by the simulator.
There are 5 Boolean-valued general fault lookups: ArmFault,
AntennaFault, PowerFault, CameraFault, and
SystemFault. A true value indicates that at least one specific
fault is set in the corresponding fault message.
There are many Boolean-valued specific fault lookups, and these are
declared in plans/ow-interface.h and plans/common/common-interface.h.
Faults can be injected and cleared from PLEXIL plans. This facility is strictly for supporting simulations, and is not a valid component of prototypical mission plans. The commands for injecting and clearing a given fault, with a given probability (ranging from 0 to 1) are as follows.
Boolean Command inject_simulated_fault (String fault_name, Real probability);
Boolean Command clear_simulated_fault (String fault_name, Real probability);
They return true if the attempted operation occurred, false otherwise.
The ow_plexil package includes a basic framework for defining
relationships between faults, subsystems, and procedures (plans). Its
use is optional.
The key component of this framework is an XML file provided by the user that specifies how specific faults or groups of faults can impact a subsystem or procedure by making it inoperable. This information can be queried and used in plans through a set of supporting Lookups.
To use this feature you must create an XML file in
ow_plexil/src/plans that lists subsystems, faults of interest
within the subsystem, and subsystems and procedures that are
disabled by each fault or set of faults. The best way to learn this
encoding is through the provided example FaultDependenciesModel.xml.
The fault framework is effected by specifying this XML file when launching the executive node, as follows, using the provided file as an example:
roslaunch ow_plexil ow_exec.launch fault_dependencies_file:="FaultDependenciesModel.xml"
The following subsections describe the contents of this file and their
associated concepts. An example plan,
ow_plexil/src/plans/TestFaultDependencies.plp, is provided, and this
is a good way to get familiar with the system.
A subsystem in this framework is defined as a grouping of faults related to a piece of hardware or system. The term can also refer to the hardware itself. A subsystem has 4 properties of interest:
- local fault: a fault present in the subsystem itself
- non_local_fault: a fault present in another subsystems that impacts this subsystem
- faulty: a condition defined by the presence of at least one local fault
- inoperable: a condition defined by the presence of at least one local or non-local fault that impacts this subsystem
To impact a subsystem or procedure means to render it inoperable. For example, an antenna locked joint fault generally makes a panoramic imaging procedure inoperable.
If a subsystem is inoperable, any impacted subsystems or procedures will also be considered inoperable.
Subsystems can be given any name.
A procedure in this framework is simply any existing PLEXIL plan. A
procedure's name is the base filename of the plan, which is also the
name of the plan's root node. For example, the procedure "ArmStow"
refers to the plan ArmStow.plx.
A fault in this framework is named by the keys used in the FaultMap
members in ow_plexil/src/plexil-adapter/LanderInterface.h and
OwInterface.h. These are the same names used in the relevant ROS
message files found in ow_simulator/owl_msgs/msg.
Three Lookups are specific to this framework: IsOperable, IsFaulty, and ActiveFaults.
IMPORTANT NOTE: these Lookups should not be used in
node conditions (e.g. StartCondition) because their dynamic form
(LookupOnChange) is not supported.
-
IsOperable: This lookup takes a subsystem or procedure name defined in the XML and returns whether or not it is operable. -
IsFaulty: This lookup takes a subsystem name defined in the XML and returns whether or not it is faulty (has local faults). -
ActiveFaults: This lookup takes a subsystem name defined in the XML and returns the active fault names in that subsystem. If "System" is passed in, all active fault names will be returned. Up to 10 names are returned due to PLEXIL's fixed array size.
These lookups will return Unknown if used without launching with the
Fault Dependencies framework. See
ow-interface.h
for their declarations.
The following diagram illustrates the key artifacts of the ow_plexil package
and their relationships.
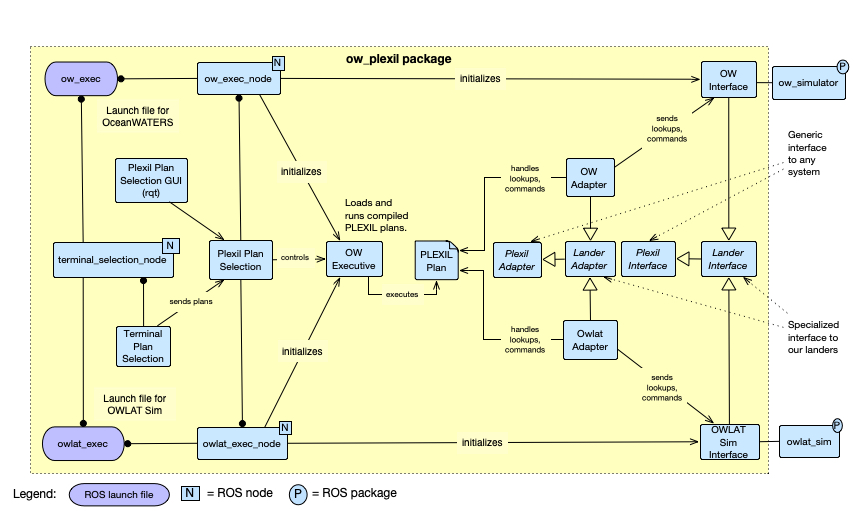
-
Due to a build system deficiency, when PLEXIL
.plpfiles are compiled, an intermediate file with.pleextension is generated and saved in the same directory as the.plpfiles. They are not automatically deleted when the ow_plexil package is cleaned, but may be safely ignored, since the.plpfiles are recompiled whenever needed. -
Due to another build system deficiency, the
ow_plexilpackage must be rebuilt any time a new plan is added. This is not the case when an existing plan is edited. To rebuild just theow_plexilpackage, perform these steps:catkin clean ow_plexil catkin build ow_plexil -
If the executive node is terminated while a plan was running, the status of this plan remains "Running" in the GUI. If you restart the executive node, you should clear this list before running another plan. This step is not required, but if omitted, the GUI will not accurately reflect the state of the new executive node session.