A curated list of promising OCR resources
website source code you can modify or add new more keywords for tracking and sharing just edit this file https://github.com/wanghaisheng/ocr-arxiv-daily/blob/main/database/topic.yml make a request
Fully-automated scripts for collecting AI-related papers. Support fuzzy and exact search for paper titles.
https://github.com/wanghaisheng/ocr-paper-collector
https://github.com/wanghaisheng/ocr-tweets-monitoring
有2个api
都支持图片
百度自家的 :基本可以放弃
化验单识别:也只能提取化验单上三个字段的一个
第三方和阿里自己提供的 API 集中在身份证、银行卡、驾驶证、护照、电商商品评论文本、车牌、名片、贴吧文本、视频中的文本,多输出字符及相应坐标,卡片类可输出成结构化字段,价格在0.01左右
另外有三家提供了简历的解析,输出结果多为结构化字段,支持文档和图片格式 价格在0.1-0.3次不等
目前无第三方入驻,仅有腾讯自有的api 涵盖车牌、名片、身份证、驾驶证、银行卡、营业执照、通用印刷体,价格最高可达0.2左右。
OcrKing 从哪来?
OcrKing 源自2009年初 Aven 在数据挖掘中的自用项目,在对技术的执着和爱好的驱动下积累已近七载经多年的积累和迭代,如今已经进化为云架构的集多层神经网络与深度学习于一体的OCR识别系统2010年初为方便更多用户使用,特制作web版文字OCR识别,从始至今 OcrKing一直提供免费识别服务及开发接口,今后将继续提供免费云OCR识别服务。OcrKing从未做过推广,
但也确确实实默默地存在,因为他相信有需求的朋友肯定能找得到。欢迎把 OcrKing 在线识别介绍给您身边有类似需求的朋友!希望这个工具对你有用,谢谢各位的支持!
OcrKing 能做什么?
OcrKing 是一个免费的快速易用的在线云OCR平台,可以将PDF及图片中的内容识别出来,生成一个内容可编辑的文档。支持多种文件格式输入及输出,支持多语种(简体中文,繁体中文,英语,日语,韩语,德语,法语等)识别,支持多种识别方式, 支持多种系统平台, 支持多形式API调用!
-
Tesseract.js is a pure Javascript port of the popular Tesseract OCR engine.
-
List of Tesseract add-ons including wrappers in different languages.
超轻量级模型,大小低至9.4M.支持80+语言模型,且内置训练模块、半监督标注工具、板面分析模型,中文方面识别占优。
继承PaddleOCR优势,在此基础上提供了ONNX后端,并额外支持了DirectX加速支持,在Windows部署有显著的兼容性和性能优势。
-
A small C++ implementation of LSTM networks, focused on OCR.by Adnan Ul-Hasan
-
End to end OCR system for Telugu. Based on Convolutional Neural Networks.
-
'caffe-ocr - OCR with caffe deep learning framework' by pannous
-
A implementation of LSTM and CTC to recognize image without splitting
-
warp-ctc A fast parallel implementation of CTC, on both CPU and GPU. by BAIDU
Connectionist Temporal Classification is a loss function useful for performing supervised learning on sequence data, without needing an alignment between input data and labels. For example, CTC can be used to train end-to-end systems for speech recognition, which is how we have been using it at Baidu's Silicon Valley AI Lab.
Warp-CTC是一个可以应用在CPU和GPU上高效并行的CTC代码库 (library) 介绍 CTCConnectionist Temporal Classification作为一个损失函数,用于在序列数据上进行监督式学习,不需要对齐输入数据及标签。比如,CTC可以被用来训练端对端的语音识别系统,这正是我们在百度硅谷试验室所使用的方法。 端到端 系统 语音识别
-
Test mxnet with own trained model,用训练好的网络模型进行数字,少量汉字,特殊字符(./等)的识别(总共有210类)
-
OCRmyPDF uses Tesseract for OCR, and relies on its language packs.
-
OwncloudOCR uses tesseract OCR and OCRmyPDF for reading text from images and images in PDF files.
-
多标签分类,端到端的中文车牌识别基于mxnet, End-to-End Chinese plate recognition base on mxnet
-
Added support for CTC in both Theano and Tensorflow along with image OCR example. #3436
-
A curated list of resources dedicated to scene text localization and recognition
-
Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (CRNN) for image-based sequence recognition.
-
Part of eMOP: Franken+ tool for creating font training for Tesseract OCR engine from page images.
