15 minutes, Intermediate, Start Building
This sample is a fully reactive version of the Spring PetClinic application using Spring WebFlux.
To build and play with this app, follow the build instructions that are located here: https://github.com/DataStax-Examples/spring-petclinic-reactive
Let's do some initial setup by creating a serverless(!) database.
-
Create a DataStax Astra DB account if you don't already have one:
-
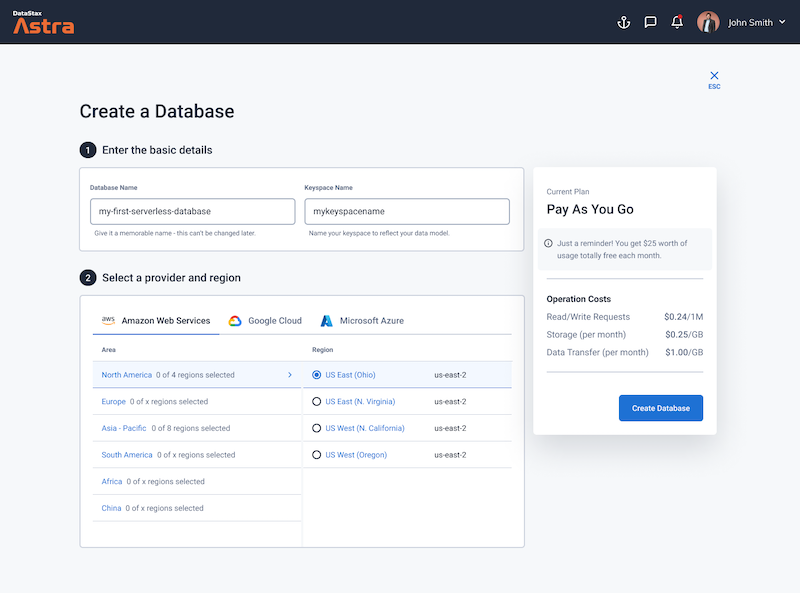
Define a database name, keyspace name and select a database region, then click create database.
-
Your Astra DB will be ready when the status will change from
PendingtoActive💥💥💥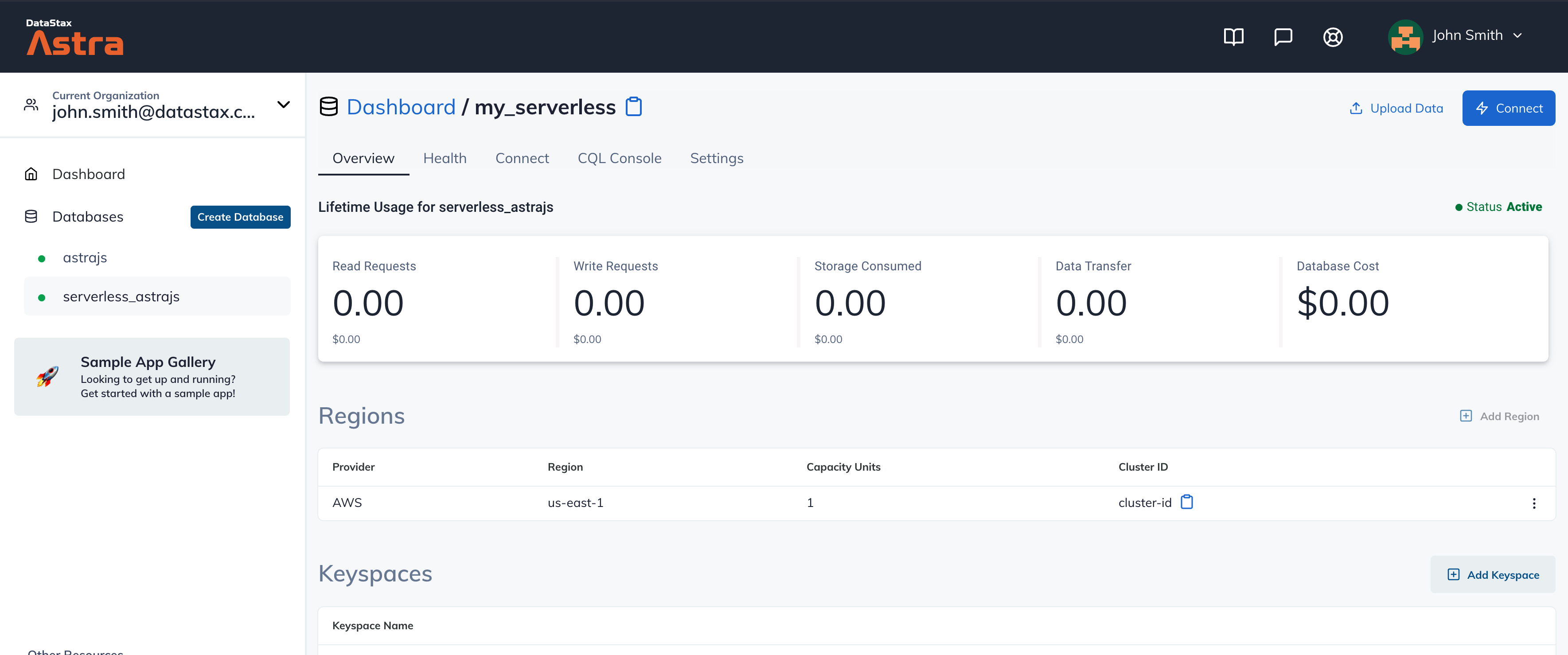
-
