The purpose of this library is to facilitate access to KDB+ servers from the modern web browsers as much as possible. In the extreme case all you need to do is just add two html tags without any settings to an html page (and kdb-wc.js script) and data will be loaded and added to the page automatically.
<kdb-srv></kdb-srv>
<kdb-table>([] sym: 50?(5?`5);time:.z.T+til[50]*00:00:10; price: 50?40*50?1.0)</kdb-table>
This library is based on the new HTML5 feature - web components - entities that look like the ordinary html tags but can encapsulate arbitrary logic and perform complex tasks behind the scene. Currently not all browsers support them or enable this functionality by default thus you may need to include document-register-element.js library (can be found in external directory) that provides the same functionality (it is used in all examples).
This library is intended for presentations, prototyping, visualizing datasets.
The library supports the latest 3.4 SSL feature. You can connect either via https or wss.
To use this library include kdb-wc.js into your html page:
<script type="text/javascript" src="kdb-wc.js"></script>
Components: kdb-srv, kdb-query, kdb-table, kdb-chart, kdb-editor, KDBLex.
The library should work with IE10 (maybe IE9 too), the latest Firefox and Chrome and probably all other modern browsers.
Some other libraries may be needed (all with open source licenses like MIT):
document-register-element.js- required if document.registerElement is not supported.c.js- serialization/deserialization of KDB objects for Websocket.c3- charts library C3.d3- charts library D3 (C3 is based on it).dygraph- another charts library for timeseries.datatables- datatables library.jsgrid- grid library.jquery- jquery (required by jsgrid and datatables).ace- ace editor.
All libraries can be found in external directory.
The core of the library is kdb-srv component. It allows users to execute arbitrary queries either via an Ajax http(s) request or via a websocket/secure websocket. It supports string
and binary protocols for websockets and json, xml and string data formats.
kdb-srv can be used with the default .z.ph handler(and/or -E flag). You may need to add fix-json attribute if your .z.ph fails to process queries like 'json? query' or if you want
to use cross domain (CORS) requests.
Websockets allow you to connect to any server not just the default one. You can even load your page as 'file://' and still be able to use them. You should though set
the correct ws handler on the target server because the default .z.ws does nothing - use srv.q as an example.
Some exotic http(s) request methods are supported including cross origin requests (xhttp) and JSONP.
xhttp requests require the server side support - you need to set Access-Control-Allow-Origin header. .h namespace can be automatically patched via fix-json attribute.
JSONP requests also require the server side support (they are not restricted like xhttp requests but the server need to be aware of them). Your server (and your optional query prefix)
must accept (`id;query) string as an argument and return KDB.processJSONP("id",jsObject) string as the response. fix-json will inject the default implementation into
.h namespace (jsp? prefix - it is also the default prefix in this case).
For secure connection using xhttp or jsonp provide the server name with the protocol prefix: https://srv.com
Example:
# default http srv with json format (beware of 3.2 json issue)
<kdb-srv></kdb-srv>
# websocket srv with an optional k-srv-uri setting
<kdb-srv k-srv-type="ws" k-srv-uri="localhost:5566" debug="true"></kdb-srv>
Supported attributes:
k-return-type- optional,jsonby default. Data format returned by the server. It can bejson,xml,qortxt. Websockets supportjsonandq. Http -json,xmlandtxt,qis supported viak-deserializeoption over json.k-srv-type- optional, ws, wss, jsonp, xhttp, https or http (default). xhttp and jsonp mean cross origin requests and requirek-srv-uri+ server side support. ws(s) - websockets.k-feed- optional, valid only for websockets. If true the first query establishes a subscription and then all data from the connection will be sent to it.k-srv-uri- optional, target websocket or xhttp server. Format: "host:port". By default it is the current web server. If you use xhttp or jsonp you may add an optional protocol prefix: "https://host:port"k-srv-user- optional, a user for http(s) requests.k-srv-pass- optional, a password for http(s) requests.k-target- optional, a server name ork-idof an element with this name. It can be used withsrv.qto turn it into a proxy. Queries will be executed viasrv.qon another server. When the name is '' this option is ignored.k-prefix- optional, a prefix to be added to every query.xml?for example. It is set to eitherjson?enlistorjsn?enlistorjsp?if it is not provided and the result type isjson.k-id- optional, this id can be used to link other components to this one.k-deserialize- optional, if set to true in an http(s) srv with json return type results like ("deserialize";`int$-8!expr) will be deserialized via c.js. This will help if there are json parse exceptions. You should convert the result byte array to int or long.fix-json- optional, if it is set kdb-srv will send an additional query to fix the json serialization issue in the default .z.ph in kdb+ 3.2(it will set .h.tx[`jsn] to .j.j'). If srv type is xhttp it will also patch some .h functions to include the correct CORS (cross origin) header. If srv type is jsonp it will also add jsp handler to .h.tx.debug- optional. Can be set to true to see debug prints in the browser console.
