-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 220
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
[TUTORIAL] APIs, REST and RESTful APIs. #303
base: master
Are you sure you want to change the base?
Changes from all commits
8e71d05
d13ce3d
c2d33cb
909578e
7f52ecd
f97a712
bb7511d
96abe07
39e9593
16b9ffc
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Jump to
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,210 @@ | ||
| # What are API | ||
| - API stands for Application Program Interface, which developers use to access web tools or information on the cloud. It allows different cross-platform applications to talk to each other. APIs are accessible way to extract and share data within and across organization. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| - APIs are that we can use to interact with GitHub. They allow us to create and manage repositories, branches, issues, pull requests, and many more. For fetching publicly available information (like public repositories, user profiles, etc.), we can call the API. | ||
|
|
||
| - Additionally, today APIs are treated more like products than code.Modern APIs stick to specific standards(typically HTTPS and RESET), which enables API to be developer-friendly, self-described, easily accessible and understood broadly. | ||
|
|
||
| # How to create an API? | ||
| Due diligence and effort are required to build an API that other developers will want to work with and trust. These are the five steps required for high-quality API design: | ||
|
|
||
| ### 1. Plan the API : | ||
| API specifications, like OpenAPI, provide the blueprint for your API design. It is better to think about different use cases in advance and ensure the API adheres to current API development standards. | ||
|
|
||
| ### 2. Build the API : | ||
| API designers prototype APIs using boilerplate code. Once the prototype is tested, developers can customize it to internal specifications. | ||
|
|
||
| ### 3. Test the API : | ||
| API testing is the same as software testing and must be done to prevent bugs and defects. API testing tools can be used to strength test the API against cyber attacks. | ||
|
|
||
| ### 4. Document the API : | ||
| While APIs are self-explanatory, API documentation acts as a guide to improve usability. Well-documented APIs that offer a range of functions and use cases tend to be more popular in a service-oriented architecture. | ||
|
|
||
| ### 5. Market the API : | ||
| Just as Amazon is an online marketplace for retail, API marketplaces exist for developers to buy and sell other APIs. Listing your API can allow you to monetize it. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Types of APIs | ||
|
|
||
| There are four types of APIs commonly used in web services-public,partner,private and composite. The APIs "type" indicates the intended scope of use. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ### Private APIs : | ||
| These are internal to an enterprise and only used for connecting systems and data within the business. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Public APIs : | ||
| These are open to the public and may be used by anyone. There may or not be some authorization and cost associated with these types of APIs. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Partner APIs : | ||
| These are only accessible by authorized external developers to aid business-to-business partnerships. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Composite APIs : | ||
| These combine two or more different APIs to address complex system requirements or behaviors. | ||
|
|
||
| # How to use an API? | ||
| #### The steps to implement a new API include: | ||
|
|
||
| - Obtaining an API key. This is done by creating a verified account with the API provider. | ||
|
|
||
| - Set up an HTTP API client. This tool allows you to structure API requests easily using the API keys received. | ||
|
|
||
| - If you don’t have an API client, you can try to structure the request yourself in your browser by referring to the API documentation. | ||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Which service is being used as a reference here? There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. The steps mentioned are general steps that can be applied to any API. There is no specific service being referenced here. Many open source services allow public access to APIs, such as OpenWeatherMap, Twitter API, GitHub API, and Google Maps API. Should we mention all these public APIs as examples? |
||
|
|
||
| - Once you are comfortable with the new API syntax, you can start using it in your code. | ||
|
|
||
| # REST APIs | ||
|
|
||
| ### What is REST? | ||
|
|
||
| - Representational State Transfer (REST) is a software architecture that imposes conditions on how an API should work. | ||
|
|
||
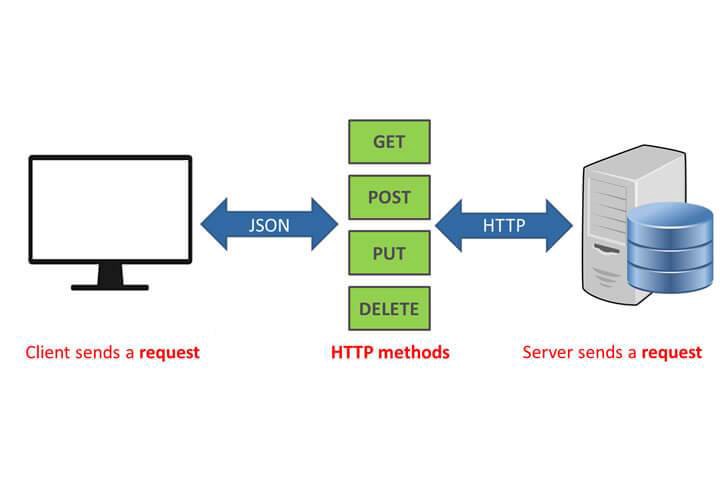
