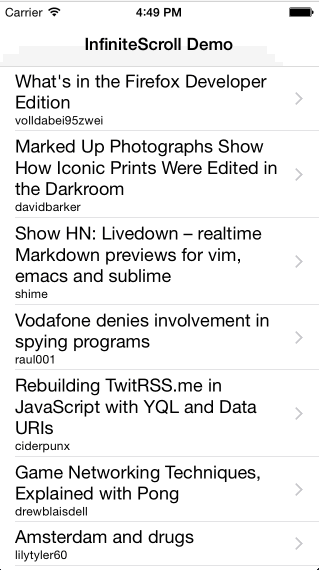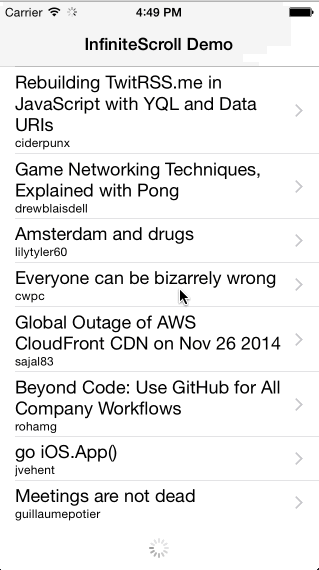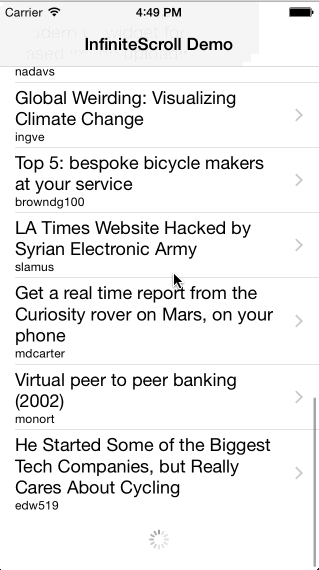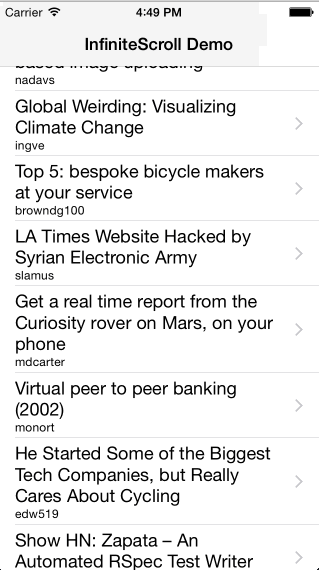
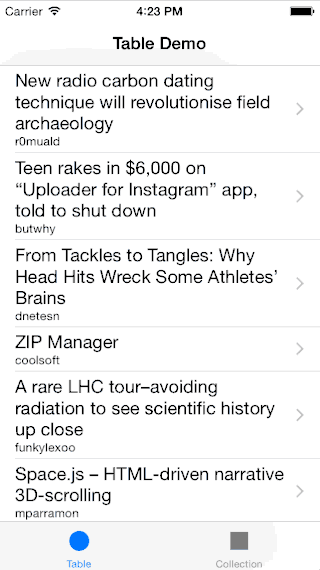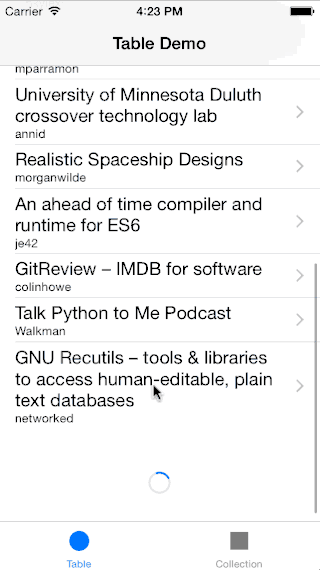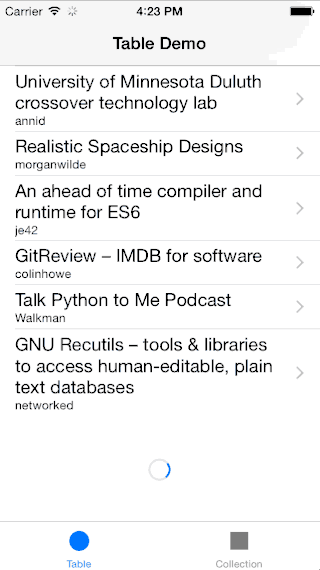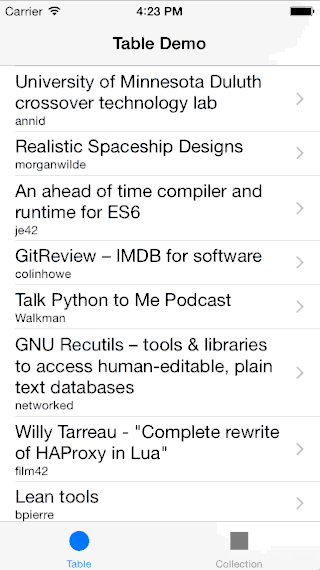
Infinite scroll implementation as a category for UIScrollView.
|
|

|
* The content used in demo app is publicly available and provided by hn.algolia.com and Flickr. Both can be inappropriate.
