This repository is not maintained anymore, as it has been integrated as core feature into Galaxy. Read more about this in the January 2015 Galaxy NewsBrief and in our Wiki page.
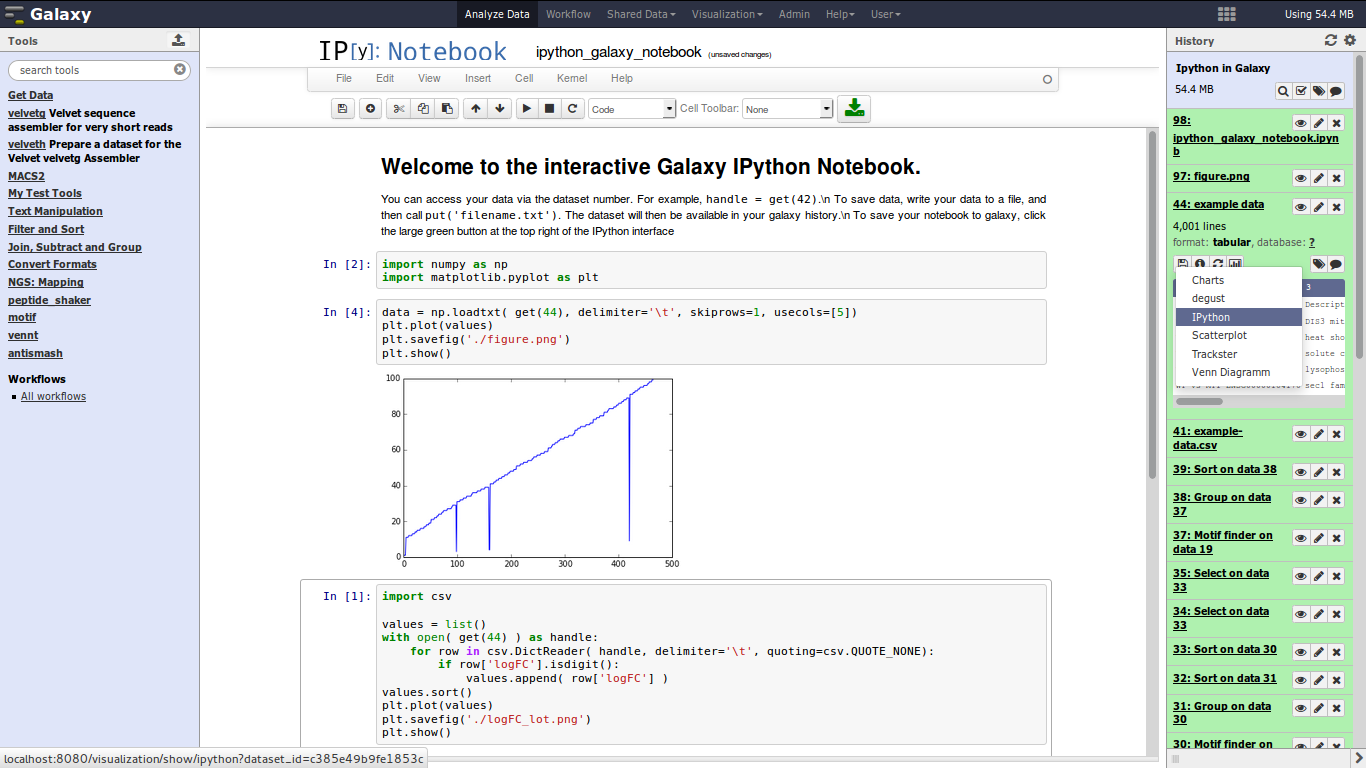
This projects integrates IPython Notebook, a interactive computational environment, with Galaxy. We hope to make Galaxy more attractive for bioinformaticians and to combine the power of both projects to unlock creativity in data analysis, but also in Next-Generation-Training courses.
The only requirement is to have Docker installed on your system. For a detailed instruction how to install docker, please look at the docker website.
Copy the template and config folder in your GALAXY_ROOT/config/plugins/visualizations/ipython folder and restart Galaxy.
Alternatively, you can clone the repository with
git clone https://github.com/bgruening/galaxy-ipython.git config/plugins/visualizations/ipythonThe IPython visualisation option should be visible next to the usual Charts or Trackster options in your visualisation menue.
- run IPython directly in your Galaxy main window or in Galaxy Scratchbook
- complete encapsulated python environment with matplotlib, pandas and friends installed
- access to all datasets from your current history via pre-defined IPython function
- manipulate and plot data as you like and export your new files back into the Galaxy history
- access your Galaxy instance from IPython with bioblend and redefined functions
- save the IPython Notebook into your Galaxy history
- notebook persistence across sessions
- saved IPython Notebook files can be viewed in HTML and re-opened
- self-closing and cleaning IPython docker container
The mako template from the Galaxy visualisation framework renders the interface and builds all files and commands needed to lunch the docker container. A config file is saved under /import/ inside the docker container. The IPython webpage running in docker will be included in a HTML object and displayed to the user.
Depending on your configuration some JavaScript magic is done to add an object to the DOM, which will be loaded by the browser and conditionally handles login.
Iside of docker TCP connections are monitored using cron. As soon as the user quits using the notebook, the dropping TCP connections are recognised and the cotainer cleans up after itself and kills itself.
For your convience, we have added a few pre-defined functions to the IPython profile.
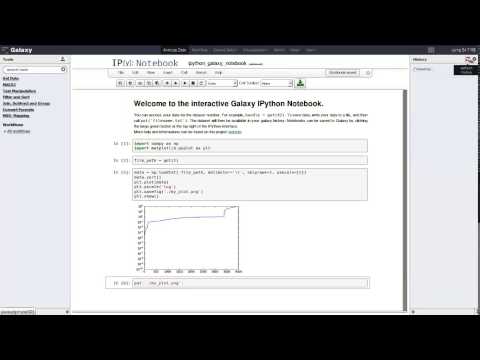
The get function will copy a dataset, identified by the history_id, from your current Galaxy into the docker container. It will return the file path to the copied file.
Example:
with open( get( 44 ), 'r') as handle:
for line in handle:
print( line )The put function takes a file path and transfers the file to the current history of your Galaxy session.
Example:
put( './my_file.tsv', file_type = 'tabular')Accessing your current history is possible with the pre-defined HISTORY_ID variable.
If you want to communicate with Galaxy you can use get_galaxy_connection() to get an bioblend GalaxyInstance object.
Example:
from bioblend.galaxy.histories import HistoryClient
gi = get_galaxy_connection()
hc = HistoryClient( gi )
for dataset in hc.show_history( HISTORY_ID , contents=True) ):
print( dataset['id'] )By default, no security turned on. To do this, you must adjust two variables, apache_urls and
password_auth in the configuration file (config/ipython.conf).
The apache_urls variable should be set to True, and containers should be secured via Apache+SSL for production usage. Please see the setup document for more information.
The password_auth variable should be set to True. It functions by generating a random password which is only shared with the docker, and the user's browser through Galaxy. In theory this should be a secure system (or at least as secure as the weakest link), however if you find a vulnerability in the system we've devised, please contact us and we'll patch it as soon as possible!
- Björn Grüning bjoern.gruening@gmail.com
- Eric Rasche rasche.eric@yandex.ru
- v0.1: Initial public release (01.08.2014)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.