Api:
runQuery(query,callBack)orrunQuery(query)- execute a query and return the result viacallBack.callBackis optional and should accept two parameters - result and error.
kdb-query encapsulates a query, searches for its parameters, executes it, distributes the result to its consumers. It can be attached to only one kdb-srv but can be used by many data consumers or data providers.
kdb-table and kdb-chart components can create kdb-query implicitly.
Example:
# basic example
<kdb-query>til 10</kdb-query>
# you can set srv explicitly, assign k-id, update another html element with the result, turn on debug prints, use k-id references to parametrize the query
<kdb-query k-srv="srv2" k-id="q1" k-update-elements="pre" debug="true">.Q.s
`select`txt`pass`check`radio`textarea`span!(`$s$;"$ft$";"$fp$";$fc$;`$fr$;"$fta$";"$t$")</kdb-query>
# multiple update
<kdb-query k-dispatch-update="true" k-update-elements="pre myObj.var">``kid1`kid2!(genRes;resForKID1;resForKID2)</kdb-query>
You can provide parameters to the query by using kdb-editor,select, textarea, input with types text, password, radio, checkbox and any other element with the meaningful textContent (span for example).
There are also special parameters: use k-interval), self, load, timer if src is self), k-attr attribute
to the event source, attributes set in k-attr will be added to the query parameters (see params example).
kdb-query can update other elements with its result. The result should have the correct format - string for text elements or kdb-editor, list of objects (table) for kdb-table and kdb-chart,
string array for select or datalist. It can also update any element that has kdbUpd function. There are 3 way the update may be done:
- consumer can subscribe to the query via
onresultfunction. - consumer
k-idor var name can be added tok-update-elements. - consumer
k-idsor var names can be set as keys of the result dictionary whenk-dispatch-updateis true. In this case the general result will be taken from key `.
Supported attributes:
-
k-query- optional, a query can be set either in this attribute or between the tags like in the example above. -
k-srv- optional, link to akdb-srv. If it is not set the first availablekdb-srvcomponent will be used. -
k-execute-on- optional, list of events that cause the query to execute. Contains onlyloadby default.load- when the document is loaded,manual- do not execute,timer- use timer,k-idof a button or some other html element - execute on click (buttons and unknown elements) or change event (inputs, select and etc), k-id ofkdb-editor- execute on its exec event, k-id of another query - execute after it (its result is available via$txt$ ). -
k-update-elements- optional, users can either subscribe tokdb-queryevents or can provide theirk-idor var names in this attribute, in this way you can update arbitrary html elements. -
k-dispatch-update- optional, if true the result must be a dictionary with keys corresponding to k-ids or var names.kdb-querywill then distribute the result. Use key ` fork-update-elements. -
k-status-var- optional, report the current number of running queries into this JS variable. -
k-on-error- optional, likek-update-elementsbut if any srv error occurs it will be sent to these object(s). -
k-delay- optional, in millis. Withtimersets the delay for the first execution. -
k-interval- optional, in millis. Withtimercauses query to rerun everyintervalmillis. The first query will be executed with the delay of eitherk-delayor thisk-interval. -
k-escape-q- optional. If set forceskdb-queryto escape " and \ symbols in the query parameters (not query itself!). -
k-filter- optional, name of a Javascript function or an object withfilterfunction that will postprocess the result. -
k-id- optional, this id can be used to link other components to this one. -
debug- optional. Can be set to true to see debug prints in the browser console.