-
Automatic License Plate Recognition library http://www.openalpr.com
-
A generative vision model that trains with high data efficiency and breaks text-based CAPTCHAs
-
STN-OCR: A single Neural Network for Text Detection and Text Recognition
-
Digit Segmentation and Recognition using OpenCV and MLP test
检测单词,而不是检测出一个文本行
-
Arbitrary-Oriented Scene Text Detection via Rotation Proposals
-
通过旋转候选框实现任意方向的场景文本检测 Arbitrary-Oriented Scene Text Detection via Rotation Proposals
-
A stand alone character recognition micro-service with a RESTful API
-
GOCR is an optical character recognition program, released under the
Building on recent advances in image caption generation and optical character recognition (OCR), we present a general-purpose, deep learning-based system to decompile an image into presentational markup. While this task is a well-studied problem in OCR, our method takes an inherently different, data-driven approach. Our model does not require any knowledge of the underlying markup language, and is simply trained end-to-end on real-world example data. The model employs a convolutional network for text and layout recognition in tandem with an attention-based neural machine translation system. To train and evaluate the model, we introduce a new dataset of real-world rendered mathematical expressions paired with LaTeX markup, as well as a synthetic dataset of web pages paired with HTML snippets. Experimental results show that the system is surprisingly effective at generating accurate markup for both datasets. While a standard domain-specific LaTeX OCR system achieves around 25% accuracy, our model reproduces the exact rendered image on 75% of examples.
We present recursive recurrent neural networks with attention modeling (R2AM) for lexicon-free optical character recognition in natural scene images. The primary advantages of the proposed method are: (1) use of recursive convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which allow for parametrically efficient and effective image feature extraction; (2) an implicitly learned character-level language model, embodied in a recurrent neural network which avoids the need to use N-grams; and (3) the use of a soft-attention mechanism, allowing the model to selectively exploit image features in a coordinated way, and allowing for end-to-end training within a standard backpropagation framework. We validate our method with state-of-the-art performance on challenging benchmark datasets: Street View Text, IIIT5k, ICDAR and Synth90k.
Clustering is central to many data-driven application domains and has been studied extensively in terms of distance functions and grouping algorithms. Relatively little work has focused on learning representations for clustering. In this paper, we propose Deep Embedded Clustering (DEC), a method that simultaneously learns feature representations and cluster assignments using deep neural networks. DEC learns a mapping from the data space to a lower-dimensional feature space in which it iteratively optimizes a clustering objective. Our experimental evaluations on image and text corpora show significant improvement over state-of-the-art methods
-
SEE: Towards Semi-Supervised End-to-End Scene Text Recognition
-
A generative vision model that trains with high data efficiency and breaks text-based CAPTCHAs
-
EXTENDING THE PAGE SEGMENTATION ALGORITHMS OF THE OCROPUS DOCUMENTATION LAYOUT ANALYSIS SYSTEM
-
Text Recognition in Scene Image and Video Frame using Color Channel Selection
In recent years, recognition of text from natural scene image and video frame has got increased attention among the researchers due to its various complexities and challenges. Because of low resolution, blurring effect, complex background, different fonts, color and variant alignment of text within images and video frames, etc., text recognition in such scenario is difficult. Most of the current approaches usually apply a binarization algorithm to convert them into binary images and next OCR is applied to get the recognition result. In this paper, we present a novel approach based on color channel selection for text recognition from scene images and video frames. In the approach, at first, a color channel is automatically selected and then selected color channel is considered for text recognition. Our text recognition framework is based on Hidden Markov Model (HMM) which uses Pyramidal Histogram of Oriented Gradient features extracted from selected color channel. From each sliding window of a color channel our color-channel selection approach analyzes the image properties from the sliding window and then a multi-label Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier is applied to select the color channel that will provide the best recognition results in the sliding window. This color channel selection for each sliding window has been found to be more fruitful than considering a single color channel for the whole word image. Five different features have been analyzed for multi-label SVM based color channel selection where wavelet transform based feature outperforms others. Our framework has been tested on different publicly available scene/video text image datasets. For Devanagari script, we collected our own data dataset. The performances obtained from experimental results are encouraging and show the advantage of the proposed method.
Recently, scene text detection has become an active research topic in computer vision and document analysis, because of its great importance and significant challenge. However, vast majority of the existing methods detect text within local regions, typically through extracting character, word or line level candidates followed by candidate aggregation and false positive elimination, which potentially exclude the effect of wide-scope and long-range contextual cues in the scene. To take full advantage of the rich information available in the whole natural image, we propose to localize text in a holistic manner, by casting scene text detection as a semantic segmentation problem. The proposed algorithm directly runs on full images and produces global, pixel-wise prediction maps, in which detections are subsequently formed. To better make use of the properties of text, three types of information regarding text region, individual characters and their relationship are estimated, with a single Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) model. With such predictions of text properties, the proposed algorithm can simultaneously handle horizontal, multi-oriented and curved text in real-world natural images. The experiments on standard benchmarks, including ICDAR 2013, ICDAR 2015 and MSRA-TD500, demonstrate that the proposed algorithm substantially outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, we report the first baseline result on the recently-released, large-scale dataset COCO-Text.
