Step by step guide on how to create a single database in Azure SQL Database without installing PowerShell or CLI, and from any device that supports a browser.
In this article you will find:
- Before you start
- Prerequisites
- How to create a single database
- How to clean up resources
- Recommended Firewall configuration
- Relevant information
- If you are yet to decide if Azure Cloud Services are appropriate for your project, please check out cloud benefits and considerations.
- You will be able to create a subscription and to access all of your resources from Azure Portal
- Keep your priorities in mind, you can always store your credentials at Azure Key Vault if Privacy and Security are main concerns for the project.
- Azure's billing model is pay per use, be sure to delete any unecessary resources. You will find out how later in this module.
- An active Azure subscription
- Basic understanding of computing basic concepts and terminology. Basic understandong of cloud computing is suggested, but not essencial.
- You may use any device that supports a browser.
-
Log into your Azure account.
-
Select Create a new resource>Databases>SQL Database.
You will most likely be able to select the SQL Database directly from the most frequent resources.
You will see the SQL Database panel.
-
Select your Azure subscription and locate your Database into your project's Resource Group or create a new one.
-
Input the following values for each option:
-
Create a Database name. Keep in mind the following specifications:
Database name should not match special Azure patterns or reserved words. Database name should be up to 128 characters. Database name should be unique in the server.
You will then need to allocate your Database on a server. If you already have a server for your project, go directly to step 7.
- Click on
Create newbelow the server list and input the following values:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Server details | |
| Server name | sqlservernnnn (Replacing with letters and digits for a unique name) |
| Location | Select the nearest location to decrease latency |
| Authentication | |
| Authentication method | Use SQL authentication |
| Server admin login | You will need this username to access your Database |
| Password | Safer passwords include uppercase and lowercase letters, plus numbers and special symbols |
-
You will then return to the main Database creation Panel, and will be prompted to use SQL elastic pool. Select
No -
Click on
Configure Databaseat Compute + Storage, and selectServerless. Other values may remain set at default. Click onApplyto return to the Panel.
-
Select the backup redundancy of your choice to improve service availability. If availability is not a major concern for your Database, you may just select
Locally redundant data storage. For more information about availability, check SQL Database Service Level of Service -
Go to the Networking tab, and select
Public endpointas the Connectivity method. You may leave not specified fields as default.
- Skip the Security tab for now. Go directly to the Additional Settings tab, and input the following values:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Data source | |
| Use existing data | Sample |
| Database collation | |
| Collation | SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS (default) |
-
Click on next and create tags according to your Organization's best practices. For more information, check out the naming and tagging strategy for Azure resources.
-
Select
Review + Createto validate your Configuration. Azure automatically will check for errors or inconsistencies. -
Select
Createand wait for the Database to deploy. It may take up to 5 minutes, depending on service availability.
Once you have created your SQL Database, is recommended to allow Azure services and resources to access the server. In order to do that:
- Select
Go to resource.
- Click on
Overviewat the left side Menu. - Select
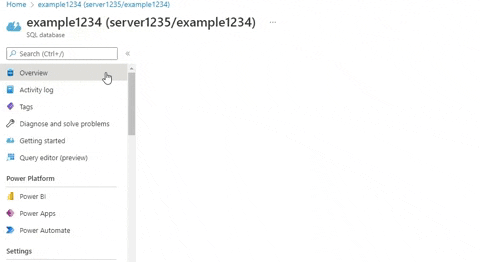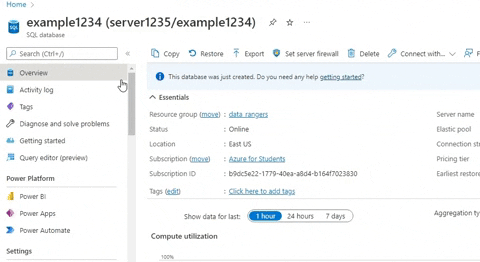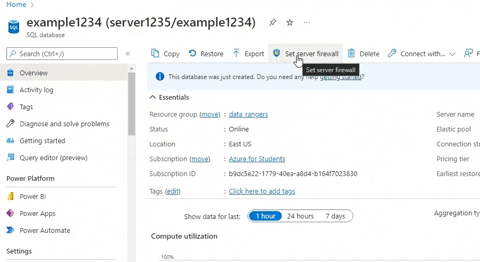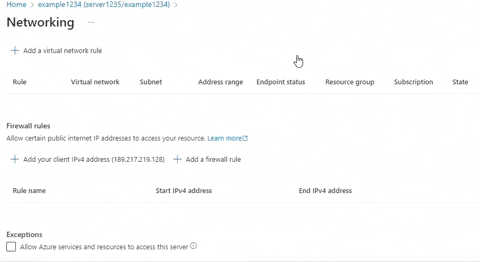
Set server firewallat the command bar at the top. - Scroll all the way down to
Exceptions, and check the Allow Azure services and resources to access this server box. - Save
When you are finished using these resources, it is recommended to delete the resource group you created to save up computing billing costs. This will also delete the server and single database within it.
To delete the resource group and the resources it contains:
- Select the resource group.
- Select Delete resource group.
This step can not be undone: Make sure you only delete resources you are done with. Azure will ask you to type the resource group name as confirmation to proceed.
- Create a SQL database Exercise on Microsoft Learn
- Quickstart: Create an Azure SQL Database single database
I'm a code junkie with a Bachelor in Philosophy.