For a truly fast, teensy, squeaky clean Webpack CLI - try webpack-nano.
Note: webpack-command is now being maintained on this fork, and will be open to Pull Requests and Issues for users that prefer this CLI. The webpack-contrib org has chosen to drop support for this module and is no longer actively maintaining it.
A superior CLI experience for webpack. Modular and opinionated.
For users coming from webpack-cli, please read about
the differences between this module and
webpack-cli.
This module requires a minimum of Node v6.14.0 and Webpack v4.0.0.
webpack-command and webpack-cli cannot be installed at the same time, as
they both export a bin file named webpack. When trying webpack-command,
please npm uninstall webpack-cli first.
webpack-command has many advantages over other CLI experiences for webpack.
These include:
- Extendable Webpack Configurations. A configuration file can extend the properties and collections from base configurations, and are filtered intelligently.
- Custom Reporters 🤯
- A beautiful default user experience with output driven by
webpack-stylish - Support for
webpackconfiguration in any language or compiler that provides arequirehook - Support for
webpackconfiguration inJSON,YAML, orJavaScript - Validation of commands, entries, and flags before further execution
- Extensible third-party commands. Include only what you need!
- A full test suite with 220 tests and 95% coverage (so close to 100% 💪)
- A
93%24% smaller package cost versuswebpack-cli(it used to be 93%, they got wise after webpack-command was released) - Highly focused on the User Experience and detail
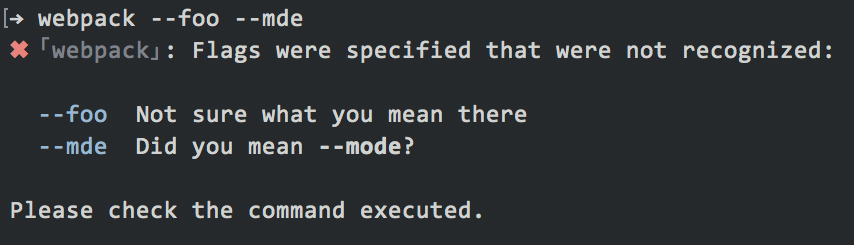
And last but not least, Did-You-Mean suggestions for flags:
To begin, you'll need to install webpack-command:
$ npm install webpack-command --save-devThe primary binary for webpack-command is wp (because who doesn't like to save
keystrokes!?) Although, you may also use the webpack binary as per usual if
your setup installs this module after webpack, and the two don't conflict.
$ wp --help
A superior CLI experience for webpack. Lightweight, modular, and opinionated.
Usage
$ webpack [<config>, ...options]
$ webpack <entry-file> [...<entry-file>] <output-file>
$ webpack <command> [...options]
Options
--context The root directory for resolving entry point and stats
--debug Switch loaders to debug mode
--devtool Enable devtool for better debugging experience.
e.g. --devtool eval-cheap-module-source-map
--entry The entry point
--help Show usage information and the options listed here
--log-level Limit all process console messages to a specific level and above
Levels: trace, debug, info, warn, error, silent
--log-time Instruct the logger for webpack-serve and dependencies to display a timestamp
--progress Instructs webpack to track and display build progress
--reporter Specifies the reporter to use for generating console output for a build
--require Preload one or more modules before loading the webpack configuration
Typically used for language-specific require hooks
--run-dev An alias for --debug --devtool eval-cheap-module-source-map --output-pathinfo
--run-prod An alias for --optimize-minimize --define process.env.NODE_ENV="production"
--version Display the webpack-command version
--watch Watch the filesystem for changes
Advanced
--bail Abort the compilation on first error
--cache Enable in memory caching
--define Define any free var in the bundle
--hot Enables Hot Module Replacement
--plugin Load this plugin
--prefetch Prefetch this request
e.g. --prefetch ./file.js
--profile Profile the compilation and include information in stats
--provide Provide these modules as free vars in all modules
e.g. --provide.jQuery jquery
--records-input-path Path to the records file (reading)
--records-output-path Path to the records file (writing)
--records-path Path to the records file
--target The targeted execution environment
--watch-aggregate-timeout Timeout for gathering changes while watching
--watch-poll The polling interval for watching (also enable polling)
--watch-stdin Exit the process when stdin is closed
Configuration File
--config Path to the config file
--config-name Name of the config to use
--config-register Deprecated. Please use --require.
