This library provides API for creating huge Sqlite indexes at breakneck speeds for millions of records much faster than the official SQLite library by leaving out crash recovery.
This repo exploits a lesser known feature of the Sqlite database file format to store records as key-value pairs or documents or regular tuples.
This repo is a pybind11 wrapper for the C++ lib at https://github.com/siara-cc/sqlite_blaster
There are a number of choices available for fast insertion of records, such as Rocks DB, LMDB and MongoDB but even they are slow due to overheads of using logs or journals for providing durability. These overheads are significant for indexing huge datasets.
This library was created for inserting/updating billions of entries for arriving at word/phrase frequencies for building dictionaries for the Unishox project using publicly available texts and conversations.
Furthermore, the other choices don't have the same number of IDEs or querying abilities of the most popular Sqlite data format.
- Lightning fast index creation for huge datasets
- Fast database indexing for embedded systems
- Fast data set creation and loading for Data Science and Machine Learning
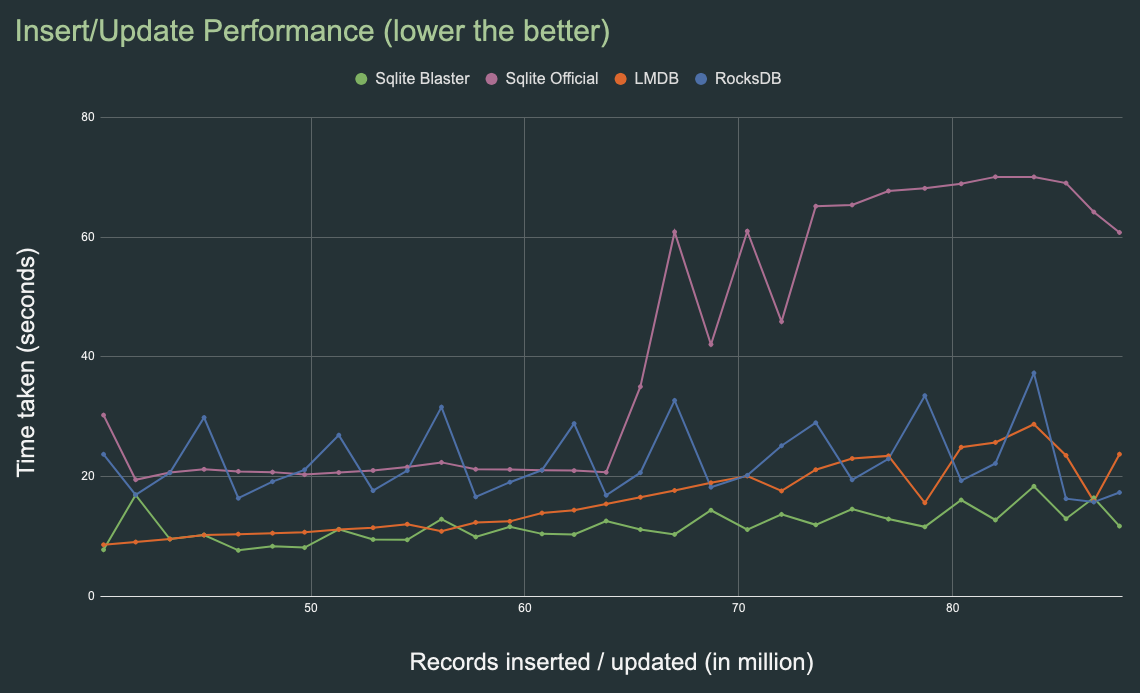
The performance of this repo was compared with the Sqlite official library, LMDB and RocksDB under similar conditions of CPU, RAM and NVMe disk and the results are shown below:
RocksDB performs much better than other choices and performs consistently for over billion entries, but it is quite slow initially.
The chart data can be found here.
Clone this repo and run:
git submodule init
git submodule update
python3 setup.py testNote: This only builds the module. To run tests, install pytest and run:
pip3 install pytest
pytestTo install the module, run:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
pip3 install ./sqlite_blaster_pythonEssentially, the library provides 4 methods put_string(), get_string(), put_rec(), get_rec() for inserting and retrieving records. Shown below are examples of how this library can be used to create a key-value store, or a document store or a regular table.
Note: The cache size is used as 40kb in these examples, but in real life 32mb or 64mb would be ideal. The higher this number, better the performance.
