Eglot aims to support the Language Server Protocol, but none of its unofficial extensions. Eglot-x adds support for some of these protocol extensions.
If you find a bug in Eglot, please, try to reproduce it without Eglot-x, because Eglot-x substantially modifies Eglot's normal behavior as well.
Add the following lines to your init file to enable eglot-x
(with-eval-after-load 'eglot
(require 'eglot-x)
(eglot-x-setup))To adjust which extensions are enabled:
M-x customize-group RET eglot-x RET
This extension allows the client and the server to have
separate file systems. For example, the server can run inside a
Docker container, or the source code can be on a remote system
accessed by Tramp. The client can send files to the server only from
the result of project-files. The list of eligible files can further
limited by eglot-x-files-visible-regexp and
eglot-x-files-hidden-regexp. This feature works if project-roots
and project-external-roots are set correctly.
Enabling extension disables Eglot's built-in support for Tramp files.
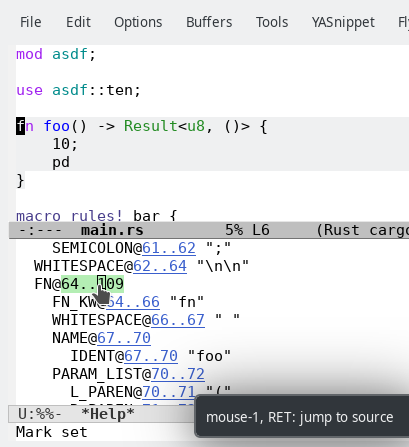