After your database is provisioned, we need to generate an Application Token for our App. Go to the
Settingstab in the database home screen.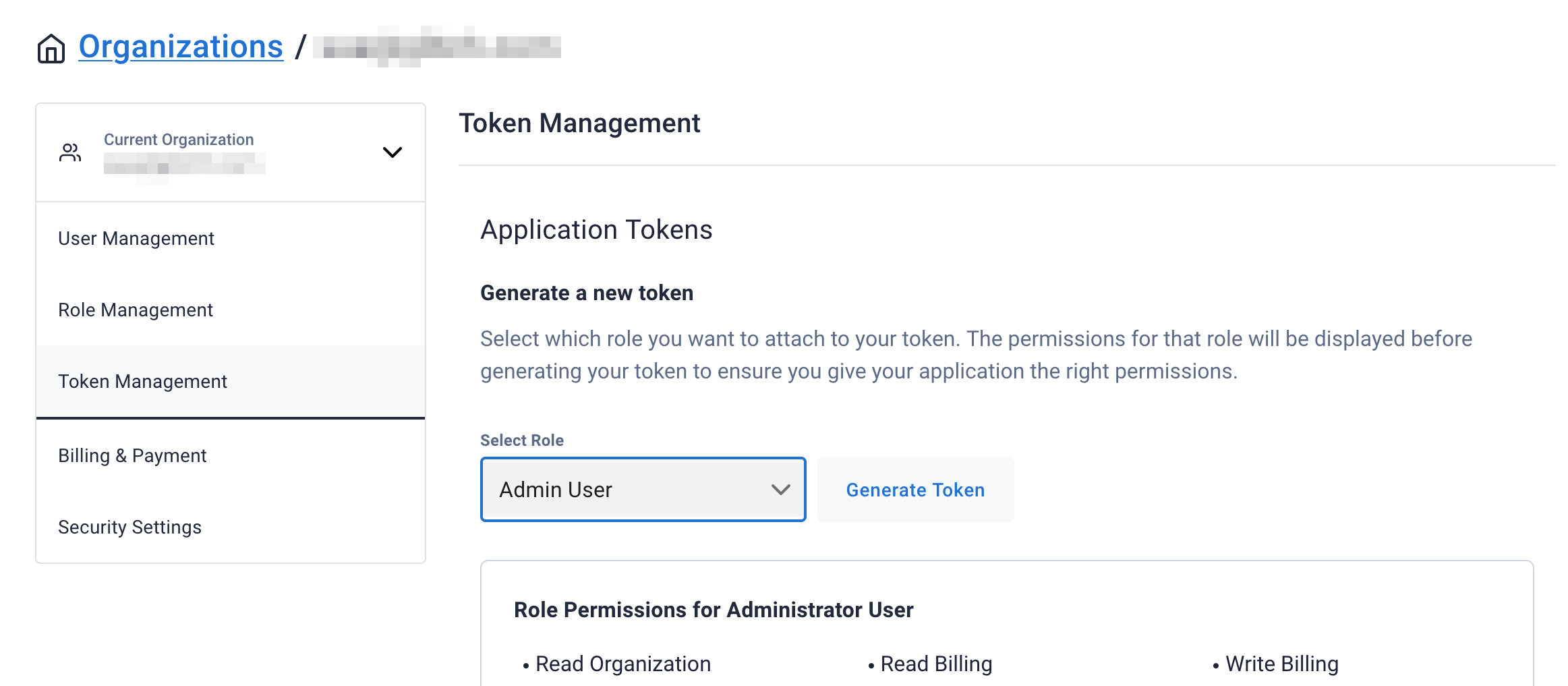
-
Select
Admin Userfor the role for this Sample App and then generate the token. Download the CSV so that we can use the credentials we need later.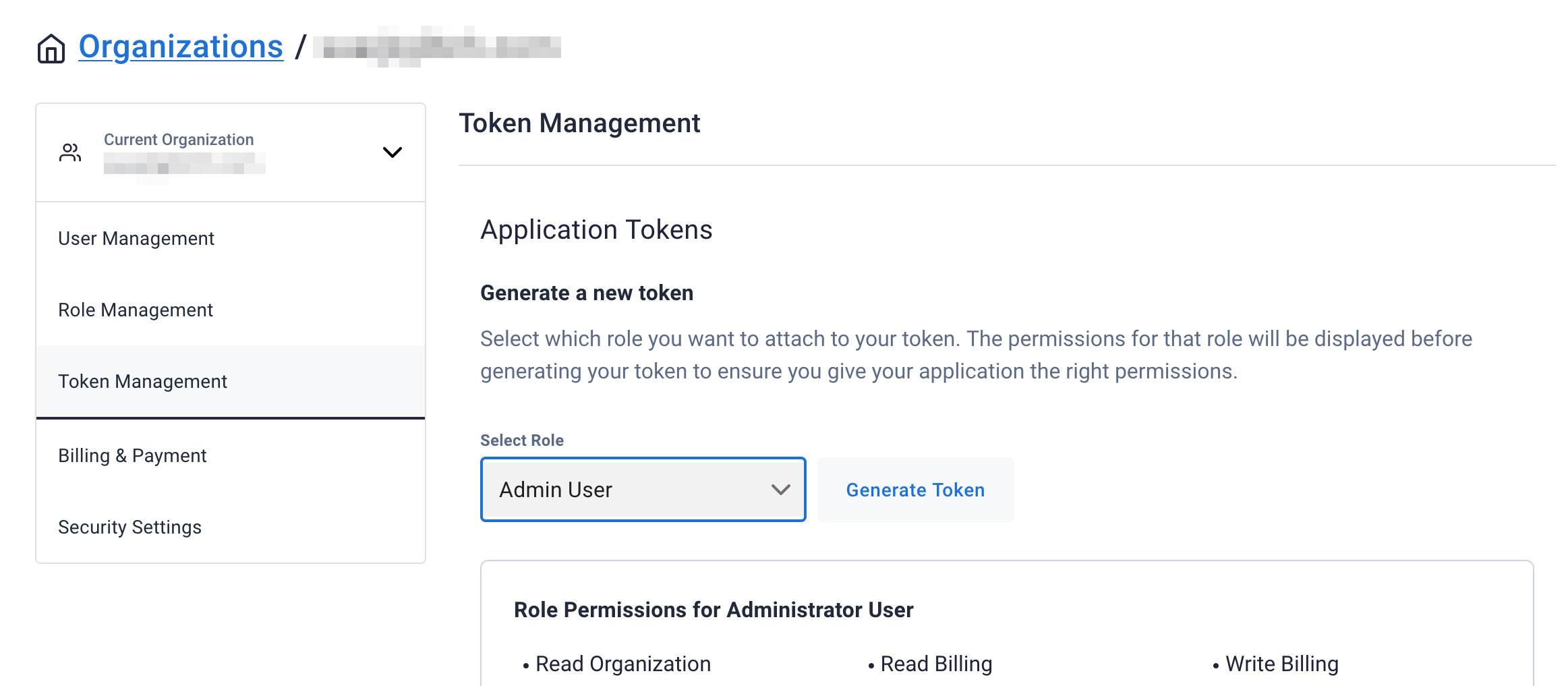