There are attributes that kdb-query understands on its target elements:
k-append- on text elements defines how the new result is added. Possible values: 'top', 'bottom', 'overwrite'.k-content-type- text or html, how the result is added to the element: as html or text.k-id- this id can be used to link other components tokdb-query.k-preserve- selects will preserve their values on updates (if the new list contains the previous value).
Api:
onresult(f)- subscribe to 'newResult' event. If the result is already ready thenfwill be called immediately.fshould have one parameter - result.setupQuery()- call it after you change the attributes.runQuery(args)- run the query if it was not run before. Args is an optional object like {param1:val1, ...}.rerunQuery(args)- rerun the query.KDB.rerunQuery(kID,args)- rerun a query with the specific k-id (onclick="KDB.rerunQuery('id1',{data:10})").
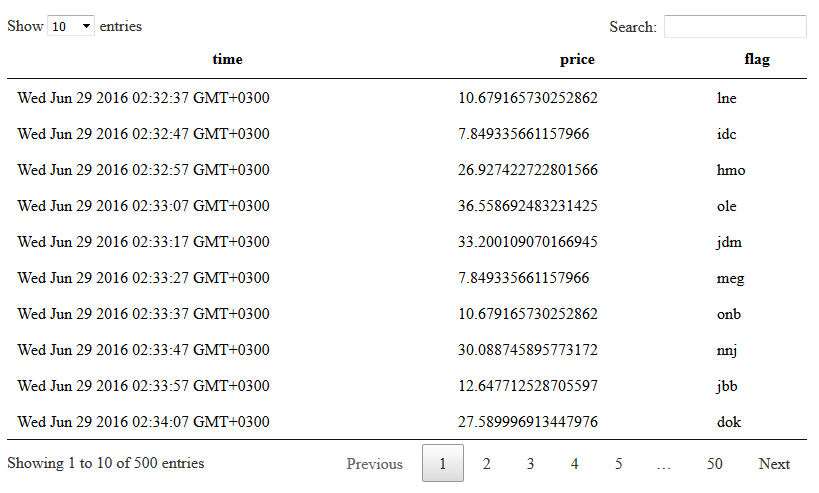
kdb-table can be used to show a table. kdb-table relies on kdb-query to run the actual query. kdb-query can be set either with its k-id or created implicitly via k-query attribute or the content of the tag.
kdb-table can use Datatables library to show tables. Set k-lib to datatables. You can also provide additional configuration to it via k-config. You may have to download
additional themes and plugins for this library because only the basic files are provided in external/datatables directory.
kdb-table can use jsGrid library to show tables. Set k-lib to jsgrid. You can also provide additional configuration to it via k-config.
Example
# basic case
<kdb-table>([] sym: 50?(5?`5);time:.z.T+til[50]*00:00:10; price: 50?40*50?1.0)</kdb-table>
# update tbl from a query
<kdb-table k-id="tbl"></kdb-table>
# datatables
<kdb-table k-id="tbl3" k-lib="datatables" k-config='{"ordering": false, "paging":false, "scrollY":400}' k-style="width:800px;"></kdb-table>
# jsGrid
<kdb-table k-id="tbl" k-lib="jsgrid" k-style="width:800px; height: 400px;"></kdb-table>
# jsGrid, custom cfg, also k-search is set to true so search boxes are shown for columns
<kdb-table k-id="tbl3" k-search="true" k-lib="jsgrid" k-config='{"sorting": false, "heading":false}' k-style="width:800px; height: 400px;"></kdb-table>
# jsGrid - load by page large tables, see grid example for more details
<kdb-table k-query="Q" k-lib="jsgrid" k-config='{"pageLoading":true}' k-style="width:800px; height: 400px;"></kdb-table>
Supported attributes:
k-srv- optional, will be passed tokdb-queryif it needs to be created.k-query- optional,k-idlink tokdb-queryor query text itself. If it is not present the content is used as in the example above.k-id- optional, this id can be used to link other components to this one.k-escape-html- escape or not HTML symbols in the result (valid only for raw tables).k-lib- can be set todatatablesorjsgridfor more fancy tables.k-search- show search boxes indatatablesandjsgridtables.k-config- change the defaultdatatablesorjsgridconfig via this attribute. It should be either a JSON string or a variable name with the config.debug- optional. Can be set to true to see debug prints in the browser console.
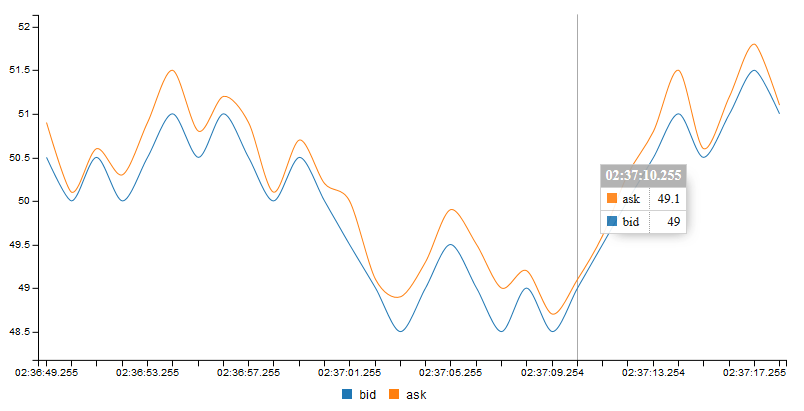
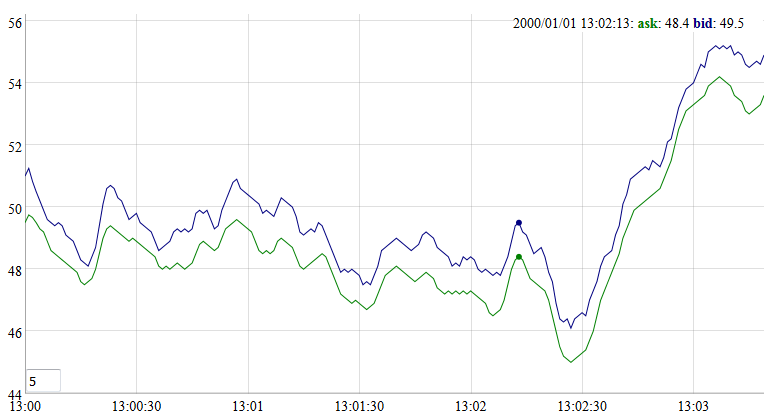
kdb-chart can be used to visualize data. It supports two chart libraries - C3 and Dygraph and can work in the following modes:
- You can provide the full correct C3/Dygrpah config. Absolutely all C3/Dygraph features are available. See chart examples.
- If the result is a table
kdb-chartcan determine params (time and data) itself. If it succeeds it will create a timeseries chart. - If the result is a table you can also set explicitly data and time columns and line type (for C3).
- If the result is a dictionary
kdb-chartwill create a pie chart (type can be changed to donut or gauge). C3 only. - If you set type to 'merge-config' or 'dygraph-merge-config' it will merge the provided config with its own config, in this way you can add additional params to the config.
- Finally you can set type to 'use-config' or 'dygraph-use-config' then
kdb-chartwill use your config and insert data into it. This gives you full control like in the first item.