| - REST defines a set of functions like GET, PUT, DELETE, etc. that clients can use to access server data. Clients and servers exchange data using HTTP. | ||
|
|
||
| - REST was initially created as a guideline to manage communication on a complex network like the internet. | ||
| ### What are REST APIs? | ||
|
|
||
| - The main feature of REST API is statelessness. Statelessness means that servers do not save client data between requests. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| - Client requests to the server are similar to URLs you type in your browser to visit a website. The response from the server is plain data or in one of several formats HTTP: JSON(Javascript Object), HTML, XLT, Python or PHP. | ||
|
|
||
| - JSON is the most generally popular file format to use because, despite its name, it's language-agnostic, as well as readable by both humans an machines. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Benefits of RESTful APIs | ||
| - #### Scalability : | ||
| RESTful APIs are highly scalable as they use standard protocols and formats, making it easier to scale up or down the system. | ||
|
|
||
| - #### Flexibility : | ||
| RESTful APIs are highly flexible as they can be used with any programming language and can be inplemented on any platform or device. | ||
|
|
||
| - #### Portability : | ||
| RESTful APIs can be used across different systems, making it easier to integrate different software system. | ||
|
|
||
| - #### Efficiency : | ||
| RESTful APIs are designed to be efficient, with low overheads and minimal processing requirements, making them ideal for use in high-performance applications. | ||
|
|
||
| - #### Security : | ||
| RESTful APIs can be secured using standard security protocols such as OAuth, SSL/TLS and HTTPS, providing a secure way to exchange data between systems. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## How do RESTful API works? | ||
|
|
||
| The basic function of a RESTful API is the same as browsing the internet. The client contacts the server by using the API when it requires a resource. | ||
| API developers explain how the client should use the REST API in the server application API documentation. These are the general steps for any REST API call: | ||
|
|
||
| - The client sends a request to the server. The client follows the API documentation to format the request in a way that the server understands. | ||
|
|
||
| - The server authenticates the client and confirms that the client has the right to make that request. | ||
| - The server returns a response to the client. The response contains information that tells the client whether the request was successful. The response also includes any information that the client requested. | ||
|
|
||
| The REST API request and response details vary slightly depending on how the API developers design the API. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Client Request : | ||
|
|
||
| RESTful APIs client requests contain the following main components: | ||
|
|
||
| ### Unique resource identifier | ||
| - The server identifies each resource with unique resource identifiers. For REST services, the server typically performs resource identification by using a Uniform Resource Locator (URL). | ||
|
|
||
| - The URL specifies the path to the resource. A URL is similar to the website address that you enter into your browser to visit any webpage. The URL is also called the request endpoint and clearly specifies to the server what the client requires. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Method | ||
| - Developers often implement RESTful APIs by using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). An HTTP method tells the server what it needs to do to the resource. | ||
| - The following are four common HTTP methods: | ||
| #### GET : | ||
|
|
||
| Clients use GET to access resources that are located at the specified URL on the server. They can cache GET requests and send parameters in the RESTful API request to instruct the server to filter data before sending. | ||
|
|
||
| #### POST : | ||
|
|
||
| Clients use POST to send data to the server. They include the data representation with the request. Sending the same POST request multiple times has the side effect of creating the same resource multiple times. | ||
|
|
||
| #### PUT : | ||
|
|
||
| Clients use PUT to update existing resources on the server. Unlike POST, sending the same PUT request multiple times in a RESTful web service gives the same result. | ||
|
|
||
| #### DELETE : | ||
|
|
||
| Clients use the DELETE request to remove the resource. A DELETE request can change the server state. However, if the user does not have appropriate authentication, the request fails. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ### HTTP headers | ||
| Request headers are the metadata exchanged between the client and server. For instance, the request header indicates the format of the request and response, provides information about request status, and so on. | ||