-
After you have your Application Token, head to the database connect screen and select the driver connection that we need. Go ahead and download the
Secure Bundlefor the driver.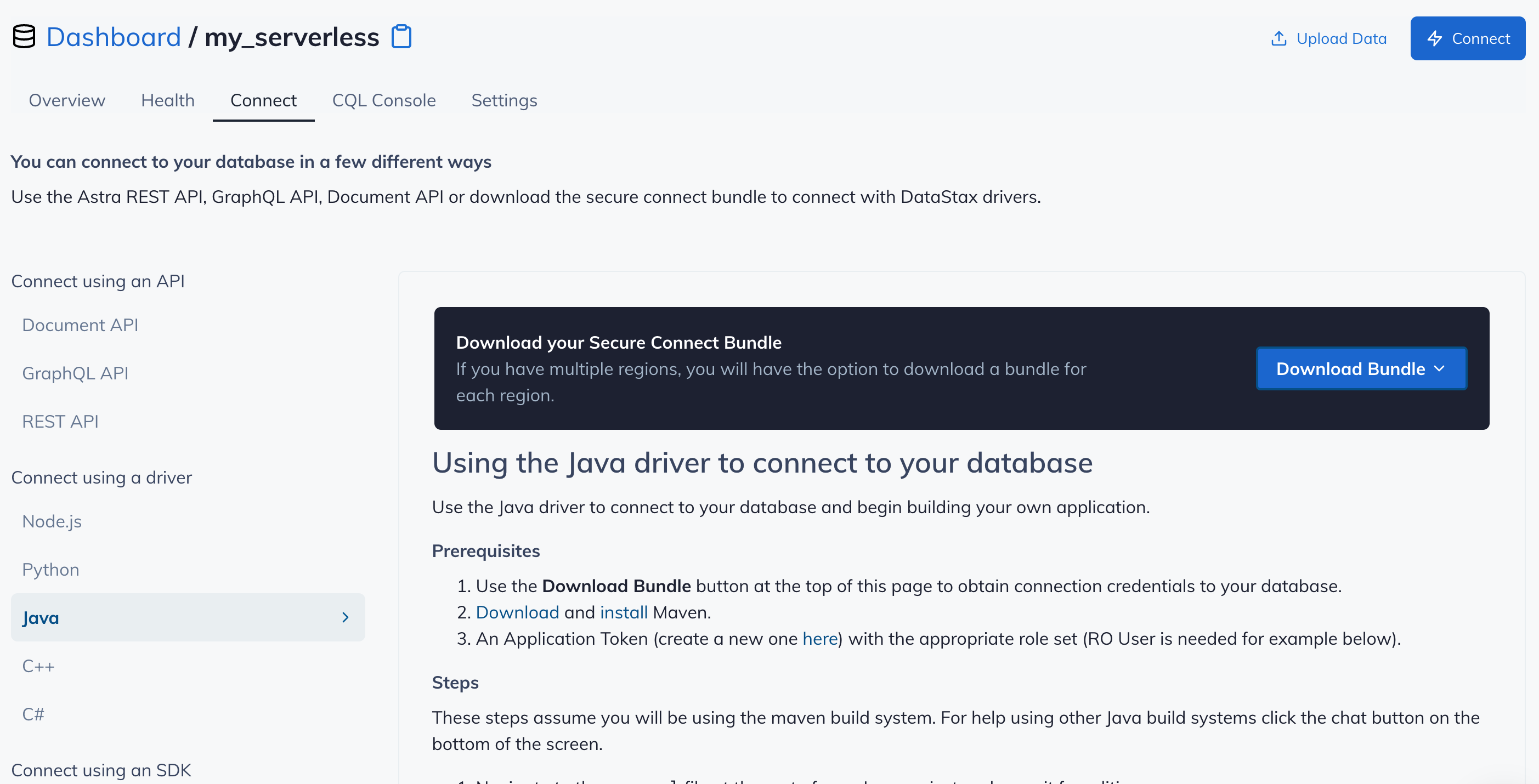
-
Make note of where to use the
Client IdandClient Secretthat is part of the Application Token that we generated earlier.
