AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper is a Node.js LDAP server built on top of (ldapjs) that allows users and groups from Azure Active Directory to be accessed through the LDAP protocol. User authentication is performed using Microsoft Graph API on every login attempt. This enables other applications to connect to the LDAP server and utilize AzureAD login credentials, making it a possible solution for older applications that lack AzureAD support or for scenarios where managing a local AD controller is undesirable.
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
participant LDAP client
participant AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper
participant AAD (Graph API)
Note over AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper: start LDAP server
AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper->>AAD (Graph API): Fetch users and groups
Note over AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper: cache users and groups locally
LDAP client->>+AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper: Attempt to bind with user credentials
AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper->>+AAD (Graph API): Check user credentials
AAD (Graph API)-->>-AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper: Valid credentials
Note over AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper: save password hash locally in the cache
AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper->>-LDAP client: Successful bind/authenticate
loop every 30 minutes
AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper->>AAD (Graph API): Fetch users and groups again
Note over AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper: merge and cache users and groups locally
end
The AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper starts an LDAP server and fetches users and groups from the AAD Graph API. These are cached and merged locally.
When an LDAP client attempts to bind with user credentials, the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper checks these credentials by communicating with the AAD Graph API. If the credentials are valid, the AAD Graph API sends a success response to the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper, which then sends a successful bind message to the user's LDAP client. Additionally, the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper saves the user's password hash in the sambaNTPassword attribute and sets the sambaPwdLastSet attribute to "now". This allows the user to access samba shares, such as those on a NAS, from Windows PCs.
The AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper periodically fetches user and group information from the AAD Graph API every 30 minutes, merging and caching the results locally. This process preserves attributes like uid, gid, sambaNTPassword, and sambaPwdLastSet.
To use the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper, you will need:
-
An Azure Active Directory (AD) tenant with at least one registered user.
-
An Azure AD application registered in your tenant, with the following permissions:
- For type
ApplicationgrantUser.Read.AllandGroup.Read.All. - For type
DelegatedgrantUser.Read.
You can follow the instructions in the installation guide to set up your application.
- For type
To run the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper, you'll need to have your Tenant ID, Application ID, and Application Secret available. These values are required to authenticate and authorize the application to access your Azure AD resources. You can find these values in the Azure portal.
Once you have created your Azure AD application, you can run the LDAP wrapper on your local machine, on a server or even a Synology NAS. Depending on your setup you will either need:
- Node.js version 17 or higher, which can be downloaded from the official Node.js website.
or
- Docker, which can be downloaded from the official Docker website.
Note that some features of the wrapper may require additional configuration or dependencies, such as a NAS for network storage access.
There are multiple ways to run the LDAP-wrapper. For more information, please consult the documentation to get started.
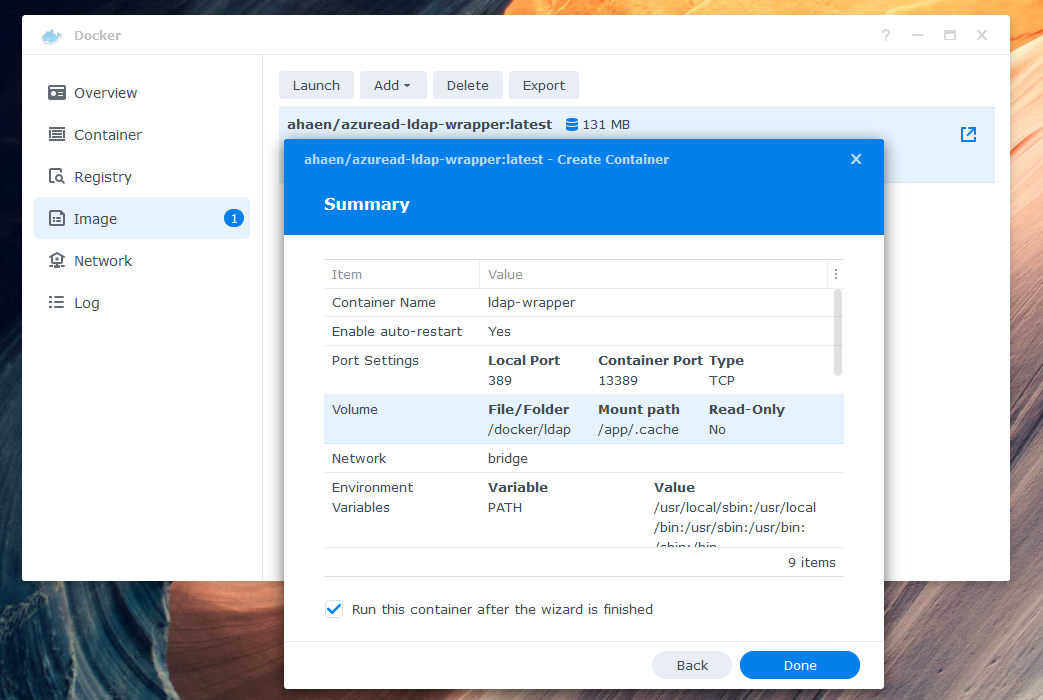
One way to run the LDAP-wrapper is, to start a Docker container on a Synolog NAS like this:
-
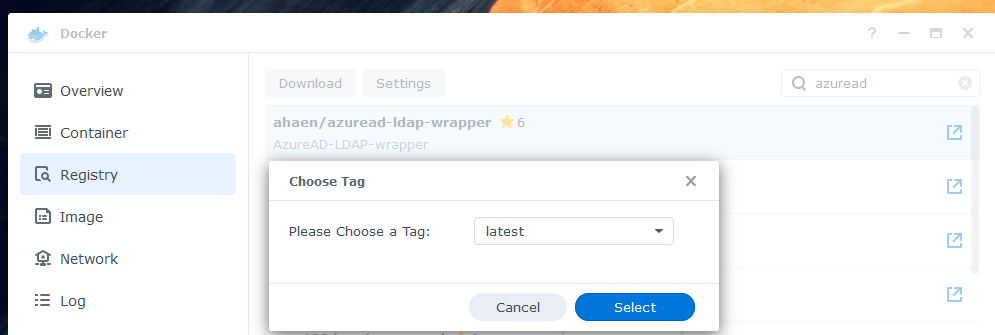
In Docker, go to "Registry" to download the latest container image.
