A data structure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used effectively.
For example, we can store a list of items having the same data-type using the array data structure.
This page contains detailed explanation on different data structures (DS) with topic-wise problems.
-Heap
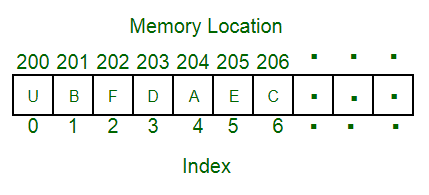
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array).
The above image can be looked as a top-level view of a staircase where you are at the base of the staircase. Each element can be uniquely identified by their index in the array (in a similar way as you could identify your friends by the step on which they were on in the above example).
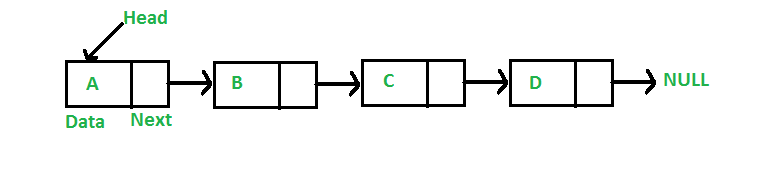
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
In simple words, a linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list.
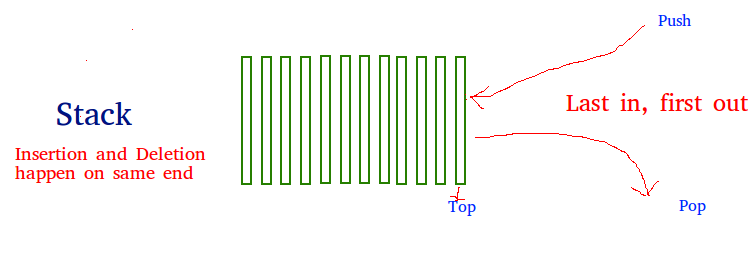
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FIFO(First In Last Out).
Consider a real life example of stack, an example of plates stacked over one another in the canteen. The pkate ehich is at the top is the first one to be removed, i.e. the plate which has been placed at the bottommost position remains in the stack for longest period of time. So, it can is simply LIFO/FIFO order.
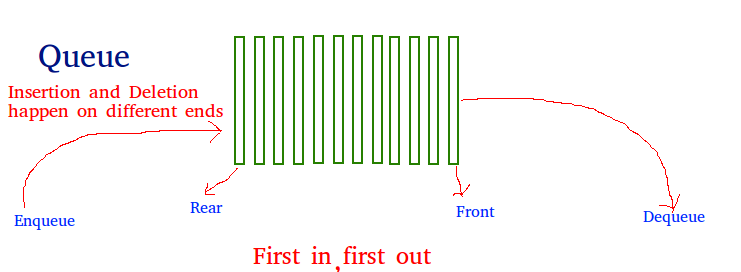
A Queue is a linear structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order is First In First Out(FIFO). A good example of a queue is any queue of consumers for a resourse where the consumer that came first is served first.
The difference between stacks and queue is in removing. In a stack we remove the item the most recently added; in a queue, we remove the item the least recently added.
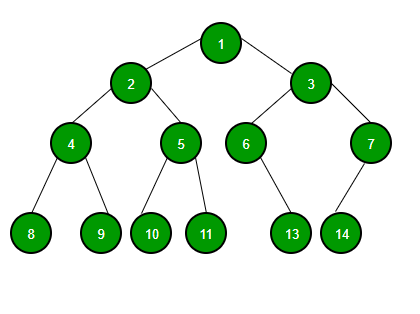
A tree whose elements have at most 2 children is called a binary tree. Since each element in a binary tree can have 2 children, we typically name them the left and right child.
A Binary Tree node contains following parts. -1.Data -2.Pointer to left child -3.Pointer to right child
Binary Search Tree is a node-based binary tree data structure which has the following properties:
-The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key. -The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key. -The left and right subtree each must also be a binary search tree.
A Heap is a special Tree-based data structure in which the tree is a complete binary tree. Generally, Heaps can be of two types:
-1.Max-Heap: In a Max-Heap the key present at the root node must be greatest among the keys present at all of it’s children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree. -2.Min-Heap: In a Min-Heap the key present at the root node must be minimum among the keys present at all of it’s children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
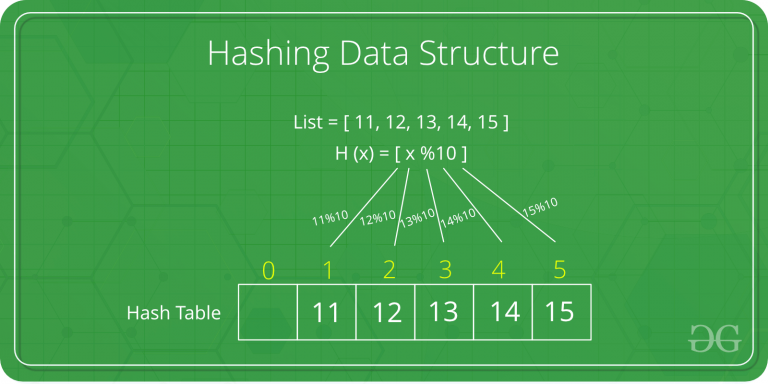
Hashing is a technique or process of mapping keys, values into the hash table by using a hash function. It is done for faster access to elements. The efficiency of mapping depends on the efficiency of the hash function used.
Let a hash function H(x) maps the value x at the index x%10 in an Array. For example if the list of values is [11,12,13,14,15] it will be stored at positions {1,2,3,4,5} in the array or Hash table respectively.
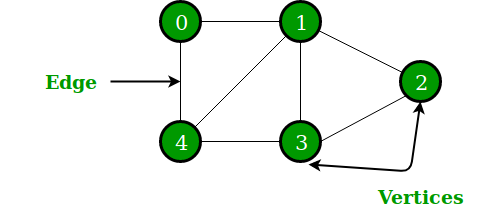
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of nodes and edges. The nodes are sometimes also referred to as vertices and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph.