rs1090 is a Rust library to decode Mode S, ADS-B and FLARM messages.
It takes its inspiration from the Python pyModeS library, and uses deku in order to decode binary data in a clean declarative way. The project started as a fork of a very similar project called adsb-deku, but modules have been refactored to match pyModeS design, implementations extensively reviewed, simplified, corrected, and completed.
The directions ambitioned by rs1090 include:
- improving the performance of Mode S decoding in Python;
- exporting trajectory data to cross-platform formats such as JSON, gRPC, arrow;
- providing efficient multi-receiver Mode S decoding;
- serving real-time enriched trajectory data to external applications.
If you just want something stable to decode ADS-B messages from your Raspberry and visualize the data on a map, you may want to stick to one of the dump0190 implementations.
The rs1090 library comes with:
- a companion application decode1090,
- a live decoder jet1090,
- a Python binding rs1090.
- and a WebAssembly binding rs1090-wasm.
The documentation for the core library is available on docs.rs, generated directly from the source code.
The decode module is probably the most useful part, in order to understand the content of various types of messages.
Benchmarking performed on the decoding of a gate-to-gate European flight:
- pyModeS in full Python mode;
- pyModeS with Cython compiled functions;
rs1090with Python bindings on a single core (for a fair comparison);rs1090with Python bindings on many cores (default);- full Rust
rs1090benchmark on many cores (default).
The Python script for benchmarking is in python/examples.
The Rust benchmark is executed with cargo bench.
Both scripts are run on an Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10850H CPU @ 2.70GHz.
Note
The default out-of-the-box mode of rs1090 is an execution distributed on all your cores. This benchmark was performed on a regular laptop. It can be much faster on supercomputers, but considering that most laptops now have at least 4 cores, this benchmark yields the speed-up you should get on your own computer.
Run the following Cargo command in your project directory:
cargo add rs1090Or add the following line to your Cargo.toml:
rs1090 = "1.0.0" # check for the latest version, we are not there yetuse hexlit::hex;
use rs1090::prelude::*;
fn main() {
let bytes: [u8; 14] = hex!("8c4841753a9a153237aef0f275be");
// ADS-B decoding
if let Ok(msg) = Message::try_from(bytes.as_slice()) {
// JSON output
let json = serde_json::to_string(&msg).expect("JSON error");
println!("{}", json);
}
}See more examples in the crates/rs1090/examples folder.
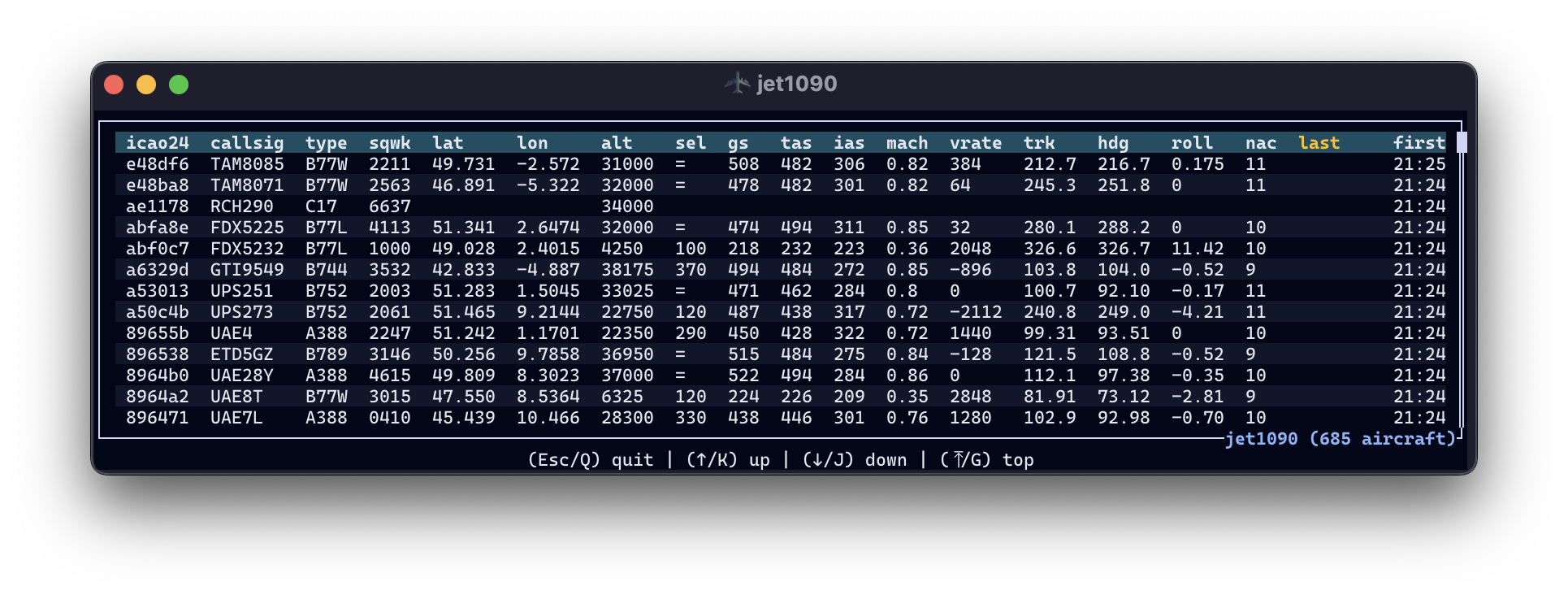
The jet1090 executable is documented on https://mode-s.org/jet1090
You may install the bindings compiled for most Python versions with:
pip install rs1090The library provides a single do-it-all function called decode():
>>> import rs1090
>>> rs1090.decode("8c4841753a9a153237aef0f275be")
{'df': '17',
'icao24': '484175',
'bds': '06',
'NUCp': 7,
'groundspeed': 17.0,
'track': 92.8125,
'parity': 'odd',
'lat_cpr': 39195,
'lon_cpr': 110320}For large sets of messages in Python (e.g. what you can download through pyopensky):
>>> import rs1090
>>> rs1090.decode(msg_list, ts_list) # includes CPR to position decoding
...
>>> rs1090.decode(msg_list, ts_list, reference=(lat0, lon0)) # useful for surface messages
...For FLARM messages (also as batches):
>>> msg = "7bf2381040ccc7e2395ecaa28e033a655d47e1d91d0bf986e1b0"
>>> rs1090.flarm(msg, 1655279476, 43.61924, 5.11755)
{'timestamp': 1655279476,
'reference_lat': 43.61924,
'reference_lon': 5.11755,
'icao24': '38f27b',
'is_icao24': True,
'actype': 'Glider',
'latitude': 43.6812864,
'longitude': 5.150585599999999,
'geoaltitude': 970,
'vertical_speed': 1.0,
'groundspeed': 18.698261951315153,
'track': 29.655457935479006,
'no_track': False,
'stealth': False,
'gps': 129}Usage is documented on https://observablehq.com/@xoolive/rs1090.
Prebuilt binaries are available on the Releases page.
Usage is available with the help command.
decode1090 --helpThis repository provides a Nix flake configuration for building and managing this project.
You may run the following to get the jet1090 and decode1090 executables in your PATH
nix profile installFor reference:
nix develop # open a shell with the proper environment to compile rs1090
nix build # build the jet1090 executable
nix run # run the jet1090 executable