The command `eglot-x-find-refs' is the entry point for the extra methods. You can bind it to a key:
(define-key eglot-mode-map (kbd "s-.") #'eglot-x-find-refs)Currently, the ccls and rust-analyzer are the only
servers whose extra reference methods eglot-x supports.
The extension allows the client and the server to negotiate a proper encoding to be used in transmitting column positions.
-
Snippet TextEdits: see variable
eglot-x-enable-snippet-text-edit. -
Join Lines: see defun
eglot-x-join-lines. -
Move Item: see defun
eglot-x-move-item-downandeglot-x-move-item-up. -
On Enter: see defun
eglot-x-on-enter. -
Matching Brace: see
eglot-x-matching-brace. However, emacs' ownbackward-sexp, andforward-sexpseem to be more useful. -
Open External Documentation: see defun
eglot-x-open-external-documentation. -
Local Documentation: see variable
eglot-x-enable-local-docs-support. -
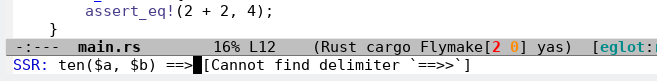
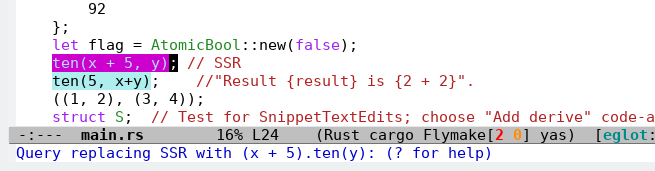
Structural Search Replace (SSR): see defun
eglot-x-structural-search-replace.The server checks the correctness of the query while you type:
The replacement process is similar to
query-replace: -
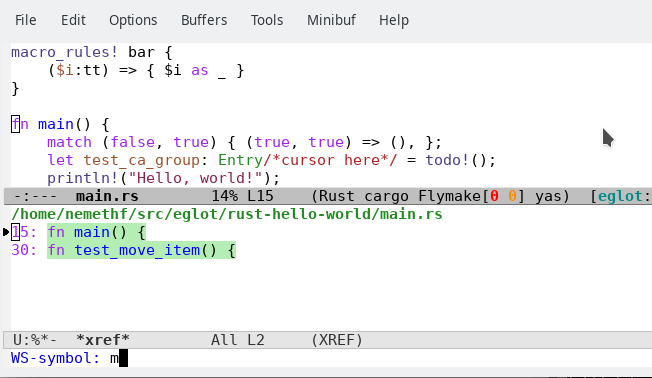
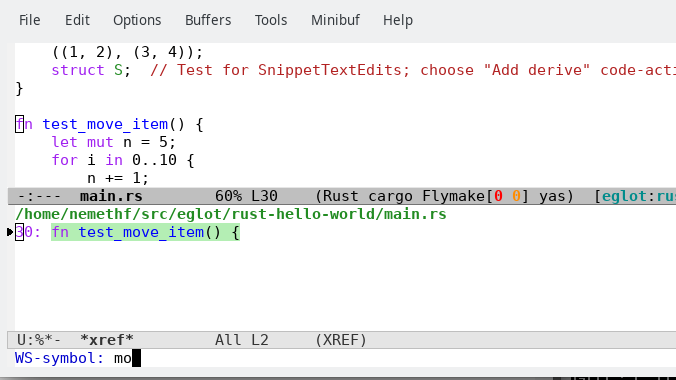
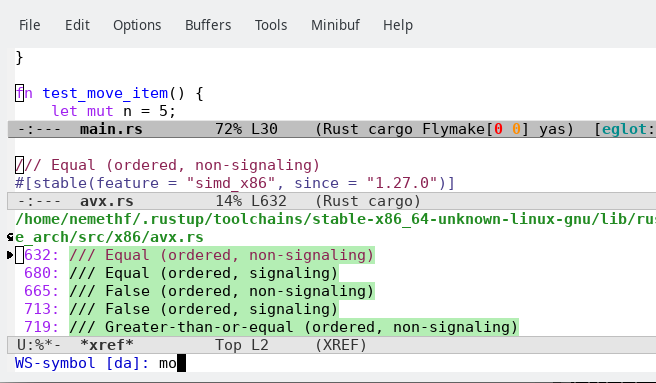
Workspace Symbols Filtering: see defun
eglot-x-find-workspace-symbol.The xref buffer shows the current matches while the user iteratively types the query and another buffer shows the location of the first match.
Additional input refines the results and the point in main.rs is changed once again to the location of the new first result:
You can change the search scope and kind with
C-landC-M-l, respectively. See variableeglot-x-ws-keymap. The non-default settings are shown between braces:Currently, the xref buffer shows the first lines of the matches. This is not always helpful.
-
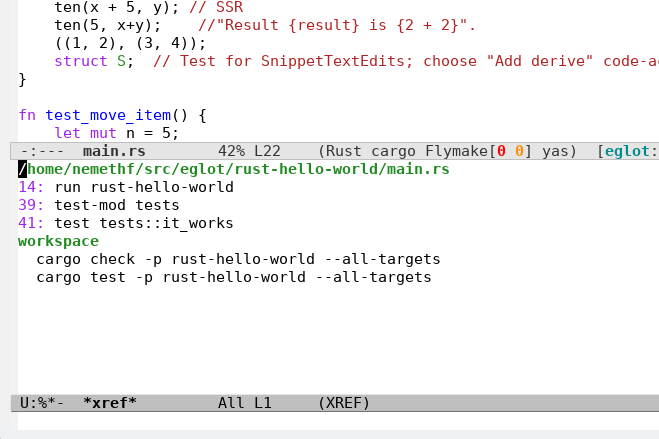
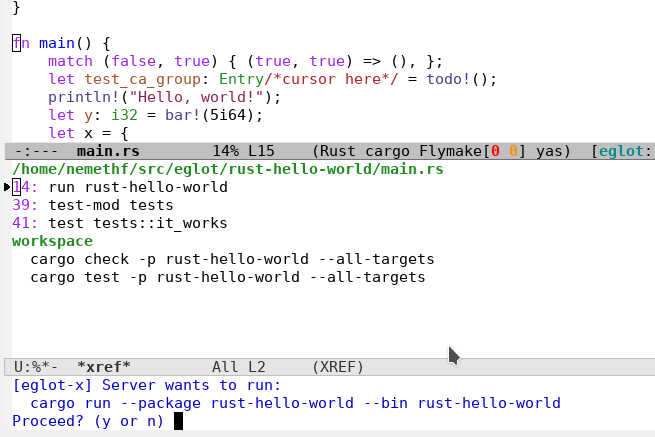
Runnables: see defun
eglot-x-ask-runnables.Results for the whole buffer:
Selecting the first "runnable":
The "runnable" is executed as a
compile-command: -
Server Status: see variable
eglot-x-enable-server-status. The mode-line displays the status unless it is "permanently OK". -