-
Click
Use this templateat the top of the GitHub Repository: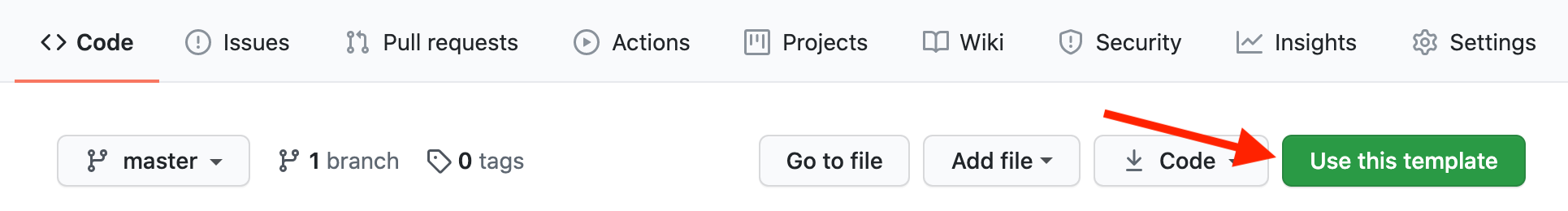
-
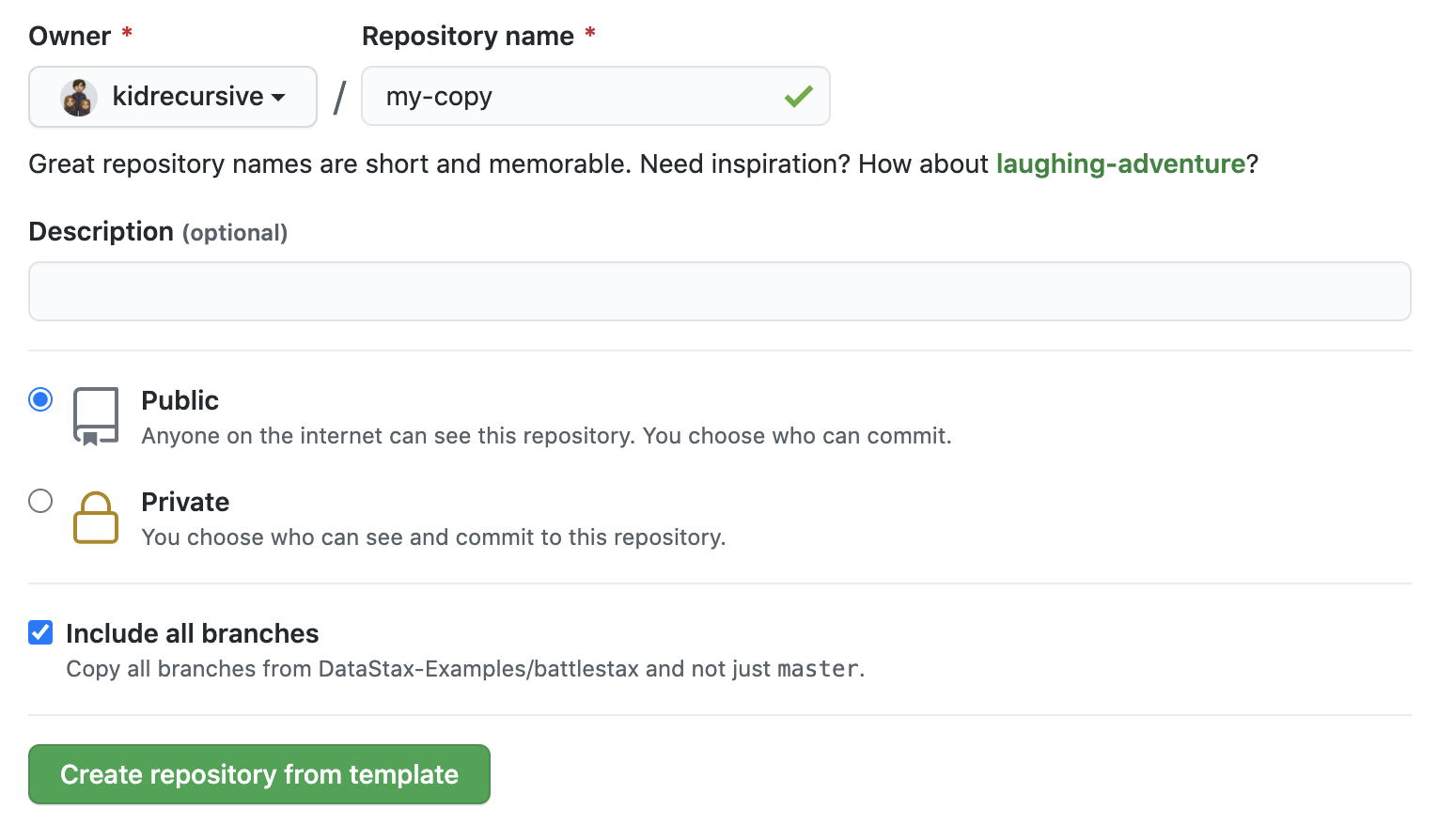
Enter a repository name and click 'Create repository from template':
Make sure you've completed the prerequisites before starting this step
✅ View your Database and connect
View your database. It may take 2-3 minutes for your database to spin up. You will receive an email at that point.