-
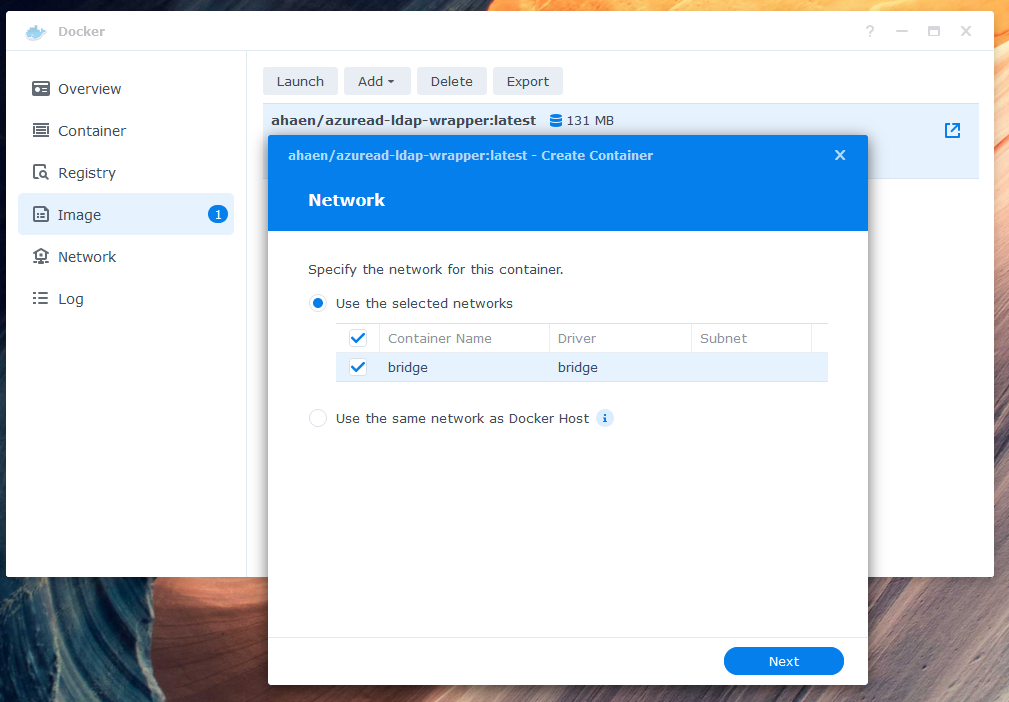
In Docker, go to "Image" to launch a new container. Use "bridge" as your network.
Use "bridge" as your network.