-
Joint Line Segmentation and Transcription for End-to-End Handwritten Paragraph Recognition
-
Scene Text Recognition with Sliding Convolutional Character Models
特征描述的完整过程 http://dataunion.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/640.webp_2.jpg
- 学霸君archsubmit上的演讲提到了他们的ocr算法 使用cnn来识别中文 链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kUoSyV1 密码: p92n
作者:chenqin
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/19593313/answer/18795396
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
1,识别率极高。我使用过现在的答案总结里提到的所有软件,但遇到下面这样的表格,除了ABBYY还能保持95%以上的识别率之外(包括秦皇岛三个字),其他所有的软件全部歇菜,数字认错也就罢了,中文也认不出。血泪的教训。
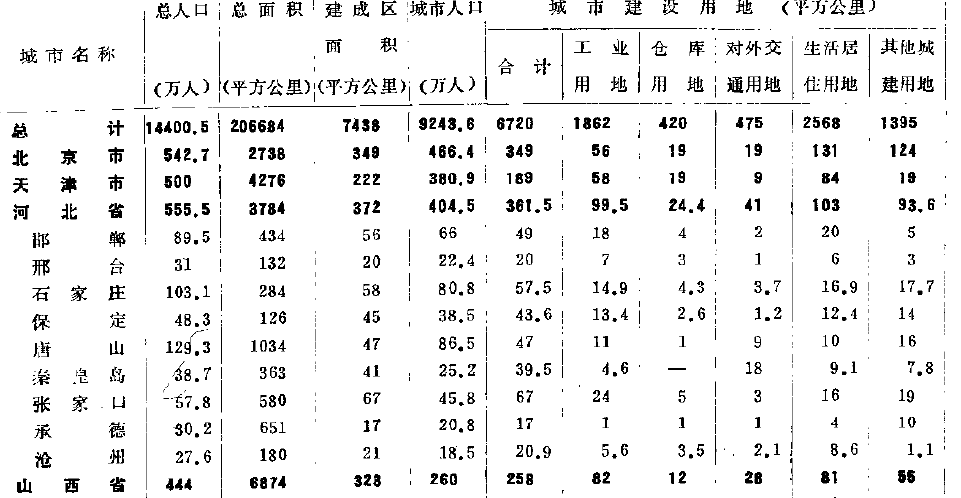
2,自由度高。可以在同一页面手动划分不同的区块,每一个区块也可以分别设置表格或文字;简体繁体英文数字。而此时大部分软件还只能对一个页面设置一种识别方案,要么表格,要么文字。
3,批量操作方便。对于版式雷同的年鉴,将一页的版式设计好,便可以应用到其他页,省去大量重复操作。
4,可以保持原有表格格式,省去二次编辑。跨页识别表格时,选择“识别为EXCEL”,ABBYY可以将表格连在一起,产出的是一整个excel文件,分析起来就方便多了。
5,包括梯形校正,歪斜校正之类的许多图片校正方式,即使扫描得歪了,或者因为书本太厚而导致靠近书脊的部分文字扭曲,都可以校正回来。
Convert scanned images of documents into rich text with advanced Deep Learning OCR APIs. Free forever plans available.
- IRIS
真正能把中文OCR做得比较专业的,一共也没几家,国内2家,国外2家。国内是文通和汉王,国外是ABBYY和IRIS(台湾原来有2家丹青和蒙恬,这两年没什么动静了)。像大家提到的紫光OCR、CAJViewer、MS Office、清华OCR、包括慧视小灵鼠,这些都是文通的产品或者使用文通的识别引擎,尚书则是汉王的产品,和中晶扫描仪捆绑销售的。这两家的中文识别率都是非常不错的。而国外的2家,主要特点是西方语言的识别率很好,而且支持多种西欧语言,产品化程度也很高,不过中文方面速度和识别率还是有差距的,当然这两年人家也是在不断进步。Google的开源项目,至少在中文方面,和这些家相比,各项性能指标水平差距还蛮大的呢。
作者:张岩
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/19593313/answer/14199596
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
https://github.com/cisocrgroup
目前看到最棒的免费的API 当然也提供商业版
欢迎扫码加入 参与讨论分享 过期请添加个人微信 edwin_whs