--mode Specifies the build mode to use; development or production
Modules
--module-bind Bind an extension to a loader
--module-bind-post Bind an extension to a postLoader
--module-bind-pre Bind an extension to a preLoader
Optimization
--optimize-max-chunks Try to keep the chunk count below a limit
--optimize-min-chunk-size Try to keep the chunk size above a limit
--optimize-minimize Minimize javascript and switches loaders to minimizing
Output
--output The output path and file for compilation assets
--output-chunk-filename The output filename for additional chunks
--output-filename The output filename of the bundle
--output-jsonp-function The name of the JSONP function used for chunk loading
--output-library Expose the exports of the entry point as library
--output-library-target The type for exposing the exports of the entry point as library
--output-path The output path for compilation assets
--output-pathinfo Include a comment with the request for every dependency (require, import, etc.)
--output-public-path The public path for the assets
--output-source-map-filename The output filename for the SourceMap
Resolver
--resolve-alias Setup a module alias for resolving
e.g. --resolve-alias.jquery jquery.plugin
--resolve-extensions Setup extensions that should be used to resolve modules
e.g. .es6,.js
--resolve-loader-alias Setup a loader alias for resolving
For further documentation, visit https://webpack.js.org/api/cli
Commands
help
teach
Type `webpack help <command>` for more informationAs a convenience for alternative package managers, the webpack-command binary
is also installed with this package.
This module supports extending webpack configuration files with
ESLint-style
extends functionality. This feature allows users to create a "base" config and
in essence, "inherit" from that base config in a separate config. A bare-bones
example:
// base.config.js
module.exports = {
name: 'base',
mode: 'development',
plugins: [...]
}// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
extends: path.join(..., 'base-config.js'),
name: 'dev'The resulting configuration object would resemble:
{
name: 'dev',
mode: 'development',
plugins: [...]
}Read More about Extending Configuration Files
webpack-command allows users to extend the webpack CLI experience by
including a few helpful built-in commands, and providing a means to develop
third-party commands.
For more documentation on flags, please see the
webpack-cli documentation.
While this project aims for parity with webpack-cli in nearly all aspects,
there are some notable differences. Included in those differences is the note
that this module includes the bare minimum of commands to provide a webpack
CLI. Commands like init, migrate, and update are relegated to separate,
user-installed modules.
That said, the following differences should also be noted:
Environment Variables have
been around a very, very long time. webpack-cli chose to introduce a feature
that let users specify environment variables via a flag. This module does not
include that feature. Instead, users should make use of environment variables
the traditional, standard way:
$ NEAT_VAR=woo webpack ...
And access the values via process.env. Alternatively, if users are in need of
cross-platform environment variables, a tool such as
cross-env should be leveraged.
Certain flags passed in webpack-cli allow for a key-value pair for
pairing an alias with the alias value. e.g. --entry name=file. This module
adopts a CLI-standard approach by using the syntax --flag.key value instead,
and does not support the key=value syntax.
Specifying entries by either flag (--flag) or input (webpack <file>) require
that the file or directory specified exist.
Entries passed with a comma-separated value --entry file,file2 are deprecated
and should be migrated to use the CLI-standard --entry file --entry file2
syntax.
Entries passed by flag in webpack-cli using --entry name=file should be
migrated to use the --entry.name file syntax.
Resolve aliases passed by flag in webpack-cli using
--resolve-alias alias=value should be migrated to use the --resolve-alias.{alias} {value}
syntax.
Resolve aliases passed by flag in webpack-cli using
--resolve-loader-alias alias=value should be migrated to use the
--resolve-loader-alias.alias value syntax.
webpack-command supports custom, user-defined reporters which allow users
full control over how build data is presented. By default, it ships with two
available reporters:
Displays the default webpack output, the same you'll see
using webpack-cli.
The default reporter and displays beautiful output using the same code
that drives webpack-stylish.
Building your own reporter is as easy as inheriting from the Reporter class
located at lib/reporters/Reporter.js.
webpack-command allows users to leverage any language that provides a require
hook. To leverage this feature, define your configs as such for the following
languages/compilers:
- Babel ES6 Modules:
webpack.config.jsorwebpack.config.es6, and use--require babel-register - Flow:
webpack.config.jsorwebpack.config.flow, and use--require flow-remove-types/register - TypeScript:
webpack.config.ts, and use--require ts-node/register
Other hooks may work for additional language or compiler support.
Note: Compilers are not part of, nor built-into this module. To use a specific compiler, you must install it first.
Any entry files specified will overwrite entries in a webpack.config.js file
as of this Pull Request in
webpack-cli.
Please take a moment to read our contributing guidelines if you haven't yet done so.