-
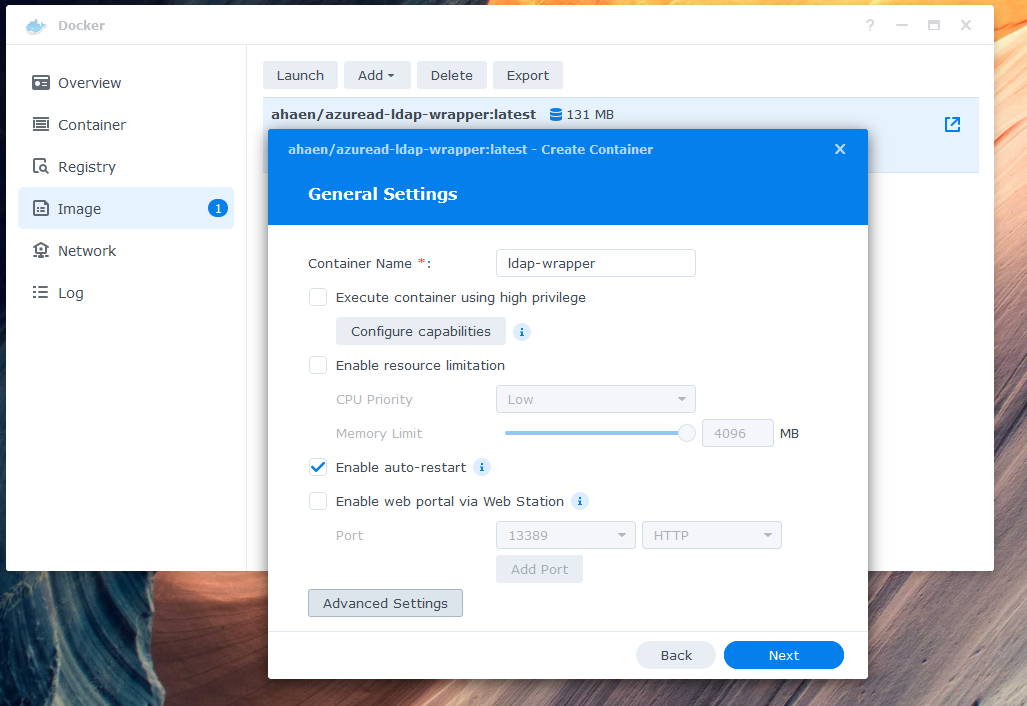
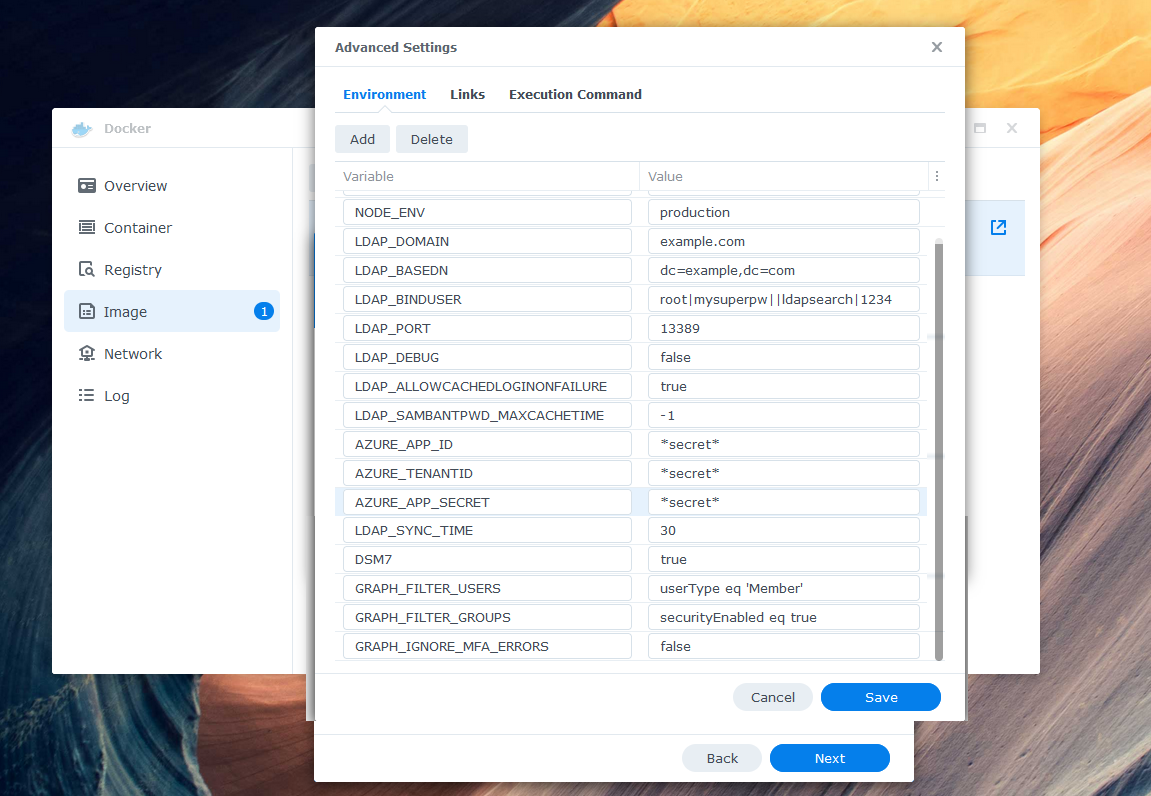
Configure the environment variables in "Advanced Settings". Be sure to double check your Azure values and define at least one binduser. The binduser (superuser like root) does not need to exist in your AzureAD. Replace example.com with your domain. Here is an example of a minimum required configuration:
TZ: "Europe/Zurich" # optional AZURE_TENANTID: "0def2345-ff01-56789-1234-ab9d6dda1e1e" AZURE_APP_ID: "abc12345-ab01-0000-1111-a1e1eab9d6dd" AZURE_APP_SECRET: "iamasecret~yep-reallyreallysecret" LDAP_DOMAIN: "example.com" LDAP_BASEDN: "dc=example,dc=com" LDAP_BINDUSER: "ldapsearch|*secretldapsearch123*||root|*secretroot*" LDAP_DEBUG: "false" # set this to true for more logs GRAPH_IGNORE_MFA_ERRORS: "false" # set this to true to bypass MFA DSM7: "true" # set this to false if you are running DSM 6 or lower
A full list of all environment variables can be found here.