|
|
||
| #### Data : | ||
|
|
||
| REST API requests might include data for the POST, PUT, and other HTTP methods to work successfully. | ||
|
|
||
| #### Parameters : | ||
|
|
||
| RESTful API requests can include parameters that give the server more details about what needs to be done. The following are some different types of parameters: | ||
|
|
||
| - Path parameters that specify URL details. | ||
| - Query parameters that request more information about the resource. | ||
| - Cookie parameters that authenticate clients quickly. | ||
| ## Authentication methods : | ||
|
|
||
| - Authentication is the process of verifying an identity. For example, you can prove your identity by showing an ID card or driver's license. Similarly, RESTful service clients must prove their identity to the server to establish trust. | ||
|
|
||
| - RESTful API has three common authentication methods: | ||
|
|
||
| ### HTTP authentication | ||
| HTTP defines some authentication schemes that you can use directly when you are implementing REST API. The following are two of these schemes: | ||
|
|
||
| #### Basic authentication : | ||
|
|
||
| In basic authentication, the client sends the user name and password in the request header. It encodes them with base64, which is an encoding technique that converts the pair into a set of 64 characters for safe transmission. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| #### Bearer authentication : | ||
|
|
||
| The term bearer authentication refers to the process of giving access control to the token bearer. The bearer token is typically an encrypted string of characters that the server generates in response to a login request. The client sends the token in the request headers to access resources. | ||
|
|
||
| ### API keys | ||
| API keys are another option for REST API authentication. In this approach, the server assigns a unique generated value to a first-time client. Whenever the client tries to access resources, it uses the unique API key to verify itself. API keys are less secure because the client has to transmit the key, which makes it vulnerable to network theft. | ||
|
|
||
| ### OAuth | ||
| OAuth combines passwords and tokens for highly secure login access to any system. The server first requests a password and then asks for an additional token to complete the authorization process. It can check the token at any time and also over time with a specific scope and longevity. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Server Response : | ||
|
|
||
| - server response means a client sends a message in form of a HTTP Request and the server responds in the form of an HTTP Response. This technique is termed as Messaging. | ||
|
|
||
| - REST principles require the server response to contain the following main components: | ||
|
|
||
| ### Status line | ||
| - The status line contains a three-digit status code that communicates request success or failure. For instance, 2XX codes indicate success, but 4XX and 5XX codes indicate errors. 3XX codes indicate URL redirection. | ||
|
|
||
| #### The following are some common status codes: | ||
| * 200: Generic success response | ||
| * 201: POST method success response | ||
| * 400: Incorrect request that the server cannot process | ||
| * 404: Resource not found | ||
|
|
||
| ### Message body | ||
| - The response body contains the resource representation. The server selects an appropriate representation format based on what the request headers contain. | ||
| - Clients can request information in XML or JSON formats, which define how the data is written in plain text. For example, if the client requests the name and age of a person named John, the server returns a JSON representation as follows: | ||
|
|
||
| { | ||
| "name" : "John", | ||
| "age" : 30 | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| ### Headers | ||
| - The response also contains headers or metadata about the response. | ||
|
|
||
| - They give more context about the response and include information such as the server, encoding, date, and content type. | ||
|
|
||
| ### References: | ||
|
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Please provide the links to the documents where the content is sourced from to ensure proper references are given. |
||
| - https://aws.amazon.com | ||
| - https://www.mailgun.com/blog/it-and-engineering/restful-api/ | ||
| - https://www.redhat.com/ | ||
| - https://www.mulesoft.com/ | ||
| - https://www.techtarget.com/ | ||
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Is this step specific to some API provider?
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
No Sir. These are general instructions. The user can choose an API based on their needs. For any API provider, the user creates an account with them and further obtains an API key.