Colored diagnostics: see variable
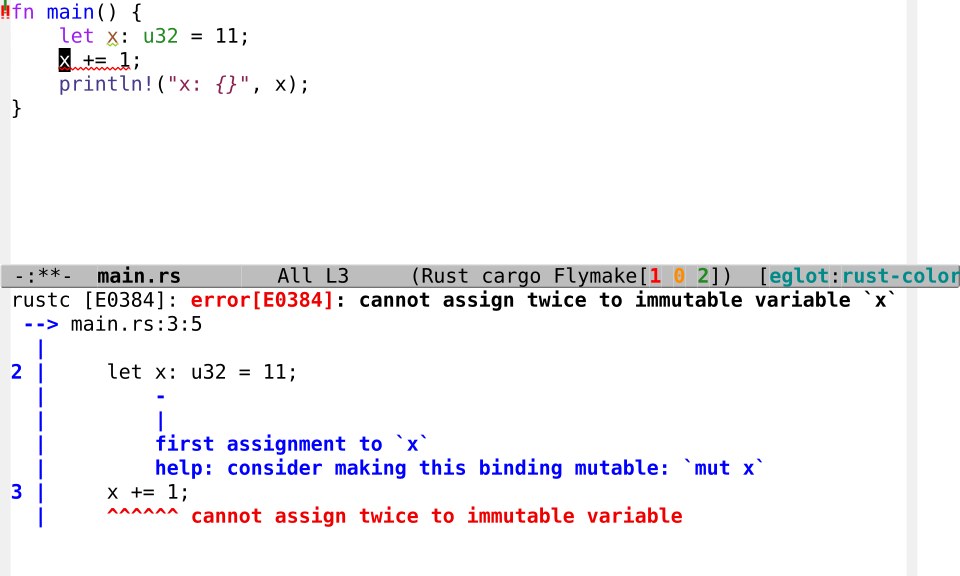
eglot-x-enable-colored-diagnostics.`flymake-goto-next-error' shows a colored diagnostic message:
(The ansi-color.el of Emacs 27 is too old for this feature, Emacs 29 is OK.)
-
Open Server Logs: LSP servers can ask the client to show their logs, see variable
eglot-x-enable-open-server-logsfor details.
-
Expand Macro: see defun
eglot-x-expand-macro. -
Related Tests: see defun
eglot-x-ask-related-tests. -
Reload Workspace: see defun
eglot-x-reload-workspace. -
Rebuild proc-macros: see defun
eglot-x-rebuild-proc-macros. -
Flycheck commands: see defuns
eglot-x-run-flycheck,eglot-x-clear-flycheck, andeglot-x-cancel-flycheck. (These commands implement lsp-extensions and have nothing to do with the flycheck Emacs package.) -
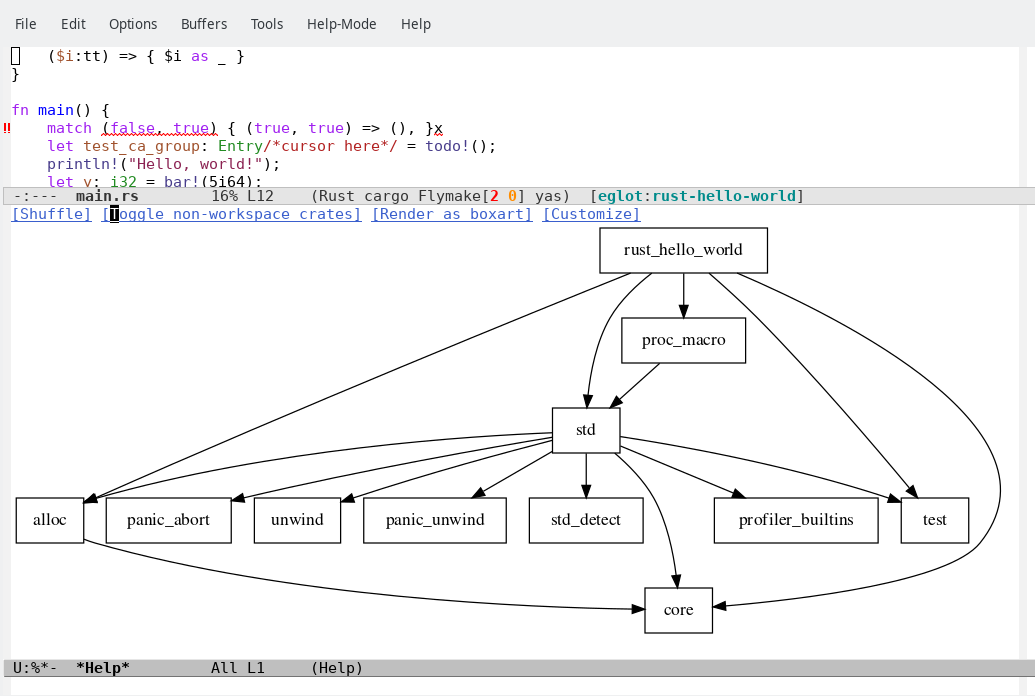
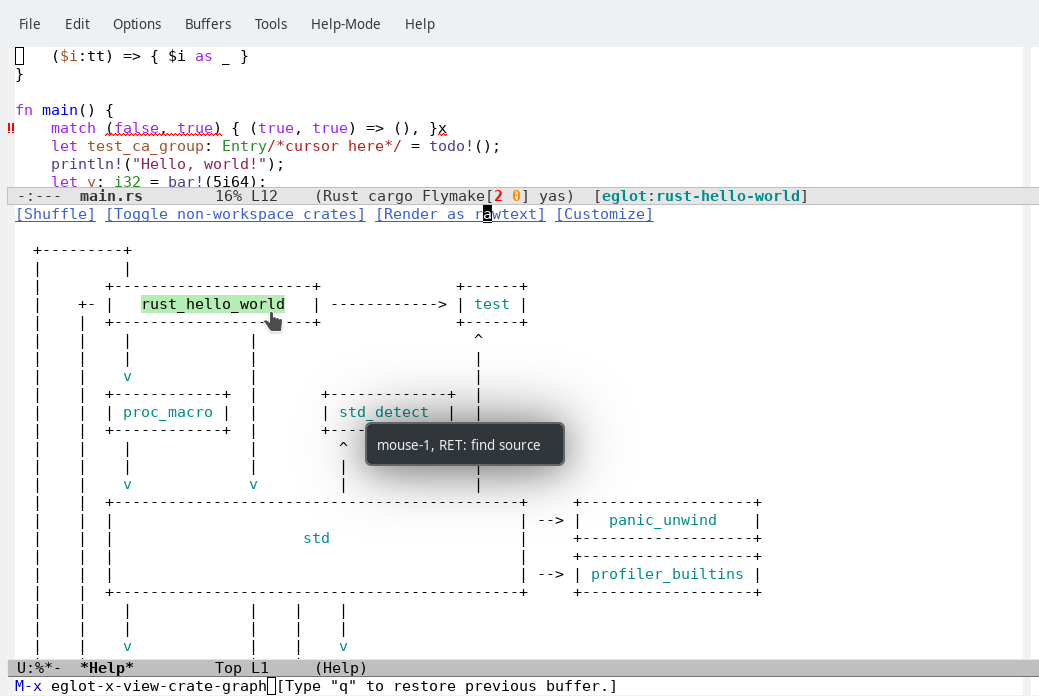
View Crate Graph: see variable
eglot-x-graph-typeand defuneglot-x-view-crate-graph.You can also jump to the crate (Cargo.toml) if the graph-type is not 'svg':
(This command requires graphviz/graph-easy.)