👁️ Expected output
Initializing
Once the database is ready, notice how the status changes from Pending to Active and Astra enables the CONNECT button.
✅ Navigate to your credentials
Locate the combo Organization: <Your email> on the top navigation. On the right side of your organization, click the ellipsis (...) then click your <Your email>.
You should land on the following screen. Scroll down to the bottom of the page to locate the Service Account in Security Settings
✅ Create Service Account
Create a service account by clicking Add Service Account button above the section as shown below
 When panel open on the right, click
When panel open on the right, click Add
✅ Copy credentials to your clipboard
Click the ellipsis at end of Service Account row to open menu as select Copy Credentials
The credentials you copied to the clipboard look like the following JSON, we will use it in gitpod to enable connectivity.
{
"clientId":"149de2c7-9b07-41b3-91ad-9453dee4dc54",
"clientName":"cedrick.lunven@datastax.com",
"clientSecret":"aaaaaaaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaaaaaaaaaa"
}✅ Open Gitpod (with creds copied to clipboard)
When you first launch gitpod, it builds the image.

✅ Paste credentials in Gitpod terminal
Once Gitpod loads the workspace, you'll be asked to paste your service account credentials in the Gitpod terminal at the bottom of the screen. The setup.sh script at the root of the repository is what asks this question.
✅ Open Swagger UI in browser
When gitpod finishes building the app, a new tab will open in your browser showing the following.
🎉 Celebrate!
You've successfully built the Spring Petclinic Reactive backend application!
✅ Start the Web UI :
You may have noticed another terminal named spring-petclinic-angular. This is where the UI should start.
After answering the question about analytics usage, you should be able to access the UI on a new tab.
NOTE If you want to run everything locally, reference the LOCAL_README.md
Let's have a look inside the main component spring-petclinic-reactive to see which libraries and frameworks have been used.
-
Spring-boot: Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run". We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need minimal Spring configuration. -
Spring-Security: Spring Security is a powerful and highly customizable authentication and access-control framework. It is the de-facto standard for securing Spring-based applications. Spring Security is a framework that focuses on providing both authentication and authorization to Java applications. Like all Spring projects, the real power of Spring Security is found in how easily it can be extended to meet custom requirements. -
Spring-WebFlux: Spring sub framework allowing to create Reactive Rest Endpoint. -
Spring-Actuator: Expose Endpoints to expose metrics to third party system: health, infos, jmx,prometheus,... -
Spring-Test: Enabled unit testing and mocking with Spring configuration and beans. -
Spring-Cloud: Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems (e.g. configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, intelligent routing, micro-proxy, control bus, one-time tokens, global locks, leadership election, distributed sessions, cluster state). Coordination of distributed systems leads to boiler plate patterns, and using Spring Cloud developers can quickly stand up services and applications that implement those patterns. They will work well in any distributed environment, including the developer’s own laptop, bare metal data centres, and managed platforms such as Cloud Foundry. -
SpringFox(Swagger): Annotation based rest documentation generation and test client generation (swagger-ui).
Here, you can find a description of the logical architecture components:
-
spring-parclinic-angular: This is the existing project that provides a user interface implementation using Angular. It has been used as well for other backend projects like the spring-petclinic-rest -
prometheus: Our component exposes some metrics through the actuator endpoint. A registry will push this information into the Prometheus database (docker-based).
Grafana: Allows to create dashboards based on data stored in prometheus.
zipkin: Our component includes thespring-cloud-sleuthdependency allowing Brave to push metrics usage of the API to the distributed tracing component Zipkin. To enable this tracing set the propertyzipkin.enabledto true inapplication.yaml. To start zipkin usedocker-compose up -d
zipkin:
enabled: true
baseUrl: http://localhost:9411
sender:
type: web
-
Apache Cassandra: A NoSQL database -
DataStax Astra: Apache Cassandra available in the Cloud for free as a managed service (DBaas)
The underlying data model implemented in Apache Cassandra is different from the one you would have defined with a relational database.
To enable scalability, Apache Cassandra does not support joins or integrity constraints. Therefore we used some denormalization.
We also created some secondary indices to queries columns that are not the PARTITION KEY. These secondary indices work well in this case because the cardinality is low (e.g, few pets for an owner).
The application generates the objects related to the data model (e.g., tables, indices, udts) at startup.
The issue trackeris the preferred channel for bug reports, features requests and submitting pull requests.
For pull requests, editor preferences are available in the editor config for easy use in common text editors. Read more and download plugins at http://editorconfig.org.