Be aware that this category swizzles setContentOffset
and setContentSize on UIScrollView.
Add new package using github repo URL:
https://github.com/pronebird/UIScrollView-InfiniteScroll
Then import module in the source code:
import UIScrollView_InfiniteScrollAdd the following line in your Podfile:
pod 'UIScrollView-InfiniteScroll', '~> 1.3.0'#import <UIScrollView_InfiniteScroll/UIScrollView+InfiniteScroll.h>or if using modules:
@import UIScrollView_InfiniteScroll;Add the following line in your bridging header file:
#import <UIScrollView_InfiniteScroll/UIScrollView+InfiniteScroll.h>Add the following line in your Cartfile:
github "pronebird/UIScrollView-InfiniteScroll" ~> 1.3.0#import <UIScrollView_InfiniteScroll/UIScrollView+InfiniteScroll.h>or if using modules:
@import UIScrollView_InfiniteScroll;import UIScrollView_InfiniteScrollThis component comes with example app written in Swift.
If you use CocoaPods you can try it by running:
pod try UIScrollView-InfiniteScrollhttp://pronebird.github.io/UIScrollView-InfiniteScroll/
In order to enable infinite scroll you have to provide a handler block using
addInfiniteScrollWithHandler. The block you provide is executed each time infinite scroll
component detects that more data needs to be provided.
The purpose of the handler block is to perform asynchronous task, typically networking or database fetch, and update your scroll view or scroll view subclass.
The block itself is called on main queue, therefore make sure you move any long-running tasks to
background queue. Once you receive new data, update table view by adding new rows and sections,
then call finishInfiniteScroll to complete infinite scroll animations and reset the state of
infinite scroll components.
viewDidLoad is a good place to install handler block.
Make sure that any interactions with UIKit or methods provided by Infinite Scroll happen on main
queue. Use dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue, { ... }) in Objective-C or
DispatchQueue.main.async { ... } in Swift to run UI related calls on main queue.
Many people make mistake by using external reference to table view or collection view within the handler block. Don't do this. This creates a circular retention. Instead use the instance of scroll view or scroll view subclass passed as first argument to handler block.
// setup infinite scroll
[tableView addInfiniteScrollWithHandler:^(UITableView* tableView) {
// update table view
// finish infinite scroll animation
[tableView finishInfiniteScroll];
}];tableView.addInfiniteScroll { (tableView) -> Void in
// update table view
// finish infinite scroll animation
tableView.finishInfiniteScroll()
}UICollectionView.reloadData causes contentOffset to reset. Instead use
UICollectionView.performBatchUpdates when possible.
[self.collectionView addInfiniteScrollWithHandler:^(UICollectionView* collectionView) {
[collectionView performBatchUpdates:^{
// update collection view
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
// finish infinite scroll animations
[collectionView finishInfiniteScroll];
}];
}];collectionView.addInfiniteScroll { (collectionView) -> Void in
collectionView.performBatchUpdates({ () -> Void in
// update collection view
}, completion: { (finished) -> Void in
// finish infinite scroll animations
collectionView.finishInfiniteScroll()
});
}You can reuse infinite scroll flow to load initial data or fetch more using
beginInfiniteScroll(forceScroll). viewDidLoad is a good place for loading initial data,
however absolutely up to you to decide that.
When forceScroll parameter is true, Infinite Scroll component will attempt to scroll down to
reveal indicator view. Keep in mind that scrolling will not happen if user is interacting with
scroll view.
[self.tableView beginInfiniteScroll:YES];tableView.beginInfiniteScroll(true)Sometimes you need to prevent the infinite scroll from continuing. For example, if your search API has no more results, it does not make sense to keep making the requests or to show the spinner.
[tableView setShouldShowInfiniteScrollHandler:^BOOL (UITableView *tableView) {
// Only show up to 5 pages then prevent the infinite scroll
return (weakSelf.currentPage < 5);
}];// Provide a block to be called right before a infinite scroll event is triggered.
// Return YES to allow or NO to prevent it from triggering.
tableView.setShouldShowInfiniteScrollHandler { _ -> Bool in
// Only show up to 5 pages then prevent the infinite scroll
return currentPage < 5
}Ideally you want your content to flow seamlessly without ever showing a spinner. Infinite scroll offers an option to specify offset in points that will be used to start preloader before user reaches the bottom of scroll view.
The proper balance between the number of results you load each time and large enough offset should give your users a decent experience. Most likely you will have to come up with your own formula for the combination of those based on kind of content and device dimensions.
// Preload more data 500pt before reaching the bottom of scroll view.
tableView.infiniteScrollTriggerOffset = 500;You can use custom indicator instead of default UIActivityIndicatorView.
Custom indicator must be a subclass of UIView and implement the following methods:
@objc func startAnimating()
@objc func stopAnimating()let frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: 24, height: 24)
tableView.infiniteScrollIndicatorView = CustomInfiniteIndicator(frame: frame)Please see example implementation of custom indicator view:
At the moment InfiniteScroll uses indicator's frame directly so make sure you size custom indicator
view beforehand. Such views as UIImageView or UIActivityIndicatorView will automatically resize
themselves so no need to setup frame for them.
Please see CHANGES
Demo app icon by PixelResort.