-
Dependency Tree: see defun
eglot-x-find-crate. -
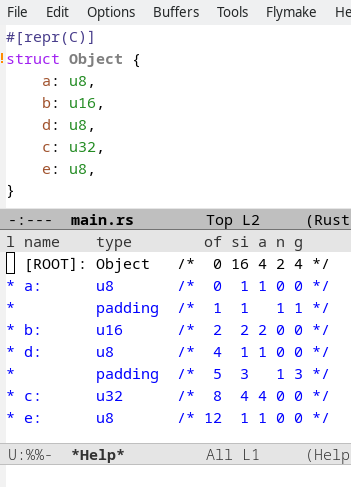
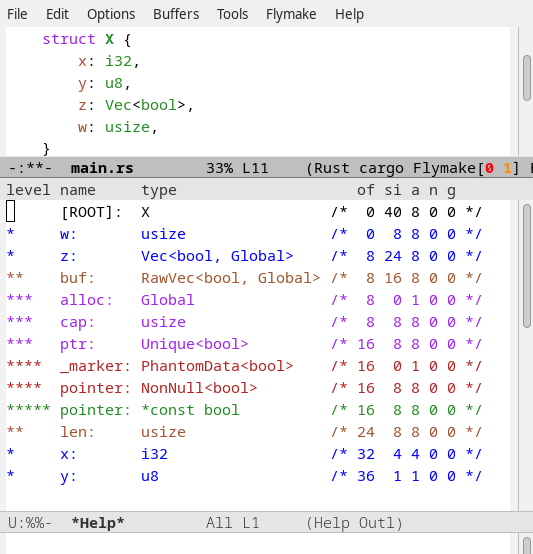
View Recursive Memory Layout: the command
eglot-x-view-recursive-memory-layoutshows the memory layout of the thing under point.Tooltips show the column names: offset, size, alignement, number of gaps, and gap-size. The output format is inspired by pahole, which (I think) more practical than the upstream graphical output:
The built-in outline-minor-mode helps to naviagate / understand a recursive layout.
A better layout optimization approach relies on run-time statistics as well, which this command does not provide.
-
Analyzer Status: see defun
eglot-x-analyzer-status. -
Syntax Tree: see defun
eglot-x-show-syntax-tree. -
View Hir: see defun
eglot-x-view-hir. -
View Mir: see defun
eglot-x-view-mir. -
Interpret Function: see defun
eglot-x-interpret-function. -
View File Text: see defun
eglot-x-debug-file-sync-problems. -
(Memory Usage): see defun
eglot-x-memory-usage.
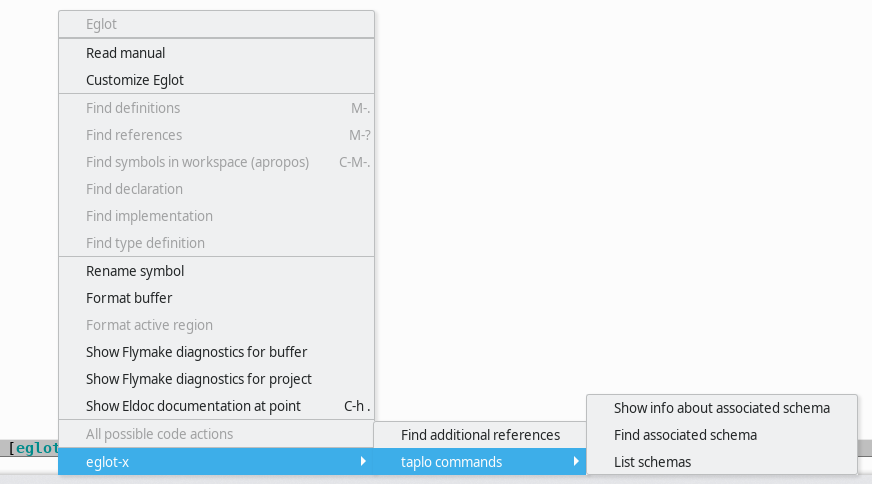
Relying on taplo/associatedSchema and taplo/listSchemas extensions eglot-x provides the following commands:
-
eglot-x-taplo-show-associated-schema -
eglot-x-taplo-find-associated-schema -
eglot-x-taplo-list-schemas
Eglot-x provides ff-find-related-file backends for some LSP servers.
See the documentation of eglot-x-enable-ff-related-file-integration.