Example:
# basic C3 chart updated from a query
<kdb-chart k-style='width:800px;height:400px;' k-id="c1"></kdb-chart>
# provide data/time columns, change line style
<kdb-chart k-style='width:800px;height:400px;' k-id="c2" k-time-col="time" k-data-cols="ask bid" k-chart-type="spline"></kdb-chart>
# add some options (you need to redefine type)
<kdb-chart k-style='width:800px;height:400px;' k-id="c5" k-time-col="time" k-data-cols="ask bid"
k-chart-type="merge-config" k-config='{"data":{"type":"spline"},"axis":{"x":{"tick":{"rotate":30}}}}'></kdb-chart>
# dygraph graph
<kdb-chart k-chart-type="dygraph" k-style='width:800px;height:400px;' k-id="c3"></kdb-chart>
# dygraph with options and flow turned on
<kdb-chart k-chart-type="dygraph-merge-config" k-style='width:800px;height:400px;' k-id="c7" k-flow="true"
k-data-cols="price" k-time-col="time" k-config='{"rollPeriod":5, "showRoller":true}'></kdb-chart>
It is quite easy to set a C3 config or Dygraph config - you just literaly translate it from json to dictionaries and set required data. You may set it on the html page itself and refer to it via its name.
In case you want just visualize some simple table remember this - if you do not set time column explicitly put it before other time-like columns. The same is true for the data column(s). kdb-chart searches for the first good enough column.
Supported attributes:
k-srv- optional, will be passed tokdb-queryif it needs to be created.k-query- optional,k-idlink tokdb-queryor query text itself. If it is not present the content of the tag is used.k-class- optional, classes to pass to the wrapper.k-style- optional, style to set to the wrapper.k-chart-type- optional, chart type as in C3 manual. 'line', 'spline' and etc.use-configmeans usek-config,merge-config- merge the default config withk-config. In the previous two cases set the chart type manually ink-config. For dygraph set it to either 'dygraph', 'dygraph-merge-config' or 'dygraph-use-config'.k-time-col- optional, time column.k-data-cols- optional, data columns.k-config- optional, either a chart config in JSON format or js name of a variable with the binary config.k-flow- optional, if true the chart will be updated with the new data on every update. See examples.k-id- optional, this id can be used to link other components to this one.k-init- optional, put this attribute at the end. When you (or some react library) will set this attribute on an emptykdb-chartelement all init functions will be called and the element will be initialized properly.debug- optional. Can be set to true to see debug prints in the browser console.
KDBEditor is based on Ace editor. Q language mode and one theme are provided in external directory. If you want to use other language modes and/or other themes download them from the Ace github repository and put them in the same directory where ace.js is (they should be noconflict or noconflict-min).
Ace is a very powerful editor and has many settings that can be adjusted via k-config attribute. The most useful are readOnly, theme, mode, showGutter.
KDBEditor is tightly integrated with kdb-query - you can use it as a source for kdb-query, kdb-query can subscribe to line/selection exec events to execute them, it can update KDBEditor with its result. Actually kdb-query and kdb-editor can be combined to provide a basic Web Editor with the ability to execute arbitrary queries.
You can update a kdb-editor with a string or with an options object. Supported options:
text- optional new/additional text.row- optional new row for the cursor.column- optional new column for the cursor.markers- optional markers like {xy:[startRow startCol endRow endCol], class:"css_class", type:"text or fullLine or screenLine"}, class must have 'position:absolute'.annotations- optional gutter annotations like {row:Num, text:"txt", html:"html", type:"error or warning or info"}breakpoints- optional gutter breakpoints. Array of numbers. Change "ace_breakpoint" class to customize.
Example:
# Basic usage - default settings, static code. !!! Always set width and height of the editor.
<kdb-editor k-style="width:800px; height:250px;">{2*x}til 10</kdb-editor>
# Advanced usage - change some settings, add k-id to allow kdb-query to update the editor, use k-append to define how it should be updated. Use k-query to explicitly subscribe to some query results.
