RSA cryptosystem implemented in Python 3.6
RSA was developed by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman is one of the first public key cryptosystems and is widely used for secure data transmission. The encryption key is public and it is different from the decryption key which is kept secret and is called private.
- Factorization.
- Large Prime Numbers.
- Two diffent keys.
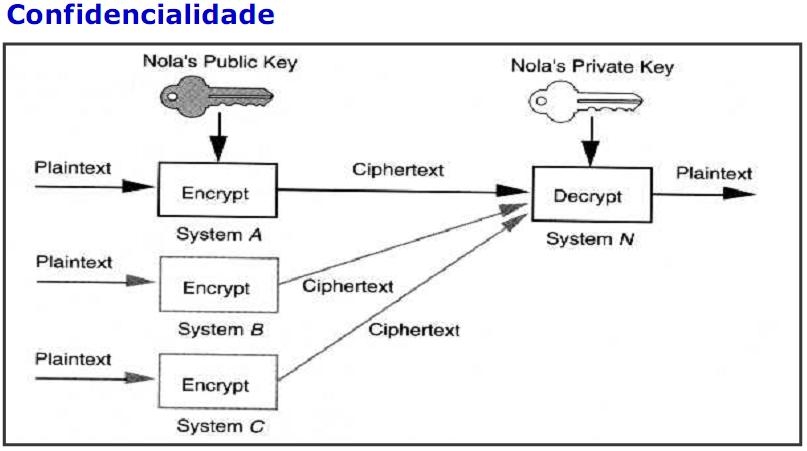
- Encrypt
It takes the text and encrypt using E and N attributes. c ≡ m^e * (mod n). - Authenticate
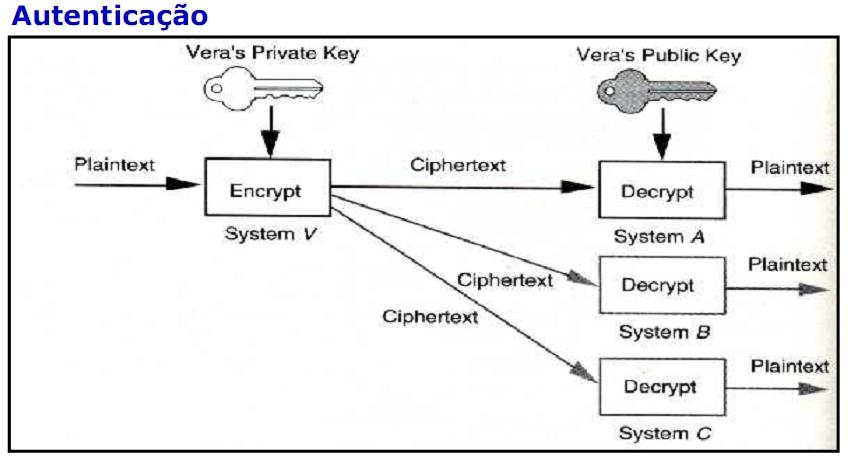
This method decrypt the PrivateKey signature to ensure that the message you recive it is legit. In other words, it ensures if the person who has the PrivateKey compatible with your PublicKey
- Decrypt
It takes the encrypt message and return the decrypt text. c ≡ m^d * (mod n). - Sign
Method that encrypt you message. This method ensures that everyone who has your PublicKey knows that was you who sent the message.
Create a new PairKey
- Import Locksmith
from rsaEcryption import Locksmith- Create the keys
lm = Locksmith()
pairkey = lm.new_key(length=3)
print(pairkey)
# PairKey(PrivateKey(11261, 19043), PublicKey(5, 19043))NOTE: The more length attribute is, the more secure your key will be. But, it'll also take some time to create them.
- Casting your PairKey (optional)
privatekey = lm.cast(pairkey, 'private')
print(privatekey)
# PrivateKey(11261, 19043)
publickey = lm.cast(pairkey, 'public')
print(publickey)
# PublicKey(5, 19043)Cryptosystem
- Encrypt
encrypt_text = tuple(publickey.encrypt('Hello, World!'))
print(encrypt_text)
# (15531, 2199, 6656, 6656, 2141, 3844, 666, 8645, 2141, 16083, 6656, 6539, 2028)- Decrypt
decrypt_text = privatekey.decrypt(encrypt_text, as_string=True)
print(decrypt_text)
# Hello, World!- Sign your message
m = "This message was created by me (PrivateKey)"
signature = tuple(privatekey.sign(m))
print(signature)
# (11736, 9733, 13698, 11524, 2, 5108, 12300, 11524, 11524, 5742, 981, 12300, 2, 8171, 5742, 11524, 2, 18920, 11221, 12300, 5742, 18822, 12300, 1470, 2, 3033, 2070, 2, 5108, 12300, 2, 1930, 8191, 11221, 13698, 8937, 5742, 18822, 12300, 13864, 12300, 2070, 14481)- Authenticate a signature
authentication = publickey.authenticate(signature, as_string=True)
print(authentication)
# This message was created by me (PrivateKey)Save different keys
- Import KeyChain
from rsaEcryption import KeyChain- Add keys to a KeyChain
kc.add('my_pair_key', pairkey)
kc.add('my_public_key', publickey)
kc.add('my_private_key', privatekey)
print(kc)
# {
# 'my_pair_key': PairKey(PrivateKey(11261, 19043), PublicKey(5, 19043)),
# 'my_public_key': PublicKey(5, 19043),
# 'my_private_key': PrivateKey(11261, 19043)
# }- Saving your keys in a file
import json
with open('my_keys.kc', 'w') as file:
keys = kc.save_keys()
keys_json = json.dumps(keys, indent=2)
file.write(keys_json)- Loading your keys from a file
import json
with open('my_keys.kc', 'r') as file:
keys_json = file.read()
keys = json.loads(keys_json)
new_kc = KeyChain()
new_kc.load_keys(keys, inplace=True)
print(new_kc.all_key)
# dict_keys(['my_pair_key', 'my_public_key', 'my_private_key'])- Removing a key from KeyChain
print(kc.all_key)
# dict_keys(['my_pair_key', 'my_public_key', 'my_private_key'])
kc.remove('my_pair_key')
print(kc.all_keys)
# dict_keys(['my_public_key', 'my_private_key'])