-
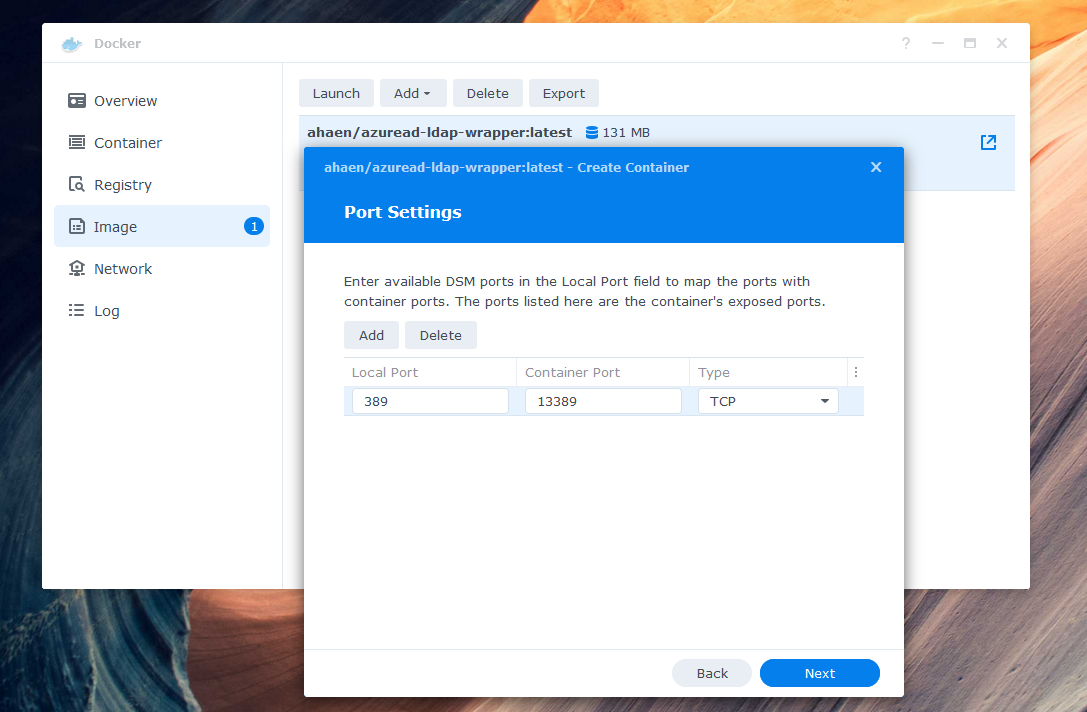
Set local Port 389 to the Container Port 13389. If you receive the error Local port 389 conflicts with other ports used by other services, make sure that Synology Directory Service and Synology LDAP Server are not installed - they also use this port.
-
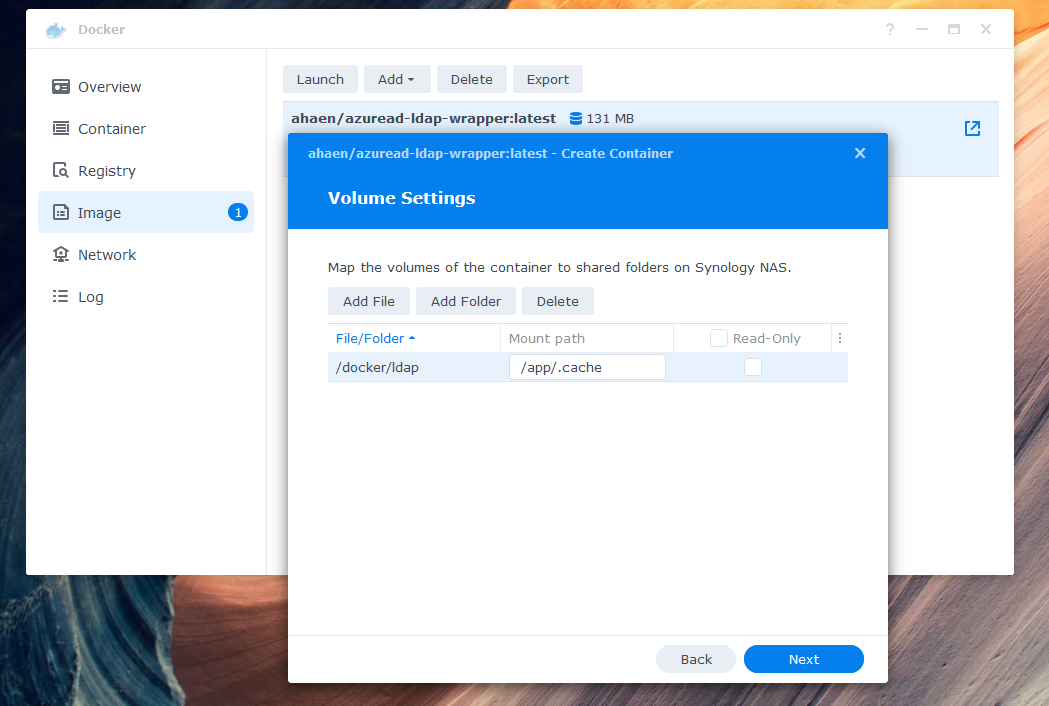
Add a local folder, such as docker/ldap, to the mount path /app/.cache in the volume settings. If you skip this step, your data will not be stored permanently.