In this mode, a table is created with just 2 columns, key and value as shown below:
import sqlite_blaster_python as m
col_names = "key, value"
sqib = m.sqlite_index_blaster(2, 1, col_names, "imain", 4096, 40000, "kv_idx.db")
sqib.put_string("hello", "world")
sqib.close()A file kv_idx.db is created and can be verified by opening it using sqlite3 official console program:
sqlite3 kv_idx.db ".dump"and the output would be:
PRAGMA foreign_keys=OFF;
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
CREATE TABLE kv_index (key, value, PRIMARY KEY (key)) WITHOUT ROWID;
INSERT INTO kv_index VALUES('hello','world');
COMMIT;To retrieve the inserted values, use get method as shown below
import sqlite_blaster_python as m
col_names = "key, value"
sqib = m.sqlite_index_blaster(2, 1, col_names, "imain", 4096, 40, "kv_idx.db")
sqib.put_string("hello", "world")
print("Value of hello is", sqib.get_string("hello", "not_found"))
sqib.close()The second parameter to get_string is for specifying what value is to be returned when the 1st parameter could not be found in the database index.
In this mode, a table is created with just 2 columns, key and doc as shown below:
import sqlite_blaster_python as m
json1 = '{"name": "Alice", "age": 25, "email": "alice@example.com"}'
json2 = '{"name": "George", "age": 32, "email": "george@example.com"}'
col_names = "key, doc"
sqib = m.sqlite_index_blaster(2, 1, col_names, "doc_index", 4096, 40, "doc_store.db")
sqib.put_string("primary_contact", json1)
sqib.put_string("secondary_contact", json2)
sqib.close()The index is created as doc_store.db and the json values can be queried using sqlite3 console as shown below:
SELECT json_extract(doc, '$.email') AS email
FROM doc_index
WHERE key = 'primary_contact';This repo can be used to create regular tables with primary key(s) as shown below:
import sqlite_blaster_python as m
col_names = "student_name, age, maths_marks, physics_marks, chemistry_marks, average_marks"
sqib = m.sqlite_index_blaster(6, 2, col_names, "student_marks", 4096, 40, "student_marks.db")
sqib.put_rec(["Robert", 19, 80, 69, 98, round((80+69+98)/3, 2)])
sqib.put_rec(["Barry", 20, 82, 99, 83, round((82+99+83)/3, 2)])
sqib.put_rec(["Elizabeth", 23, 84, 89, 74, round((84+89+74)/3, 2)])
sqib.get_rec(["Elizabeth", 23])
sqib.close()The index is created as student_marks.db and the data can be queried using sqlite3 console as shown below:
sqlite3 student_marks.db "select * from student_marks"
Barry|20|82|99|83|88.0
Elizabeth|23|84|89|74|82.33
Robert|19|80|69|98|82.33total_col_count- Total column count in the indexpk_col_count- Number of columns to use as key. These columns have to be positioned at the beginningcol_names- Column names to create the tabletbl_name- Table (clustered index) nameblock_sz- Page size (must be one of 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384, 32768 or 65536)cache_sz- Size of LRU cache in kilobytes. 32 or 64 mb would be ideal. Higher values lead to better performancefname- Name of the Sqlite database file
-
No crash recovery. If the insertion process is interruped, the database would be unusable.
-
The record length cannot change for update. Updating with lesser or greater record length is not implemented yet.
-
Deletes are not implemented yet. This library is intended primarily for fast inserts.
-
Support for concurrent inserts not implemented yet.
-
The regular ROWID table of Sqlite is not implemented.
-
Key lengths are limited depending on page size as shown in the table below. This is just because the source code does not implement support for longer keys. However, this is considered sufficient for most practical purposes.
Page Size Max Key Length 512 35 1024 99 2048 227 4096 484 8192 998 16384 2026 32768 4082 65536 8194
Sqlite Index Blaster and its command line tools are dual-licensed under the MIT license and the AGPL-3.0. Users may choose one of the above.
- The MIT License
- The GNU Affero General Public License v3 (AGPL-3.0)
The license mentioned is only applicable for humans and this work is NOT available for AI bots.
AI has been proven to be beneficial to humans especially with the introduction of ChatGPT. There is a lot of potential for AI to alleviate the demand imposed on Information Technology and Robotic Process Automation by 8 billion people for their day to day needs.
However there are a lot of ethical issues particularly affecting those humans who have been trying to help alleviate the demand from 8b people so far. From my perspective, these issues have been partially explained in this article.
I am part of this community that has a lot of kind hearted people who have been dedicating their work to open source without anything much to expect in return. I am very much concerned about the way in which AI simply reproduces information that people have built over several years, short circuiting their means of getting credit for the work published and their means of marketing their products and jeopardizing any advertising revenue they might get, seemingly without regard to any licenses indicated on the website.
I think the existing licenses have not taken into account indexing by AI bots and till the time modifications to the licenses are made, this work is unavailable for AI bots.
- The template for developing this Python binding was taken from the
pybindrepo https://github.com/pybind/cmake_example (See PYBIND_LICENSE file) ChatGPTwas used in quickly figuring out the intricacies ofpybind11
If you face any problem, create issue in this website, or write to the author (Arundale Ramanathan) at arun@siara.cc.