<kdb-editor k-query="myQ" k-append="top" k-id="e2" k-config='{"readOnly":false}' k-style="width:800px; height:250px;">{2*x} each til 10</kdb-editor>
Always add k-ace-editor css class to your html. It can be found in ace.html example.
Attributes:
k-query- optional, kdb-queryk-id.kdb-editorwill subscribe to this query.k-config- optional, JSON config or a variable name with the config. Use it to change the default settings.k-append- optional,overwriteby default. How to update the editor with the new data -overwrite,top,bottom.k-style- optional. CSS style for the editor.k-class- optional, CSS class for the editor.k-ace-editoris always added.k-id- optional, this id can be used to link other components to this one.debug- optional, print debug info.
Default settings:
theme: 'ace/theme/textmate'
mode: 'ace/mode/q'
readOnly: true
scrollPastEnd: false
fadeFoldWidgets: false
behavioursEnabled: true # editor will be much smarter with this option turned on, it will do correct indentation, match brackets and etc.
useSoftTabs: true
animatedScroll: true
verticalScrollBar: false
horizontalScrollBar: false
highlightSelectedWord: true
showGutter: true
displayIndentGuides: false # gray lines that show where indentation is
showInvisibles: false # invisible symbols are shown as gray marks
highlightActiveLine: true
selectionStyle: 'line' # line or text - how looks the selection decoration
wrap: 'off' # off 40 80 free (til end of the container)
foldStyle: 'markbegin' # markbegin markbeginend manual - show marks where folding starts, starts and ends or nothing
fontSize: 12
keybindings: 'ace' # ace emacs vim, emacs and vim should be first downloaded
showPrintMargin: true # gray line at 80th column
execLine: win: 'Ctrl-Return', mac: 'Command-Return'
execSelection: win: 'Ctrl-e', mac: 'Command-e'
Interface (kdb-editor object):
kEditor- the underlying editor.onexec(f)- subscribe to exec events.kdbUpd(string || options)- update the editor.
Converts Q text into an array of tokens. It also can produce html from the text.
KDBLex instance is available as KDB.KDBLexer. It can be used with kdb-query in k-filter attribute to colorify q text.
KDB.KDBLexer2 can be used with dictionaries - it will update the default ` field.
l = new KDB.KDBLex() || KDB.KDBLexer
l.getHtml("a: 100")
Suitable container div:
<div style="line-height:normal;text-autospace:none;font-size: 8pt; font-family: Consolas; white-space: nowrap;"></div>
Functions:
getTokens(text or array of strings)- get tokens array.getHtml(text or array of strings, map of token types to css classes or null)- produce html from text where tokens are wrapped inspanwith the corresponding classes, lines are wrapped indiv.filter(text)- to be used withkdb-queryto post process q text into colored html.
Default types (classes): k-const, k-number-guid, k-number-float, k-number-int, k-number-datetime, k-number-time, k-number-date, k-const-sym, k-keyword-language, k-command, k-keyword-function, k-keyword-control, k-keyword-operator, k-name, k-variable, k-comment, k-simple-comment, k-eof-comment, k-string, k-text, k-operator.
A simple proxy server for html components. It has .z.ph and .z.ws handlers and can forward requests to other servers (via k-target attribute on kdb-srv). You can update trgMap dictionary in srv.q with logical names (trgMap[`hdbEMEAstock]:`:somehost:port) and then set k-target like k-target="hdbEMEAstock".
Examples can be used to quickly overview all available functionality. Simply start srv.q:
q srv.q
And enter localhost:5566/index.html in your browser. For secure examples start q 3.4 with -E 1 or -E 2 option and enter https://localhost:5566/index.html.
If you start srv.q from another directory redefine '.h.HOME' to point to srv.q directory otherwise it will not be able to find examples and etc.