A high-performance pure-javascript SHA1 implementation suitable for large binary data.
Rusha is available via npm:
npm install rusha
Rusha is available via bower:
bower install rusha
It is highly recommended to run CPU-intensive tasks in a Web Worker. To do so, just follow the instructions on Using the Rusha Worker.
If you have a good reason not to use Web Workers, follow the instructions on Using the Rusha Hash API instead.
You can create a new worker in two ways. The preferred way is using Rusha.createWorker(), which spawns a webworker containing the hashing logic, and returns back a Worker object:
const worker = Rusha.createWorker();If for some reason this does not work for you, you can also just point the Worker constructor
at rusha.js or rusha.min.js, like so:
const worker = new Worker("dist/rusha.min.js");Note: In order to make the latter work, Rusha will by default subscribe to incoming messages when it finds itself inside a worker context. This can lead to problems when you would like to use Rusha as a library inside a web worker, but still have control over the messaging. To disable this behaviour, you can call
Rusha.disableWorkerBehaviour()from within the worker.
You can send your instance of the web worker messages in the format {id: jobid, data: dataobject}. The worker then sends back a message in the format {id: jobid, hash: hash}, were jobid is the id of the job previously received and hash is the hash of the data-object you passed, be it a Blob, Array, Buffer, ArrayBuffer or String
The Rusha Hash API is inspired by the Node.js Hash API.
const hexHash = Rusha.createHash().update('I am Rusha').digest('hex'); const hash = Rusha.createHash();
hash.update('I am');
hash.update(' Rusha');
const hexHash = rusha.digest('hex');You instantiate a new Hash object by calling Rusha.createHash().
update(data): Update the hash state with the givendata, which can be a binaryString,Buffer,ArrayorArrayBuffer.digest([encoding]): Calculates the digest of all of the data passed to be hashed. Theencodingcan be'hex'or undefined. Ifencodingis provided a string will be returned; otherwise anArrayBufferis returned.
Note: Due to its synchronous nature,
Hash#updatedoes not accept data of typeBlob. If you need to work withBlobs, you can either use the Rusha Worker, or useFileReader#readAsArrayBufferto read the contents of theBlob, and then invokeHash#updatewith theArrayBufferthat was returned.
state(getter and setter): Allows getting and setting the internal hashing state.
The Rusha Object API is deprecated, and is only documented here for older code bases that might still be using it.
You should be using the Hash API instead, which is documented above.
const rusha = new Rusha();
const hexHash = rusha.digest('I am Rusha'); const rusha = new Rusha();
rusha.resetState();
rusha.append('I am');
rusha.append(' Rusha');
const hexHash = rusha.end();Your instantiate a new Rusha object by doing new Rusha(). When created, it provides the following methods:
digest(d): Create a hex digest from data of the three kinds mentioned below, or throw and error if the type is unsupported.digestFromString(s): Create a hex digest from a binaryString. A binary string is expected to only contain characters whose charCode < 256.digestFromBuffer(b): Create a hex digest from aBufferorArray. Both are expected to only contain elements < 256.digestFromArrayBuffer(a): Create a hex digest from anArrayBufferobject.rawDigest(d): Behaves just like #digest(d), except that it returns the digest as an Int32Array of size 5.resetState(): Resets the internal state of the computation.append(d): Appends a binaryString,Buffer,Array,ArrayBufferorBlob.setState(state): Sets the internal computation state. See: getState().setState(): Returns an object representing the internal computation state. You can pass this state to setState(). This feature is useful to resume an incremental sha.end(): Finishes the computation of the sha, returning a hex digest.rawEnd(): Behaves just like #end(), except that it returns the digest as an Int32Array of size 5.
- Download npm dependencies with
npm install - Make changes to the files in
src/ - Build with
npm run build - Run tests with
npm test
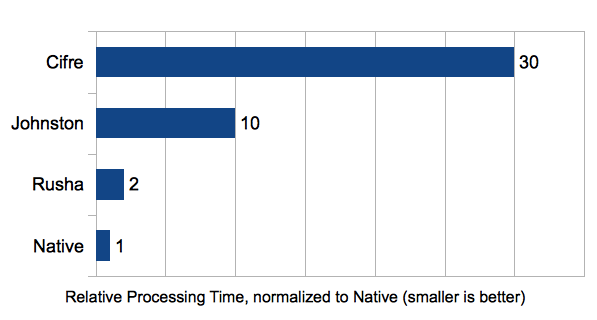
Tested were my Rusha implementation, the sha1.js implementation by P. A. Johnston, Tim Caswell's Cifre and the Node.JS native implementation.
If you want to check the performance for yourself in your own browser, I compiled a JSPerf Page.
A normalized estimation based on the best results for each implementation, smaller is better:
Results per Implementation and Platform:
All tests were performed on a MacBook Air 1.7 GHz Intel Core i5 and 4 GB 1333 MHz DDR3.