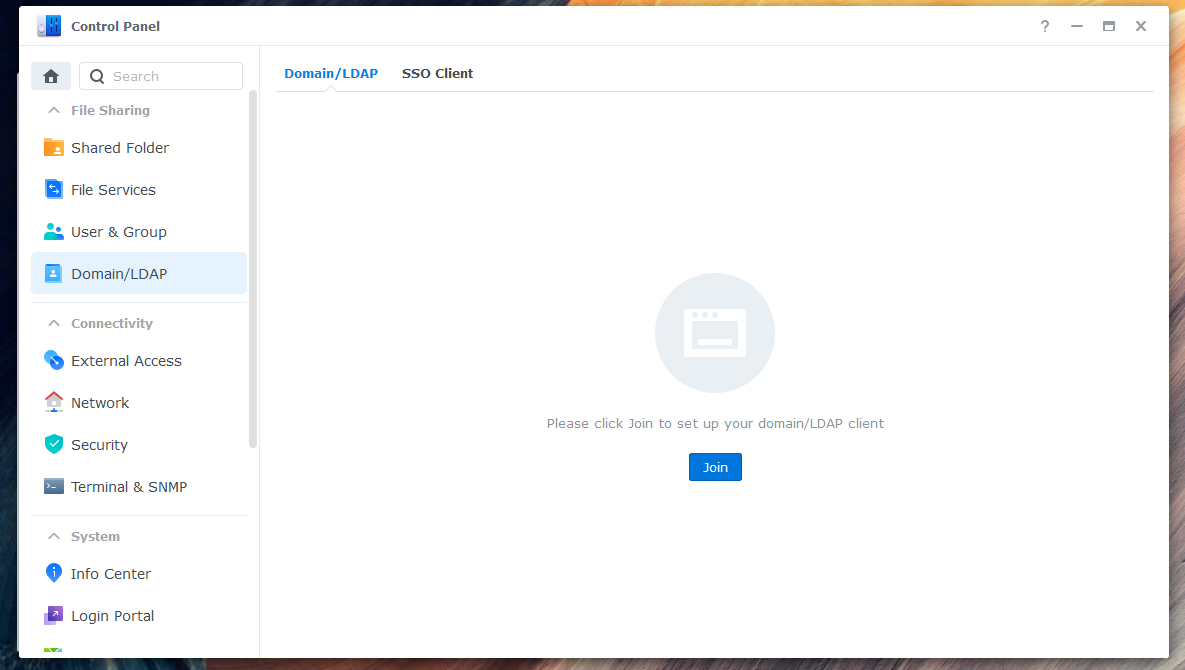
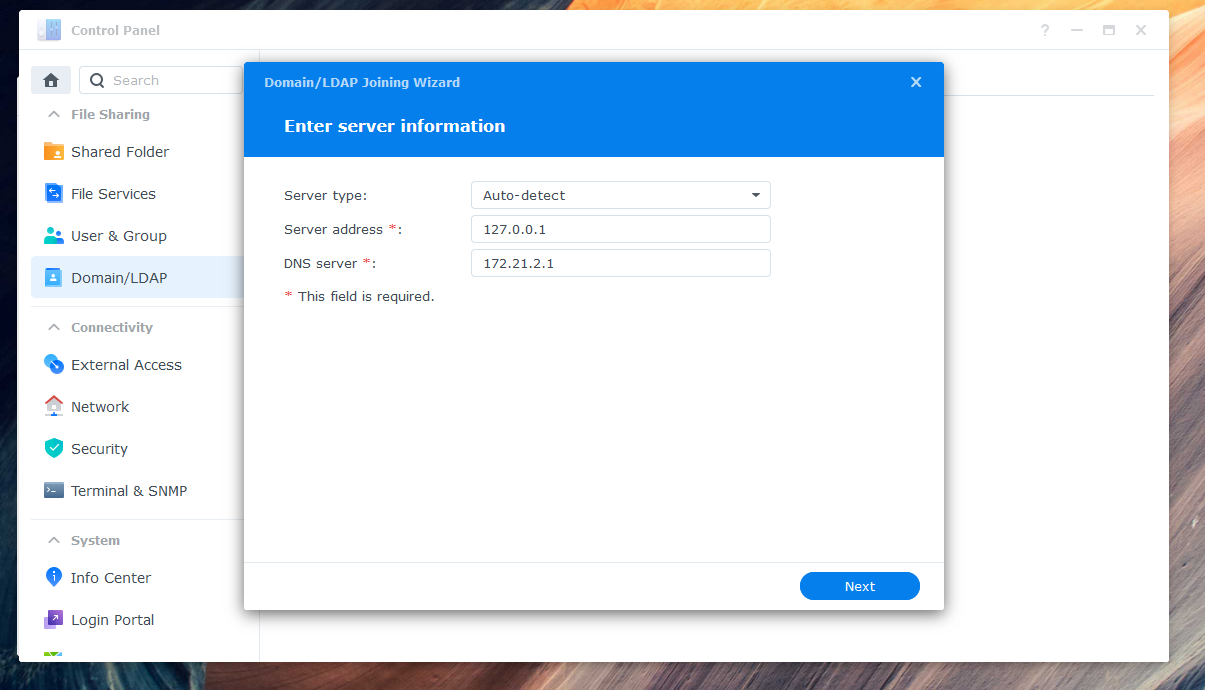
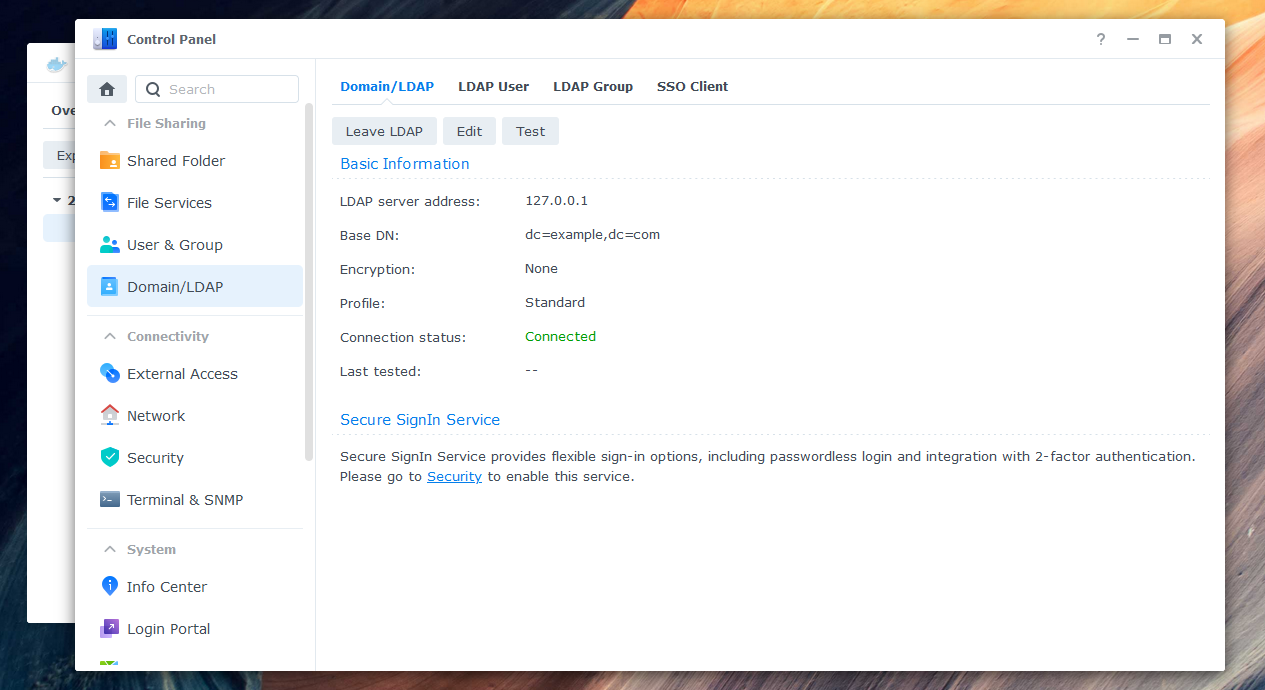
To enable users to log in to Synology NAS with their Azure credentials, you need to connect the NAS to the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper. Here are the steps:
-
Enter the IP address (e.g., 127.0.0.1) of your NAS as the server address.
-
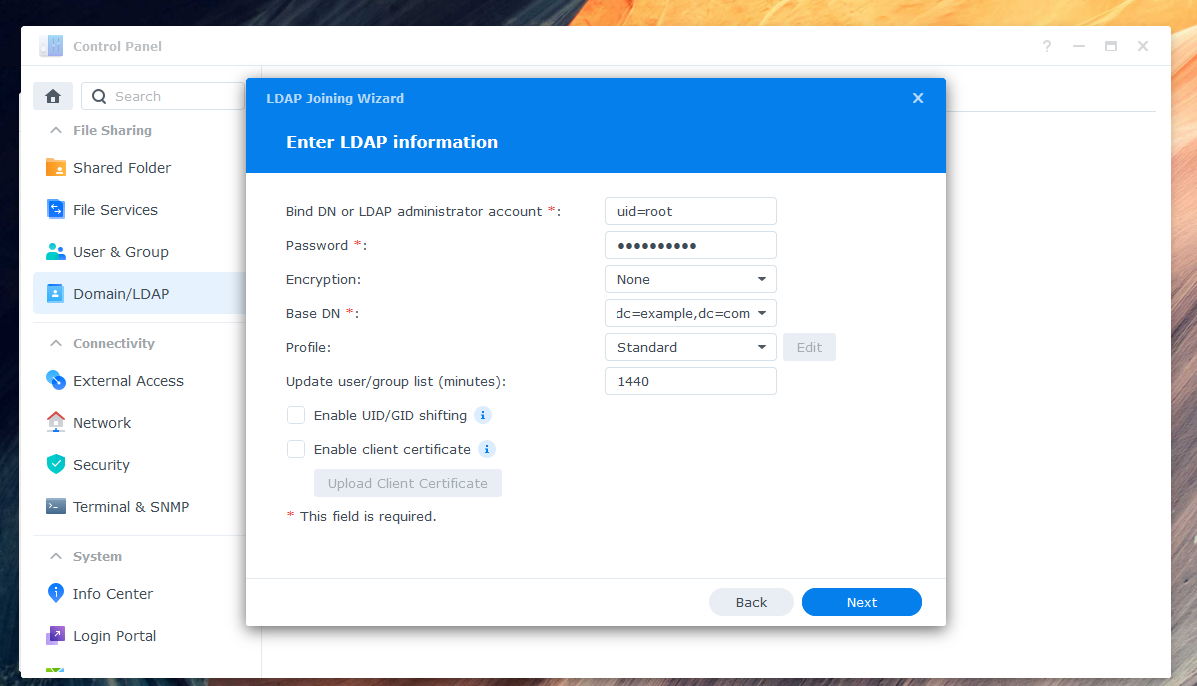
Enter the credentials of your previously defined superuser (environment variable
LDAP_BINDUSER) as Bind DN. Should your user not be found, try writing "uid=root" or the full name "uid=root,cn=users,dc=domain,dc=tld" instead of just "root". Select your domain in Base DN. -
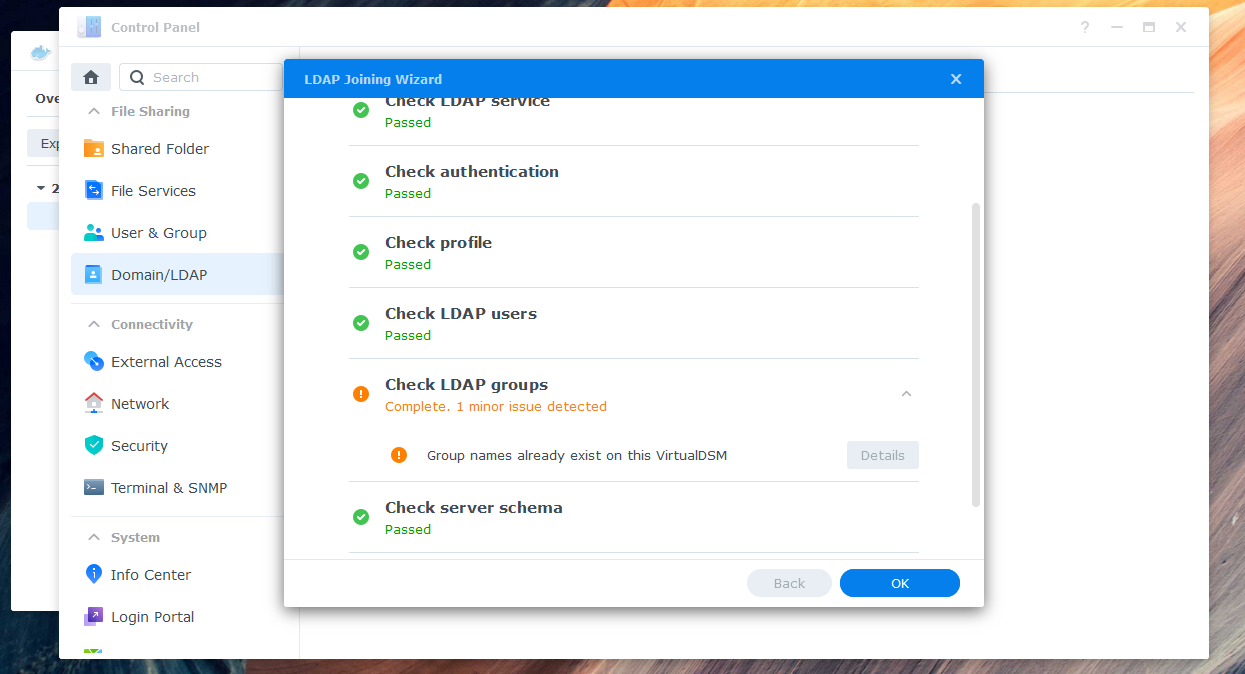
If you see a warning about a local group having the same name as a synchronized group, you can ignore it and skip the warning in "Details".
-
Your NAS should now be connected successfully to the Azure AD LDAP-wrapper.
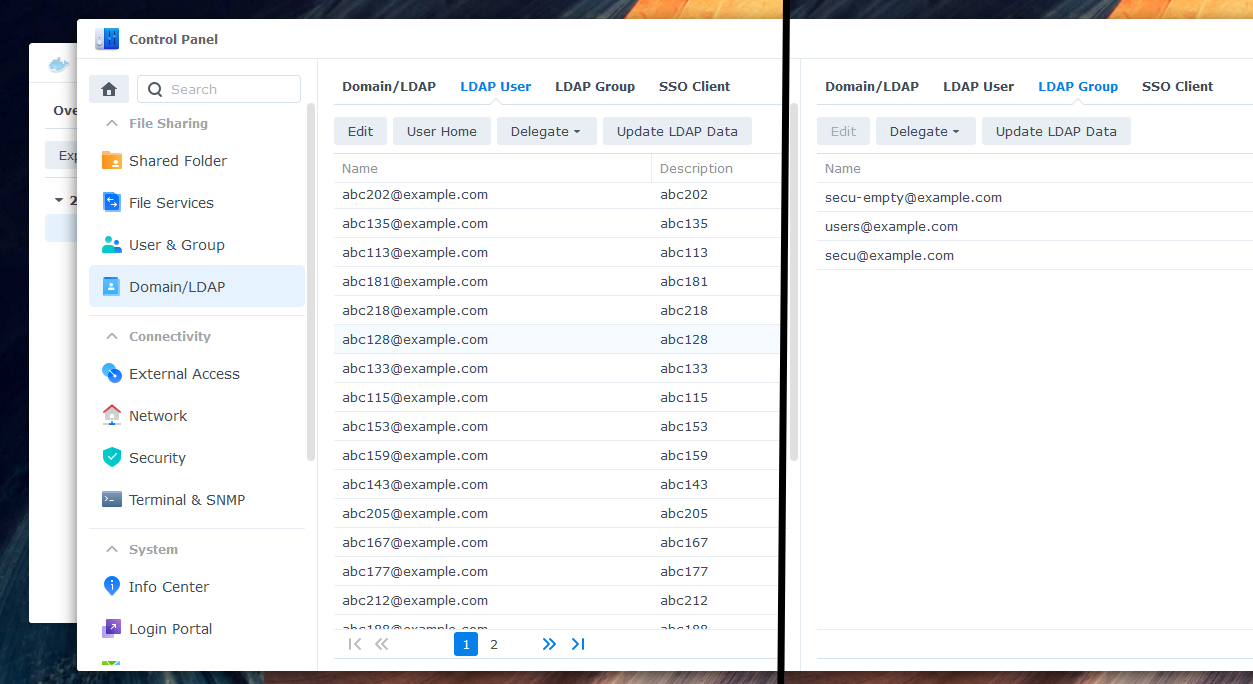
-
Check the "LDAP User" and "LDAP Group" tabs to ensure that all entries are fully synced. Assign the desired permissions to your synchronized users and groups. You can now log in with your Azure AD credentials.
-
Note that before accessing shared folders or files via network or Samba, each user must log in to DSM web GUI or another tool directly connected to the LDAP server. This step is also required after a password change, as the password hash for Samba is only set after a successful login.
To configure the LDAP-wrapper, you can use environment variables as it is intended to be used with Docker. A complete list of available variables can be found in the configuration settings page of the documentation.
If you encounter any issues, start by checking the Docker log. Many errors are logged there, and this can help you identify the root cause of the problem. Additionally, the troubleshooting page in the documentation provides further guidance on debugging common issues, including Samba-related ones. If you're still stuck, don't hesitate to open an issue, but be sure to attach relevant log files to help others diagnose the issue.
It's important to note that the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper involves transferring sensitive user information, so it's essential to ensure that it's used securely. There are several potential security risks to be aware of when using this wrapper. For more information on these risks and how to mitigate them, please read the security page in the documentation.
If you discover any security vulnerabilities, please refer to the instructions in SECURITY.md on how to report them.
Contributions to the AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper are always welcome! If you have any suggestions, bug reports, or pull requests, please feel free to open an issue or a pull request on the project's GitHub repository.
If you find this project helpful or saved you time and effort, please consider giving it a star and/or making a donation.
Your support helps me maintain and improve this project. Thank you!
The AzureAD-LDAP-wrapper is licensed under the MIT License.